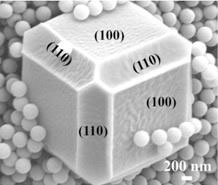
 A research team reports the ability to stabilize different metallic nanostructures by encapsulating them in porous monocrystalline materials.
A research team reports the ability to stabilize different metallic nanostructures by encapsulating them in porous monocrystalline materials.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
 Pure quartz glass is highly transparent and resistant to thermal, physical, and chemical impacts. These are optimum prerequisites for use in optics, data technology or medical engineering. Materials engineers have developed a forming technology to structure quartz glass like a polymer.
Pure quartz glass is highly transparent and resistant to thermal, physical, and chemical impacts. These are optimum prerequisites for use in optics, data technology or medical engineering. Materials engineers have developed a forming technology to structure quartz glass like a polymer.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
 Scientists have made a discovery that will impact the design of not only drug delivery systems, but also the development of newer applications in water filtration and energy production.
Scientists have made a discovery that will impact the design of not only drug delivery systems, but also the development of newer applications in water filtration and energy production.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
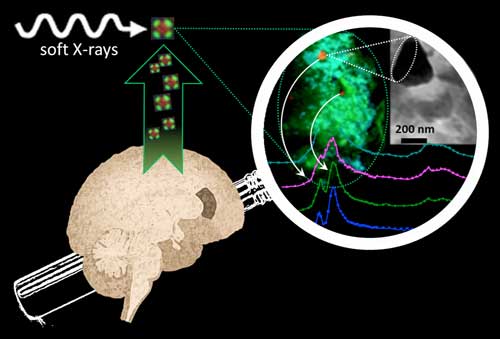 The detection of iron and calcium compounds in amyloid plaque cores.
The detection of iron and calcium compounds in amyloid plaque cores.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
 A piezoelectric ceramic foam supported by a flexible polymer support provides a 10-fold increase in the ability to harvest mechanical and thermal energy over standard piezo composites.
A piezoelectric ceramic foam supported by a flexible polymer support provides a 10-fold increase in the ability to harvest mechanical and thermal energy over standard piezo composites.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
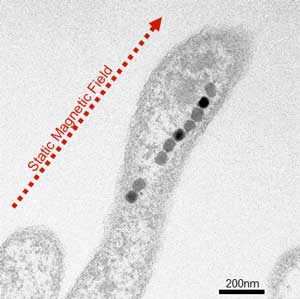 Researchers report that magnetite nanoparticles, which are mechanically rotated by external oscillating magnetic fields, could disturb the water/crystal interface and promote supercooling during the freezing process.
Researchers report that magnetite nanoparticles, which are mechanically rotated by external oscillating magnetic fields, could disturb the water/crystal interface and promote supercooling during the freezing process.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
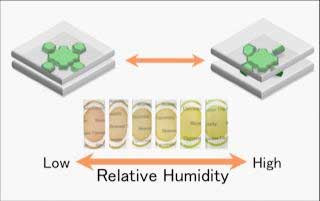 Transparent hybrid film that changes color with humidity via a novel mechanism.
Transparent hybrid film that changes color with humidity via a novel mechanism.
May 17th, 2018
Read more
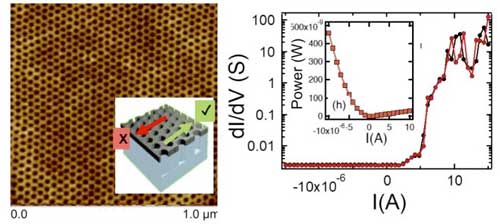 A group of physicists has developed a magnetic material that employs a unique structure - a honeycomb lattice that exhibits distinctive electronic properties.
A group of physicists has developed a magnetic material that employs a unique structure - a honeycomb lattice that exhibits distinctive electronic properties.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have developed a technique to manipulate the electrical conductivity of graphene with compression, bringing the material one step closer to being a viable semiconductor for use in today's electronic devices.
Researchers have developed a technique to manipulate the electrical conductivity of graphene with compression, bringing the material one step closer to being a viable semiconductor for use in today's electronic devices.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
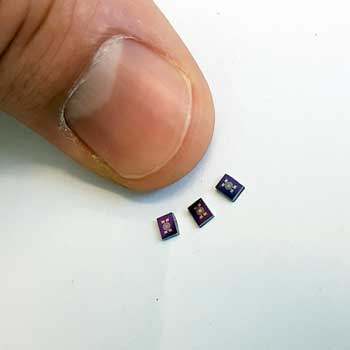 Scientists have developed small and extremely sensitive gas sensors for acetone, ammonia, and isoprene - all metabolic products that we emit in low concentrations via our breath or skin. They combined these sensors in a device with two commercial sensors for CO2 and moisture.
Scientists have developed small and extremely sensitive gas sensors for acetone, ammonia, and isoprene - all metabolic products that we emit in low concentrations via our breath or skin. They combined these sensors in a device with two commercial sensors for CO2 and moisture.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
 Chemists embark on a project to ultimately produce devices that operate mechanically on direct exposure to light.
Chemists embark on a project to ultimately produce devices that operate mechanically on direct exposure to light.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
 Novel method transfers superior nanoscale mechanics to macroscopic fibers.
Novel method transfers superior nanoscale mechanics to macroscopic fibers.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
 Physicists generate attosecond electron pulses with laser light.
Physicists generate attosecond electron pulses with laser light.
May 16th, 2018
Read more
 Cresols disperse carbon nanotubes at unprecedentedly high concentrations.
Cresols disperse carbon nanotubes at unprecedentedly high concentrations.
May 15th, 2018
Read more
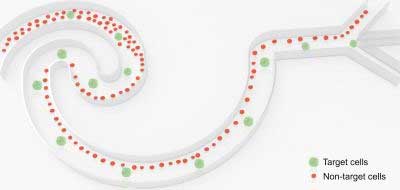 Researchers have developed a precise microscale manipulation method by rapidly flowing cell suspensions through a specially designed microchannel. This novel microfluidic device enables high-throughput sized-based cell sorting of a large amount of biological samples, which has broad applications in practical biomedical research and pharmaceutical fields.
Researchers have developed a precise microscale manipulation method by rapidly flowing cell suspensions through a specially designed microchannel. This novel microfluidic device enables high-throughput sized-based cell sorting of a large amount of biological samples, which has broad applications in practical biomedical research and pharmaceutical fields.
May 15th, 2018
Read more
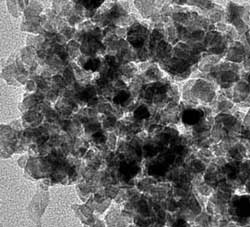 Researchers have applied a new method to study nanoparticles made of cadmium telluride. They used a peculiar feature of this compound: its interaction with light differs depending on the magnetic field.
Researchers have applied a new method to study nanoparticles made of cadmium telluride. They used a peculiar feature of this compound: its interaction with light differs depending on the magnetic field.
May 15th, 2018
Read more
 A research team reports the ability to stabilize different metallic nanostructures by encapsulating them in porous monocrystalline materials.
A research team reports the ability to stabilize different metallic nanostructures by encapsulating them in porous monocrystalline materials.















 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed