 In 2009, a borehole drilled at Krafla, northeast Iceland, as part of the Icelandic Deep Drilling Project, unexpectedly penetrated into magma (molten rock) at only 2,100 meters depth, with a temperature of 900-1,000 C. The January 2014 issue of Geothermics is dedicated to scientific and engineering results arising from that unusual occurrence.
In 2009, a borehole drilled at Krafla, northeast Iceland, as part of the Icelandic Deep Drilling Project, unexpectedly penetrated into magma (molten rock) at only 2,100 meters depth, with a temperature of 900-1,000 C. The January 2014 issue of Geothermics is dedicated to scientific and engineering results arising from that unusual occurrence.
Jan 23rd, 2014
Read more
The CoLaBats iniciative works in provide new industrial processes for the recycling of the critical metals Cobalt and Lanthanides and key economic metals Nickel and Lithium, from waste batteries, significantly improving recycling efficiencies and metal purity from existing recovery routes.
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
New Worldwatch Institute report reviews extent of global energy subsidies.
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
The National Physical Laboratory in the UK will lead seven new European collaborative projects, following the final round of project calls from the European Metrology Research Programme (EMRP) before the proposed introduction of its successor, the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR) in 2014.
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
The supply of climate change knowledge is biased towards richer countries - those that pollute the most and are least vulnerable to climate change - and skewed away from the poorer, fragile and more vulnerable regions of the world. That creates a global imbalance between the countries in need of knowledge and those that build it.
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
 Frede Blaabjerg, Professor in Energy at Aalborg University, is the recipient of the largest individual Danish research award, the Villum Kann Rasmussen Annual Award for Technical and Scientific Research of DKK 5 million (EUR 0.67 million).
Frede Blaabjerg, Professor in Energy at Aalborg University, is the recipient of the largest individual Danish research award, the Villum Kann Rasmussen Annual Award for Technical and Scientific Research of DKK 5 million (EUR 0.67 million).
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
The European ECOPROT project aims to industrialise an innovative procedure for producing corrosion-protecting environmentally friendly coatings for aluminium and magnesium alloys, to be used in the aeronautics market.
Jan 22nd, 2014
Read more
A new study indicates that even a sharp increase in the use of electric drive passenger vehicles by 2050 would not significantly reduce emissions of high-profile air pollutants carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides.
Jan 21st, 2014
Read more
Investment in renewable energy and energy smart technologies dropped 11% in 2013, after falling 10% in 2012. Japan was the most significant among several countries seeing increasing activity.
Jan 21st, 2014
Read more
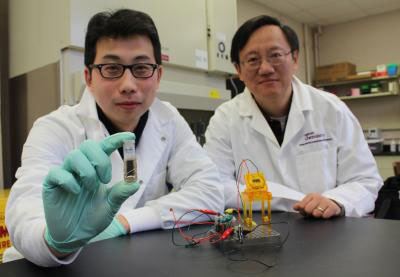 A new sugar battery that could be on the market and powering the world's gadgets in three years has an energy density and order of magnitude higher than others.
A new sugar battery that could be on the market and powering the world's gadgets in three years has an energy density and order of magnitude higher than others.
Jan 21st, 2014
Read more
How can companies break into the electromobility market faster and more effectively? In what way can innovative services help to focus electromobility solutions on users' needs? What shape should IT support take? And what will the mobility markets of the future look like? DELFIN project develops innovative services and methods.
Jan 20th, 2014
Read more
 Researchers study the properties of a novel material that could help build high heat-tolerant supercapacitors.
Researchers study the properties of a novel material that could help build high heat-tolerant supercapacitors.
Jan 17th, 2014
Read more
 Using a plant-derived chemical, University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers have developed a process for creating a concentrated stream of sugars that's ripe with possibility for biofuels.
Using a plant-derived chemical, University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers have developed a process for creating a concentrated stream of sugars that's ripe with possibility for biofuels.
Jan 16th, 2014
Read more
The costs of achieving a more ambitious EU climate target are estimated to be moderate. Upscaling greenhouse-gas emissions reduction from the current 20 percent by 2020 to 40 percent by 2030 would be likely to cost less than an additional 0.7 percent of economic activity.
Jan 16th, 2014
Read more
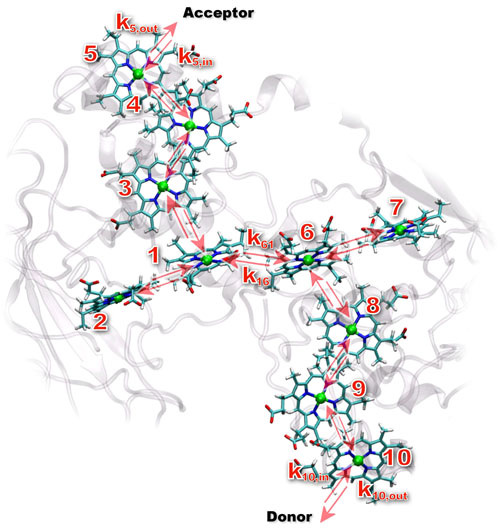 Novel biological mechanism relays electrons in proteins in mineral-breathing bacteria important for energy-related research.
Novel biological mechanism relays electrons in proteins in mineral-breathing bacteria important for energy-related research.
Jan 15th, 2014
Read more
Ambitious greenhouse-gas mitigation consistent with the 2 degrees target is likely to require substantial amounts of bioenergy as part of the future energy mix. Though this does not come without risks, global food markets would be affected much more by unmitigated climate change than by an increased bioenergy demand, a study led by scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now finds.
Jan 15th, 2014
Read more
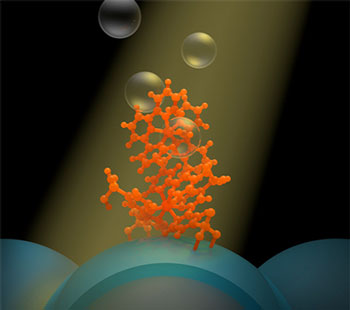 Researchers have built a system that converts the sun's energy not into electricity but hydrogen fuel and stores it for later use, allowing us to power our devices long after the sun goes down.
Researchers have built a system that converts the sun's energy not into electricity but hydrogen fuel and stores it for later use, allowing us to power our devices long after the sun goes down.
Jan 14th, 2014
Read more
When it comes to biofuels, corn leads the all-important category of biomass yield. However, focusing solely on yield comes at a high price, scientists say.
Jan 13th, 2014
Read more
 In 2009, a borehole drilled at Krafla, northeast Iceland, as part of the Icelandic Deep Drilling Project, unexpectedly penetrated into magma (molten rock) at only 2,100 meters depth, with a temperature of 900-1,000 C. The January 2014 issue of Geothermics is dedicated to scientific and engineering results arising from that unusual occurrence.
In 2009, a borehole drilled at Krafla, northeast Iceland, as part of the Icelandic Deep Drilling Project, unexpectedly penetrated into magma (molten rock) at only 2,100 meters depth, with a temperature of 900-1,000 C. The January 2014 issue of Geothermics is dedicated to scientific and engineering results arising from that unusual occurrence.
 Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed
Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed




