 Study shows that label-free digital diagnostics based on nanopore analytics and AI technology can characterize individual virions by their distinct physical features.
Study shows that label-free digital diagnostics based on nanopore analytics and AI technology can characterize individual virions by their distinct physical features.
Nov 21st, 2018
Read more
 First yeast biohybrid system using an adaptable light-harvesting semiconductor approach opens the door to more efficient and versatile biomanufacturing.
First yeast biohybrid system using an adaptable light-harvesting semiconductor approach opens the door to more efficient and versatile biomanufacturing.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 The single-layer surface of nanostructures can be incorporated into commercial optical systems, from simple to complex.
The single-layer surface of nanostructures can be incorporated into commercial optical systems, from simple to complex.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 How a molecule from a solid crystal structure is solvated in a liquid solvent has been observed at a molecular level for the first time by chemists.
How a molecule from a solid crystal structure is solvated in a liquid solvent has been observed at a molecular level for the first time by chemists.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 Scientists ave proposed a new technology for creating optical micro-waveguides using inkjet printing. Using this method it is possible to quickly create waveguides with the necessary parameters without expensive equipment and complex procedures.
Scientists ave proposed a new technology for creating optical micro-waveguides using inkjet printing. Using this method it is possible to quickly create waveguides with the necessary parameters without expensive equipment and complex procedures.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 Potential uses of new technology range from medical devices and wearables to smart packaging.
Potential uses of new technology range from medical devices and wearables to smart packaging.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 Devices operating under the principle of racetrack memory are expecting to have a much more data storage space compared to modern USB flash drives and HDDs.
Devices operating under the principle of racetrack memory are expecting to have a much more data storage space compared to modern USB flash drives and HDDs.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
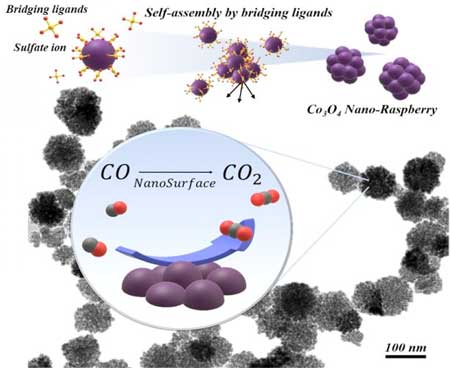 Scientists have developed a sustainable method to neutralize carbon monoxide, the odorless poison produced by cars and home boilers.
Scientists have developed a sustainable method to neutralize carbon monoxide, the odorless poison produced by cars and home boilers.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have developed a technique that uses 'layer exchange' to grow high-quality uniform crystals of maulti-layer graphene directly on an insulating material.
Researchers have developed a technique that uses 'layer exchange' to grow high-quality uniform crystals of maulti-layer graphene directly on an insulating material.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
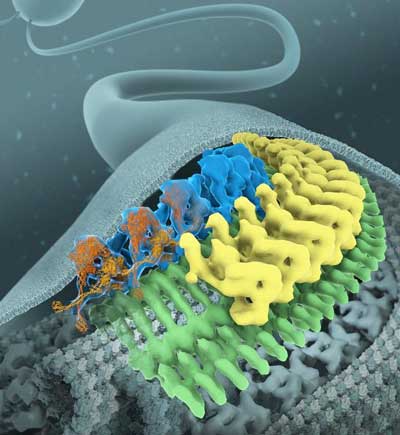 Scientists reveal the nano-structure of molecular trains and the reason for smooth transport in cellular antennas.
Scientists reveal the nano-structure of molecular trains and the reason for smooth transport in cellular antennas.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers describe the design and implementation of 3D hierarchical architectures of cellular graphene with programmed geometries and outstanding electromechanical properties through the use of mechanically guided, 3D assembly.
Researchers describe the design and implementation of 3D hierarchical architectures of cellular graphene with programmed geometries and outstanding electromechanical properties through the use of mechanically guided, 3D assembly.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
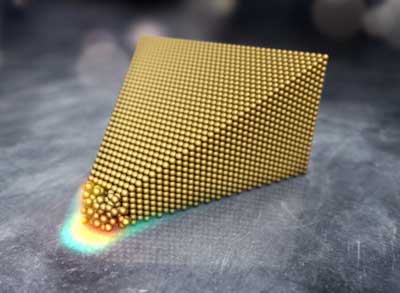 When the tension rises, unexpected things can happen -- not least when it comes to gold atoms. Researchers have now managed, for the first time, to make the surface of a gold object melt at room temperature.
When the tension rises, unexpected things can happen -- not least when it comes to gold atoms. Researchers have now managed, for the first time, to make the surface of a gold object melt at room temperature.
Nov 20th, 2018
Read more
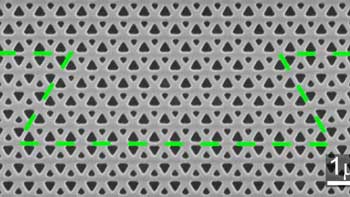 New photonic crystal waveguide based on topological insulators paves the way to build futuristic light-based computers.
New photonic crystal waveguide based on topological insulators paves the way to build futuristic light-based computers.
Nov 19th, 2018
Read more
 Gold nanoparticles, which act like 'nanolenses', concentrate the energy produced by the extremely short pulse of a femtosecond laser to create a nanoscale incision on the surface of the eye's retina cells.
Gold nanoparticles, which act like 'nanolenses', concentrate the energy produced by the extremely short pulse of a femtosecond laser to create a nanoscale incision on the surface of the eye's retina cells.
Nov 19th, 2018
Read more
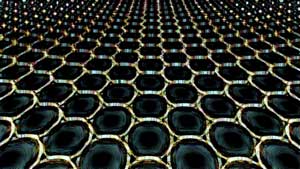 Graphene can generate clock speeds that transcend today's GHz limitations.
Graphene can generate clock speeds that transcend today's GHz limitations.
Nov 19th, 2018
Read more
 The secret ingredient for the next generation of more powerful electronics could be air, according to new research.
The secret ingredient for the next generation of more powerful electronics could be air, according to new research.
Nov 19th, 2018
Read more
 Study shows that label-free digital diagnostics based on nanopore analytics and AI technology can characterize individual virions by their distinct physical features.
Study shows that label-free digital diagnostics based on nanopore analytics and AI technology can characterize individual virions by their distinct physical features.















 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed