'Zeno effect' verified: Atoms won't move while you watch
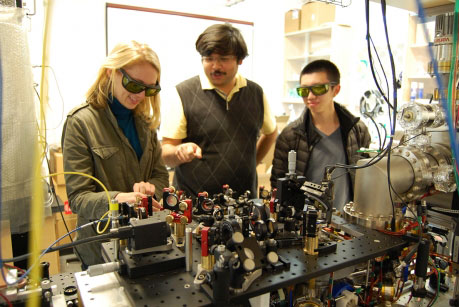 One of the oddest predictions of quantum theory - that a system can't change while you're watching it - has been confirmed in an experiment by physicists.
One of the oddest predictions of quantum theory - that a system can't change while you're watching it - has been confirmed in an experiment by physicists.
Oct 22nd, 2015
Read more
 One of the oddest predictions of quantum theory - that a system can't change while you're watching it - has been confirmed in an experiment by physicists.
One of the oddest predictions of quantum theory - that a system can't change while you're watching it - has been confirmed in an experiment by physicists.
Oct 22nd, 2015
Read more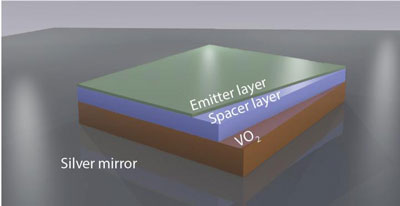 Researchers have developed a new way to control light from phosphorescent emitters at very high speeds. The technique provides a new approach to modulation that could be useful in all kinds of silicon-based nanoscale devices, including computer chips and other optoelectronic components.
Researchers have developed a new way to control light from phosphorescent emitters at very high speeds. The technique provides a new approach to modulation that could be useful in all kinds of silicon-based nanoscale devices, including computer chips and other optoelectronic components.
Oct 22nd, 2015
Read moreThree high-tech SMEs finalize the joint EU-funded PICS project on innovative ALD materials and manufacturing equipment.
Oct 22nd, 2015
Read moreNew photonic microchip component promises advances in telecommunications.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more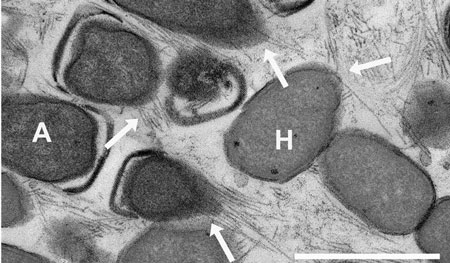 Microorganisms in the sea organise their power supply via tiny power-cables, thus oxidising the greenhouse gas methane.
Microorganisms in the sea organise their power supply via tiny power-cables, thus oxidising the greenhouse gas methane.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more Graphene doped with nitrogen and augmented with cobalt atoms has proven to be an effective, durable catalyst for the production of hydrogen from water.
Graphene doped with nitrogen and augmented with cobalt atoms has proven to be an effective, durable catalyst for the production of hydrogen from water.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more During their second annual meeting, held in Venice, Italy on 8-9 October 2015, SUN project partners presented the results obtained during the second 12 months of the SUN - Sustainable Nanotechnologies Project.
During their second annual meeting, held in Venice, Italy on 8-9 October 2015, SUN project partners presented the results obtained during the second 12 months of the SUN - Sustainable Nanotechnologies Project.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more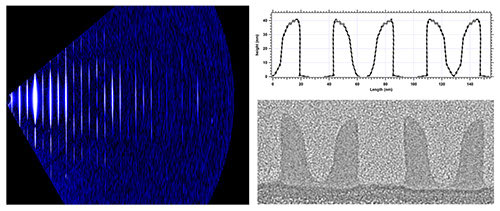 Researchers reported success using an X-ray scattering technique to accurately measure features on a silicon chip to within fractions of a nanometer, or about the width of a single silicon atom.
Researchers reported success using an X-ray scattering technique to accurately measure features on a silicon chip to within fractions of a nanometer, or about the width of a single silicon atom.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more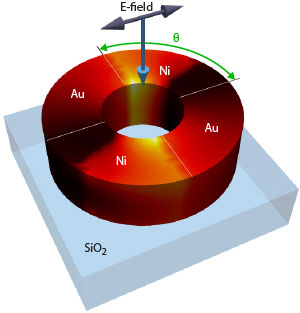 A new nanoring design shows potential for generating short magnetic pulses and could be used to explore magnetic switching in materials.
A new nanoring design shows potential for generating short magnetic pulses and could be used to explore magnetic switching in materials.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more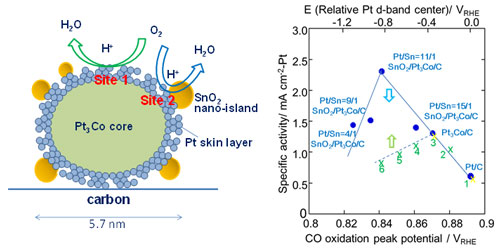 Selective electrodeposition of tin oxide on platinum alloy nanoparticles provides an effective and robust catalyst for polymer electrolyte fuel cells.
Selective electrodeposition of tin oxide on platinum alloy nanoparticles provides an effective and robust catalyst for polymer electrolyte fuel cells.
Oct 21st, 2015
Read more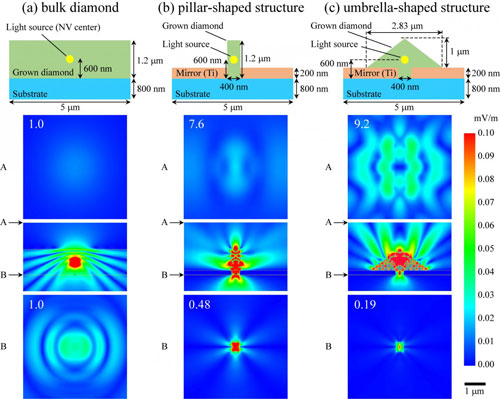 Luminescent nanostructures may prove to be useful in highly sensitive magnetic sensors or within the realm of quantum computing.
Luminescent nanostructures may prove to be useful in highly sensitive magnetic sensors or within the realm of quantum computing.
Oct 20th, 2015
Read more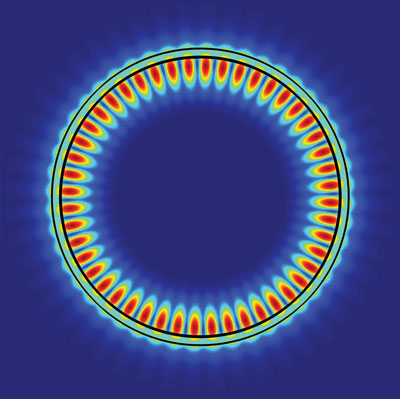 An important step towards next-generation ultra-compact photonic and optoelectronic devices has been taken with the realization of a two-dimensional excitonic laser. Scientists embedded a monolayer of tungsten disulfide into a special microdisk resonator to achieve bright excitonic lasing at visible light wavelengths.
An important step towards next-generation ultra-compact photonic and optoelectronic devices has been taken with the realization of a two-dimensional excitonic laser. Scientists embedded a monolayer of tungsten disulfide into a special microdisk resonator to achieve bright excitonic lasing at visible light wavelengths.
Oct 20th, 2015
Read moreResearchers design most durable anti-fouling material to date.
Oct 20th, 2015
Read more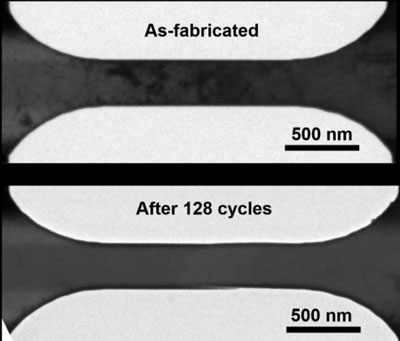 Researchers have developed a new technique called cyclic healing that uses repetitive, gentle stretching to eliminate pre-existing defects in metal crystals.
Researchers have developed a new technique called cyclic healing that uses repetitive, gentle stretching to eliminate pre-existing defects in metal crystals.
Oct 20th, 2015
Read more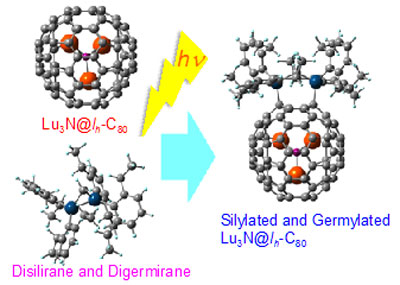 Researchers have created and analyzed the effects of silylation and germylation on an EMF called Lu3N@Ih-C80 (three lutetium atoms bonded to a nitrogen atom encased inside a carbon 80 cage).
Researchers have created and analyzed the effects of silylation and germylation on an EMF called Lu3N@Ih-C80 (three lutetium atoms bonded to a nitrogen atom encased inside a carbon 80 cage).
Oct 20th, 2015
Read moreResearchers have created a new electronic component that could replace flash storage. This memristor could also be used one day in new types of computers.
Oct 19th, 2015
Read more