Birmingham City University is set to showcase the concept and design behind what could prove to be the world's first affordable hydrogen fuel-cell powered mass transport vehicle.
Feb 5th, 2014
Read more
 Wastewater from pulp and paper mills contains large volumes of organic material that can be converted into biogas, according to findings by researchers from Water and Environmental Studies (WES) at Link�ping University.
Wastewater from pulp and paper mills contains large volumes of organic material that can be converted into biogas, according to findings by researchers from Water and Environmental Studies (WES) at Link�ping University.
Feb 4th, 2014
Read more
 A group of Washington State University researchers has developed a chewing gum-like battery material that could dramatically improve the safety of lithium ion batteries.
A group of Washington State University researchers has developed a chewing gum-like battery material that could dramatically improve the safety of lithium ion batteries.
Feb 4th, 2014
Read more
Gasoline-like fuels can be made from cellulosic materials such as farm and forestry waste using a new process invented by chemists at the University of California, Davis. The process could open up new markets for plant-based fuels, beyond existing diesel substitutes.
Feb 3rd, 2014
Read more
A breakthrough in the use of renewable raw materials in chemical production has been achieved by Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and its industrial partner AVA Biochem. The partners developed an innovative hydrothermal method to obtain the organic compound from biomass. Being a platform chemical, 5-HMF can serve as a precursor for various materials.
Feb 3rd, 2014
Read more
Annual US$4 million prize rewards individuals, organisations and schools making a positive impact in the fields of renewable energy and sustainability.
Feb 3rd, 2014
Read more
 Last week, the European Commission presented a new action plan to facilitate the further development of the renewable ocean energy sector in Europe. A central element in this action plan will be to establish an Ocean Energy Forum, bringing together stakeholders to build capacity and foster cooperation.
Last week, the European Commission presented a new action plan to facilitate the further development of the renewable ocean energy sector in Europe. A central element in this action plan will be to establish an Ocean Energy Forum, bringing together stakeholders to build capacity and foster cooperation.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
A 3-million dollar grant from the U.S. Department of Energy will allow a University of Oklahoma multi-disciplinary research team to develop a novel biomass conversion process to obtain a bio-oil compatible with refinery operations.
Jan 30th, 2014
Read more
 Facility will house work on power grid, energy efficiency, sustainability and more.
Facility will house work on power grid, energy efficiency, sustainability and more.
Jan 29th, 2014
Read more
 What do champion surfers who gathered at last week's Mavericks Invitational have in common with a UC Berkeley engineer? They all are looking to harness the power of big ocean waves.
What do champion surfers who gathered at last week's Mavericks Invitational have in common with a UC Berkeley engineer? They all are looking to harness the power of big ocean waves.
Jan 29th, 2014
Read more
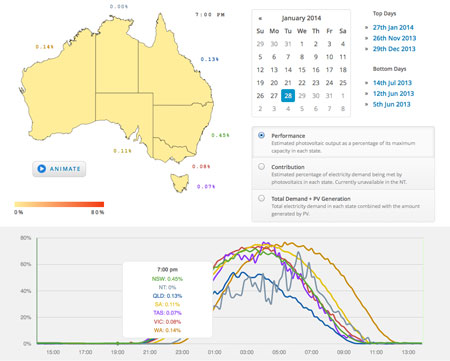 A new solar map website tracks the contribution of solar photovoltaic systems in Australia's energy mix and provides a guide to the location and capacity of PV installations across the country.
A new solar map website tracks the contribution of solar photovoltaic systems in Australia's energy mix and provides a guide to the location and capacity of PV installations across the country.
Jan 28th, 2014
Read more
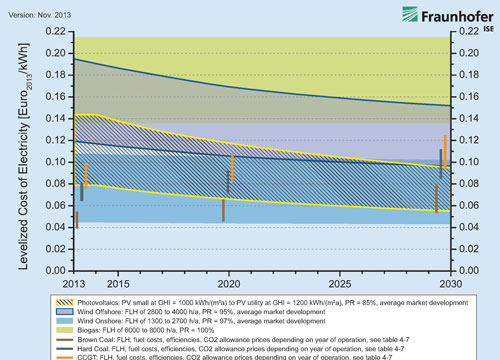 A study from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE compares the present costs for conversion of different energy forms into electricity and gives a prognosis for the further cost development up to 2030.
A study from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE compares the present costs for conversion of different energy forms into electricity and gives a prognosis for the further cost development up to 2030.
Jan 28th, 2014
Read more
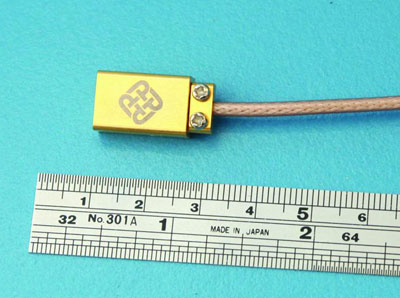 The chip can be placed on any sensing point of interest such as electrical cables, conductors, junctions, bus bars, etc. to detect electrical currents. What's more, it does not necessitate the use of additional power supplies and signal conditioners which are generally required by traditional current sensors such as Hall sensors, reluctance coils, etc.
The chip can be placed on any sensing point of interest such as electrical cables, conductors, junctions, bus bars, etc. to detect electrical currents. What's more, it does not necessitate the use of additional power supplies and signal conditioners which are generally required by traditional current sensors such as Hall sensors, reluctance coils, etc.
Jan 27th, 2014
Read more
Researchers in India have developed a relatively low-temperature process to convert certain kinds of plastic waste into liquid fuel as a way to reuse discarded plastic bags and other products.
Jan 27th, 2014
Read more
Researchers are investigating solar cells based on organic materials that have electrodes both flexible and transparent, enabling the fabrication of these solar cells at a low cost.
Jan 27th, 2014
Read more
The Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), along with partners from the Electric Power Research Institute and the University of Colorado have completed a comprehensive study to understand how wind power technology can assist the power grid by controlling the active power output being placed onto the system.
Jan 25th, 2014
Read more
Biochemical reactions sometimes have to handle dangerous things in a safe way. New work from researchers at UC Davis and Stanford University shows how cyanide and carbon monoxide are safely bound to an iron atom to construct an enzyme that can generate hydrogen gas.
Jan 24th, 2014
Read more
Last year was a record year for PV installation worldwide, with a rush of activity in China on the back of a national feed-in tariff one of the main drivers.
Jan 23rd, 2014
Read more

 Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed
Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed






