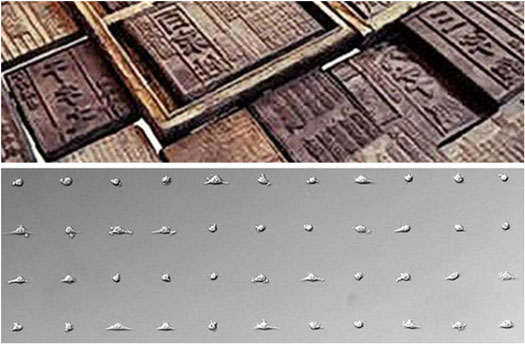
 With a nod to 3rd century Chinese woodblock printing and children's rubber stamp toys, researchers in Houston have developed a way to print living cells onto any surface, in virtually any shape. Unlike recent, similar work using inkjet printing approaches, almost all cells survive the process.
With a nod to 3rd century Chinese woodblock printing and children's rubber stamp toys, researchers in Houston have developed a way to print living cells onto any surface, in virtually any shape. Unlike recent, similar work using inkjet printing approaches, almost all cells survive the process.
Feb 10th, 2014
Read more
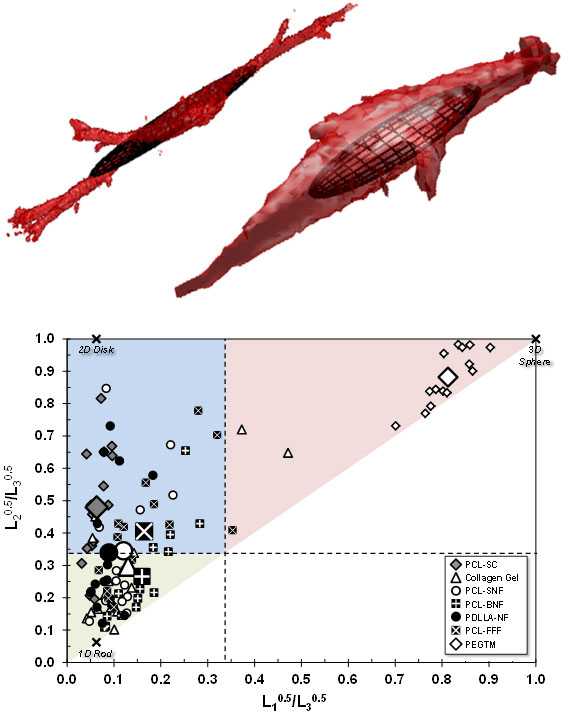 Getting in the right shape might be just as important in a biology lab as a gym. Shape is thought to play an important role in the effectiveness of cells grown to repair or replace damaged tissue in the body. To help design new structures that enable cells to "shape up," researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have come up with a way to measure, and more importantly, classify, the shapes cells tend to take in different environments.
Getting in the right shape might be just as important in a biology lab as a gym. Shape is thought to play an important role in the effectiveness of cells grown to repair or replace damaged tissue in the body. To help design new structures that enable cells to "shape up," researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have come up with a way to measure, and more importantly, classify, the shapes cells tend to take in different environments.
Feb 10th, 2014
Read more
A cochlear implant that can be wirelessly recharged would use the natural microphone of the middle ear rather than a skull-mounted sensor.
Feb 10th, 2014
Read more
 A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist and his colleagues have found a new application for the tools and mathematics typically used in physics to help solve problems in biology.
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist and his colleagues have found a new application for the tools and mathematics typically used in physics to help solve problems in biology.
Feb 8th, 2014
Read more
Researchers have shown for the first time that 'click chemistry' can be used to assemble DNA that is functional in human cells, which paves the way for a purely chemical method for gene synthesis.
Feb 7th, 2014
Read more
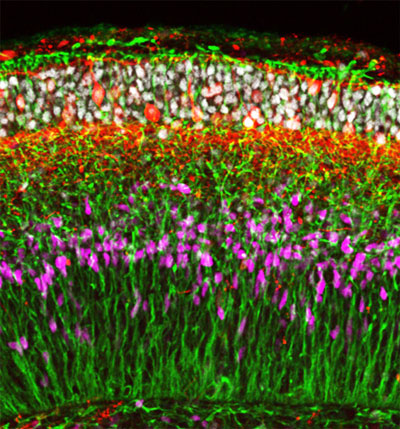 Human embryonic stem cells can be induced to spontaneously form developing brain tissue.
Human embryonic stem cells can be induced to spontaneously form developing brain tissue.
Feb 7th, 2014
Read more
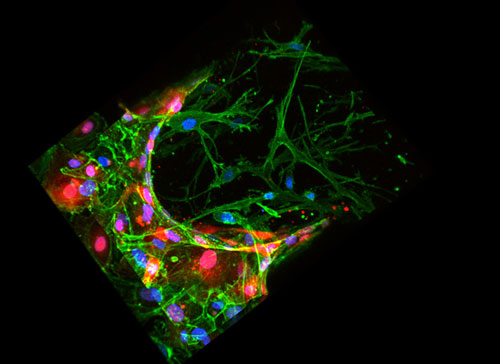 Researchers design a microfluidic platform to see how cancer cells invade specific organs.
Researchers design a microfluidic platform to see how cancer cells invade specific organs.
Feb 6th, 2014
Read more
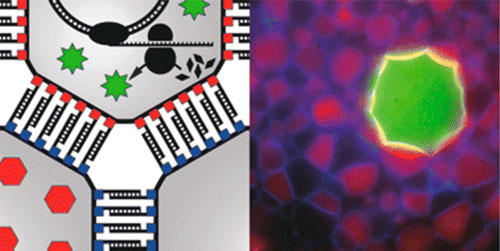 It is a big dream in science to start from scratch with simple artificial microscopic building blocks and end up with something much more complex: living systems, novel computers or every-day materials. For decades scientists have pursued the dream of creating artificial building blocks that can self-assemble in large numbers and reassemble to take on new tasks or to remedy defects. Now researchers from University of Southern Denmark have taken a step forward to make this dream come true.
It is a big dream in science to start from scratch with simple artificial microscopic building blocks and end up with something much more complex: living systems, novel computers or every-day materials. For decades scientists have pursued the dream of creating artificial building blocks that can self-assemble in large numbers and reassemble to take on new tasks or to remedy defects. Now researchers from University of Southern Denmark have taken a step forward to make this dream come true.
Feb 4th, 2014
Read more
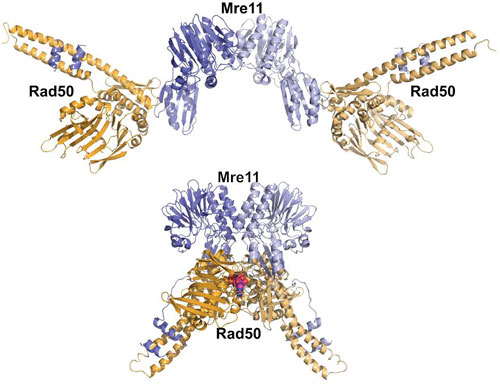 Maybe you've seen the movies or played with toy Transformers, those shape-shifting machines that morph in response to whatever challenge they face. It turns out that DNA-repair machines in your cells use a similar approach to fight cancer and other diseases.
Maybe you've seen the movies or played with toy Transformers, those shape-shifting machines that morph in response to whatever challenge they face. It turns out that DNA-repair machines in your cells use a similar approach to fight cancer and other diseases.
Feb 3rd, 2014
Read more
When it comes to finding cures for heart disease scientists have finally developed a tissue model for the human heart that can bridge the gap between animal models and human patients. Specifically, the researchers generated the tissue from human embryonic stem cells with the resulting muscle having significant similarities to human heart muscle.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
Biochemists succeeded for the first time in creating mirror-image enzymes - so-called Spiegelzymes - out of nucleic acids. The Spiegelzymes can be used in living cells for the targeted cutting of natural nucleic acids.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
Three new multidisciplinary research centres in synthetic biology will be established in Bristol, Nottingham and through a Cambridge/Norwich partnership.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
Researchers at the University Children's Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich have engineered skin cells for the very first time containing blood and lymphatic capillaries. They succeeded in isolating all the necessary types of skin cells from human skin tissue and engineering a skin graft that is similar to full-thickness skin.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
In the process of protein synthesis there is a 'stochastic' component, i.e., involving random chance, which influences the time the process takes. This aspect has been investigated by two research scientists.
Jan 29th, 2014
Read more
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen can radically alter the properties of proteins by redesigning their chemical structure. New fundamental research based on designer proteins highlights important communication processes in the human body. In the long term, this new knowledge may lead to pharmaceuticals with fewer side effects.
Jan 29th, 2014
Read more
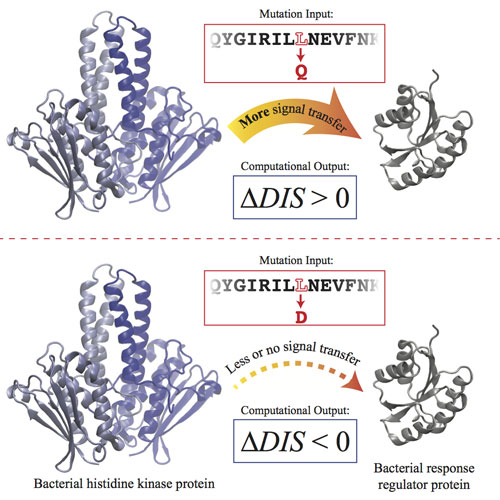 Scientists have created a way to interpret interactions among pairs of task-oriented proteins that relay signals. The goal is to learn how the proteins avoid crosstalk and whether they can be tuned for better performance.
Scientists have created a way to interpret interactions among pairs of task-oriented proteins that relay signals. The goal is to learn how the proteins avoid crosstalk and whether they can be tuned for better performance.
Jan 27th, 2014
Read more
Researchers from the Institute of Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) at Kyoto University have designed a set of DNA-based molecules capable of controlling biological networks in cells.
Jan 27th, 2014
Read more
Researchers developed a simple method to validate protein drugs in animal models.
Jan 24th, 2014
Read more
 With a nod to 3rd century Chinese woodblock printing and children's rubber stamp toys, researchers in Houston have developed a way to print living cells onto any surface, in virtually any shape. Unlike recent, similar work using inkjet printing approaches, almost all cells survive the process.
With a nod to 3rd century Chinese woodblock printing and children's rubber stamp toys, researchers in Houston have developed a way to print living cells onto any surface, in virtually any shape. Unlike recent, similar work using inkjet printing approaches, almost all cells survive the process.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed





