 A new 'active nanocomposite' is teeming with motion: small particles connect or separate, thus changing the color of the entire material.
A new 'active nanocomposite' is teeming with motion: small particles connect or separate, thus changing the color of the entire material.
Sep 10th, 2018
Read more
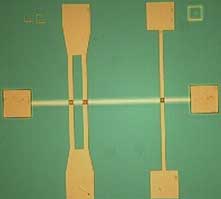 For the first time, complete logic family have been implemented in very straightforward ways.
For the first time, complete logic family have been implemented in very straightforward ways.
Sep 10th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have been studying the folding of 2D materials at the level of single atomic sheets and discovered completely new bending behaviour which is forcing us to look again at how materials deform.
Researchers have been studying the folding of 2D materials at the level of single atomic sheets and discovered completely new bending behaviour which is forcing us to look again at how materials deform.
Sep 10th, 2018
Read more
 Computational tool allows for the development of next-generation communications devices.
Computational tool allows for the development of next-generation communications devices.
Sep 10th, 2018
Read more
 A new process synthesizes vanadium dioxide nanoparticles that makes manufacturing energy-efficient smart windows economical.
A new process synthesizes vanadium dioxide nanoparticles that makes manufacturing energy-efficient smart windows economical.
Sep 8th, 2018
Read more
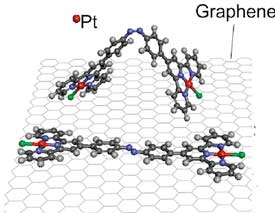 Investigations may lead to easier ways to synthesise nanoparticle supercrystals.
Investigations may lead to easier ways to synthesise nanoparticle supercrystals.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
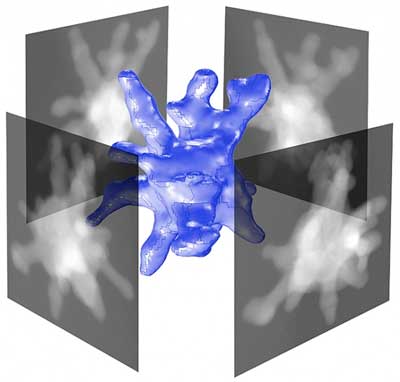 Scientists can now measure 3-D structures of tiny particles with properties that hold promise for advanced sensors and diagnostics.
Scientists can now measure 3-D structures of tiny particles with properties that hold promise for advanced sensors and diagnostics.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
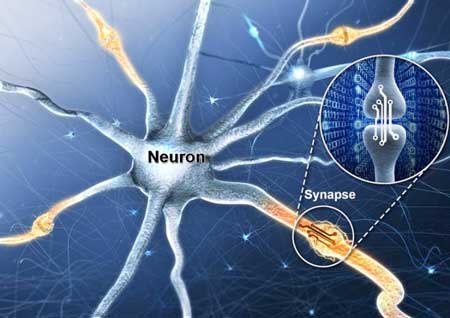 A research team has succeeded in developing an artificial synaptic device that mimics the function of the nerve cells (neurons) and synapses that are response for memory in human brains.
A research team has succeeded in developing an artificial synaptic device that mimics the function of the nerve cells (neurons) and synapses that are response for memory in human brains.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
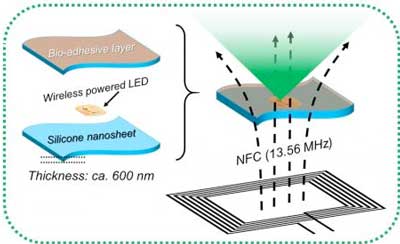 Scientists develop a new device for metronomic photodynamic therapy to facilitate a minimally-invasive and effective cancer treatment in delicate organs.
Scientists develop a new device for metronomic photodynamic therapy to facilitate a minimally-invasive and effective cancer treatment in delicate organs.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
 Physicists have discovered how to manipulate and control individual molecules for a millionth of a billionth of a second, after being intrigued by some seemingly odd results.
Physicists have discovered how to manipulate and control individual molecules for a millionth of a billionth of a second, after being intrigued by some seemingly odd results.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
 Bismuth is a heavy metal with high density and big number of shell electrons. This makes it analogous to such widely used materials as lead. However, in the ratio of the protection efficiency to mass-size parameters bismuth is the best option.
Bismuth is a heavy metal with high density and big number of shell electrons. This makes it analogous to such widely used materials as lead. However, in the ratio of the protection efficiency to mass-size parameters bismuth is the best option.
Sep 7th, 2018
Read more
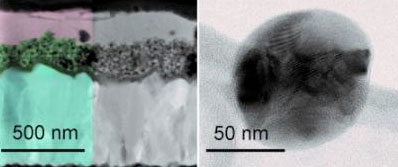 An international research group improved perovskite solar cells efficiency by using materials with better light absorption properties. For the first time, researchers used silicon nanoparticles.
An international research group improved perovskite solar cells efficiency by using materials with better light absorption properties. For the first time, researchers used silicon nanoparticles.
Sep 6th, 2018
Read more
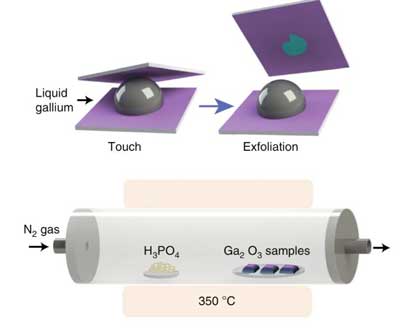 Researchers have developed a revolutionary method to 'print' large-scale sheets of two dimensional piezoelectric material, opening new opportunities for piezo-sensors and energy harvesting.
Researchers have developed a revolutionary method to 'print' large-scale sheets of two dimensional piezoelectric material, opening new opportunities for piezo-sensors and energy harvesting.
Sep 6th, 2018
Read more
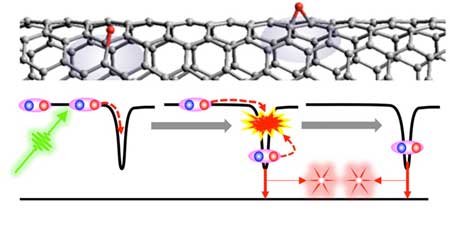 Efficient generation of photon pairs from modified carbon nanotubes shows path to new types of light sources.
Efficient generation of photon pairs from modified carbon nanotubes shows path to new types of light sources.
Sep 6th, 2018
Read more
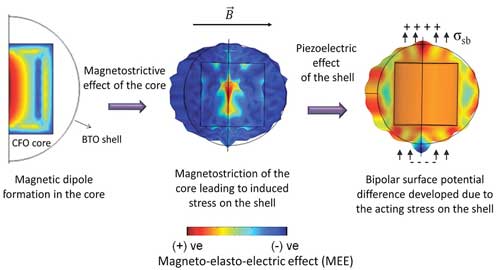 Scientists uncover a way to control terahertz radiation using tiny engineered particles in a magnetic field, potentially opening the doors for better medical and environmental sensors.
Scientists uncover a way to control terahertz radiation using tiny engineered particles in a magnetic field, potentially opening the doors for better medical and environmental sensors.
Sep 6th, 2018
Read more
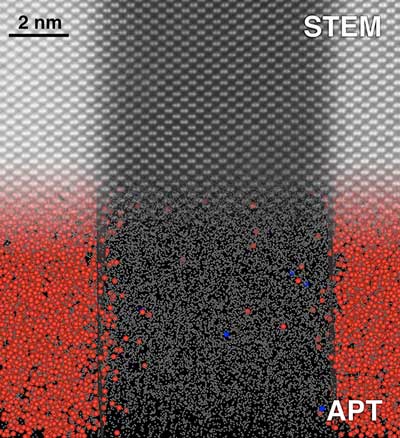 A new approach to atom probe tomography promises more precise and accurate measurements vital to semiconductors used in computers, lasers, detectors, and more.
A new approach to atom probe tomography promises more precise and accurate measurements vital to semiconductors used in computers, lasers, detectors, and more.
Sep 6th, 2018
Read more
 A new 'active nanocomposite' is teeming with motion: small particles connect or separate, thus changing the color of the entire material.
A new 'active nanocomposite' is teeming with motion: small particles connect or separate, thus changing the color of the entire material.















 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed