New nano building block takes a bow
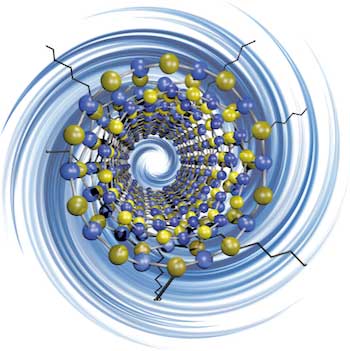 Researchers enhance boron nitride nanotubes for next-gen composites.
Researchers enhance boron nitride nanotubes for next-gen composites.
May 21st, 2018
Read more
 Researchers enhance boron nitride nanotubes for next-gen composites.
Researchers enhance boron nitride nanotubes for next-gen composites.
May 21st, 2018
Read more Scientists create gold catalysts capable of working as artificial enzymes inside living cells, thus triggering chemical reactions which do not exist in nature.
Scientists create gold catalysts capable of working as artificial enzymes inside living cells, thus triggering chemical reactions which do not exist in nature.
May 21st, 2018
Read more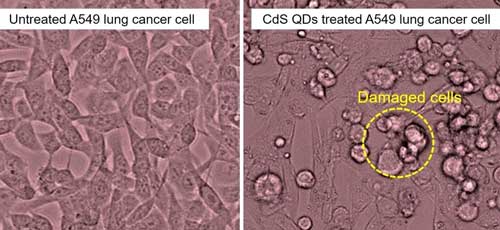 New research shows that nanoparticles derived from tea leaves inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells, destroying up to 80% of them.
New research shows that nanoparticles derived from tea leaves inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells, destroying up to 80% of them.
May 21st, 2018
Read more Researchers exploit tiny defects in diamonds to pave the way for enhanced biological imaging and drug studies.
Researchers exploit tiny defects in diamonds to pave the way for enhanced biological imaging and drug studies.
May 18th, 2018
Read more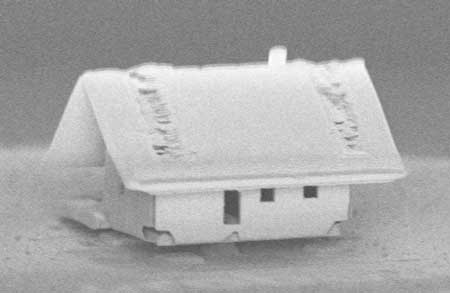 Nanorobotics team demonstrates their new capability to manufacture optical nanotechnologies.
Nanorobotics team demonstrates their new capability to manufacture optical nanotechnologies.
May 18th, 2018
Read more It's great in the lab, but will it actually work? That's the million-dollar question perpetually leveled at engineering researchers. For a family of layered nanomaterials that answer is now, yes.
It's great in the lab, but will it actually work? That's the million-dollar question perpetually leveled at engineering researchers. For a family of layered nanomaterials that answer is now, yes.
May 18th, 2018
Read more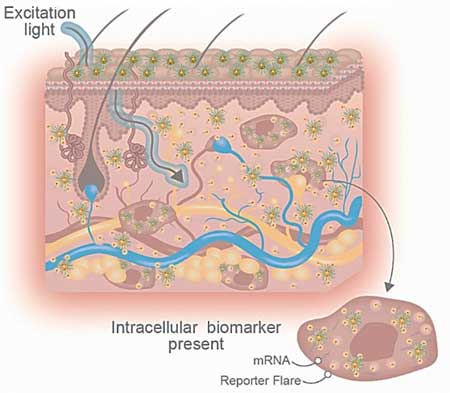 Researchers share more insight into their unique method for skin disease diagnosis using NanoFlare nanotechnology.
Researchers share more insight into their unique method for skin disease diagnosis using NanoFlare nanotechnology.
May 18th, 2018
Read more Flexible display technology with quantum dots.
Flexible display technology with quantum dots.
May 18th, 2018
Read more A team of researchers have made a key step towards understanding the boundary between the quantum world and our everyday classical world.
A team of researchers have made a key step towards understanding the boundary between the quantum world and our everyday classical world.
May 18th, 2018
Read more In exploring the optical properties of the Madagascar comet moth's cocoon fibers, a research team discovers the fibers' exceptional capabilities to reflect sunlight and to transmit optical signals and images, and develops methods to spin artificial fibers mimicking the natural fibers? nanostructures and optical properties.
In exploring the optical properties of the Madagascar comet moth's cocoon fibers, a research team discovers the fibers' exceptional capabilities to reflect sunlight and to transmit optical signals and images, and develops methods to spin artificial fibers mimicking the natural fibers? nanostructures and optical properties.
May 17th, 2018
Read more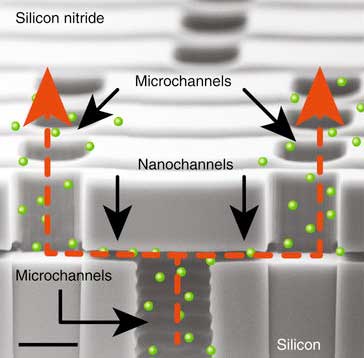 A research team investigating how drug molecules in a solution travel through a nanofluidic membrane found that the molecules and membrane do not interact as expected.
A research team investigating how drug molecules in a solution travel through a nanofluidic membrane found that the molecules and membrane do not interact as expected.
May 17th, 2018
Read more The test, which is at the proof-of-concept stage, can rapidly screen a drop of blood for biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. It can provide results in less than an hour.
The test, which is at the proof-of-concept stage, can rapidly screen a drop of blood for biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. It can provide results in less than an hour.
May 17th, 2018
Read more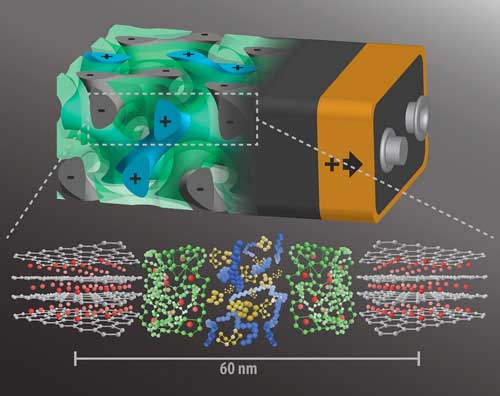 Instead of having the batteries' anode and cathode on either side of a nonconducting separator, researchers intertwine the components in a self-assembling, 3D gyroidal structure, with thousands of nanoscale pores filled with the elements necessary for energy storage and delivery.
Instead of having the batteries' anode and cathode on either side of a nonconducting separator, researchers intertwine the components in a self-assembling, 3D gyroidal structure, with thousands of nanoscale pores filled with the elements necessary for energy storage and delivery.
May 17th, 2018
Read more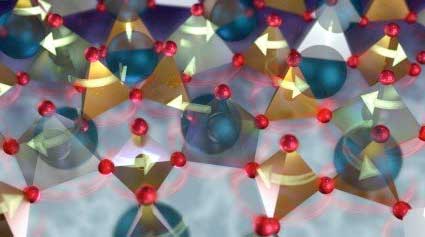 Researchers made the first observations of waves of atomic rearrangements, known as phasons, propagating supersonically through a vibrating crystal lattice - a discovery that may dramatically improve heat transport in insulators and enable new strategies for heat management in future electronics devices.
Researchers made the first observations of waves of atomic rearrangements, known as phasons, propagating supersonically through a vibrating crystal lattice - a discovery that may dramatically improve heat transport in insulators and enable new strategies for heat management in future electronics devices.
May 17th, 2018
Read more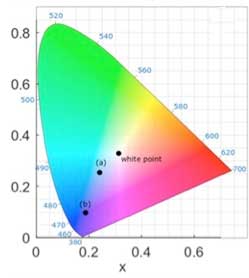 Researchers have developed a novel concept that enables colorants which are based on non-toxic materials, which further do not bleach in the sunlight and which do not lose their appearance under high processing temperatures (as needed for glazes of ceramics).
Researchers have developed a novel concept that enables colorants which are based on non-toxic materials, which further do not bleach in the sunlight and which do not lose their appearance under high processing temperatures (as needed for glazes of ceramics).
May 17th, 2018
Read more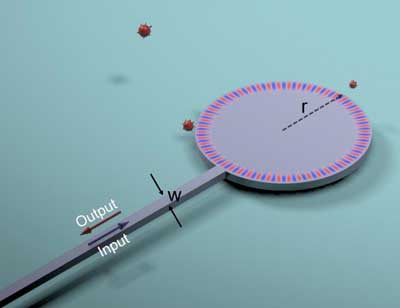 New approach improves practicality of high-sensitivity sensors for cancer, other diseases.
New approach improves practicality of high-sensitivity sensors for cancer, other diseases.
May 17th, 2018
Read more