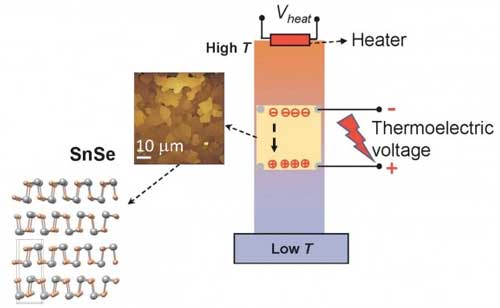
 Researchers discover that nanometer-thick tin selenide crafted in thin films of connected ?nanoflakes? shows promise for thermoelectric energy conversion.
Researchers discover that nanometer-thick tin selenide crafted in thin films of connected ?nanoflakes? shows promise for thermoelectric energy conversion.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
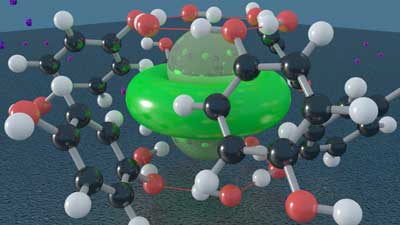 Organic prison too crowded for molecular inmates to move about freely.
Organic prison too crowded for molecular inmates to move about freely.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
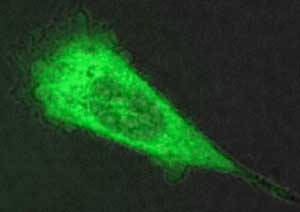 Researchers have created new nanomaterials able to cross cell membranes, establishing a novel platform for the intracellular delivery of molecular drugs and other cargo.
Researchers have created new nanomaterials able to cross cell membranes, establishing a novel platform for the intracellular delivery of molecular drugs and other cargo.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
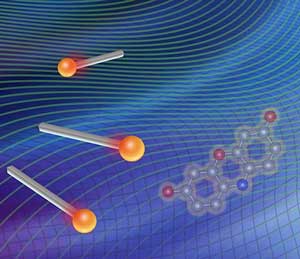 Scientists published a paper, the culmination of years of study, that lays out a conceptual framework for understanding how a nanocatalyst particle works. The work could help inform better design of synthetic nanocatalysts down the road.
Scientists published a paper, the culmination of years of study, that lays out a conceptual framework for understanding how a nanocatalyst particle works. The work could help inform better design of synthetic nanocatalysts down the road.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
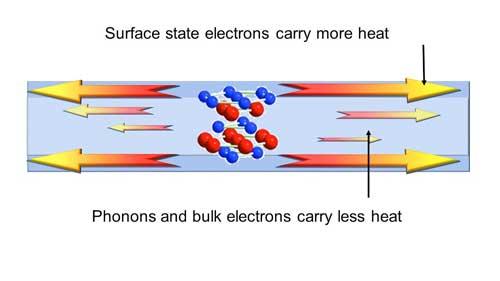 Researchers have demonstrated the ability of a thin film to conduct heat on just its surfaces, identifying a potential solution to overheating in electronic devices such as phones and computers.
Researchers have demonstrated the ability of a thin film to conduct heat on just its surfaces, identifying a potential solution to overheating in electronic devices such as phones and computers.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
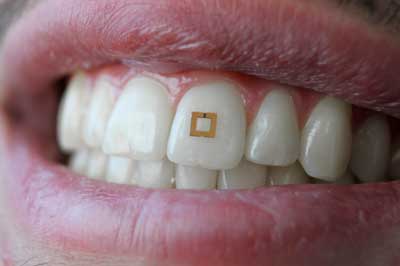 Wireless real-time monitoring could add precision to the linkage between diet and health.
Wireless real-time monitoring could add precision to the linkage between diet and health.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
Single-layer metal oxide nanosheets sandwiched between graphene layers exhibit record energy storage figures of merit.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
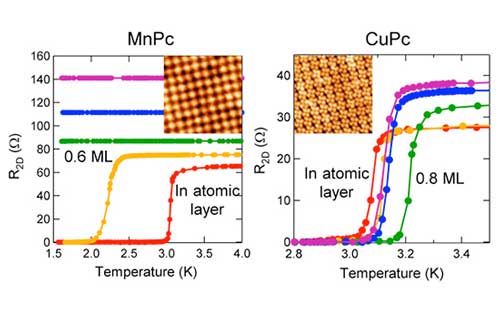 Charge and spin transfer from copper-phthalocyanine organic molecules self-assembled on superconducting atomic layers of indium modifies the superconducting transition temperature of the indium.
Charge and spin transfer from copper-phthalocyanine organic molecules self-assembled on superconducting atomic layers of indium modifies the superconducting transition temperature of the indium.
Mar 27th, 2018
Read more
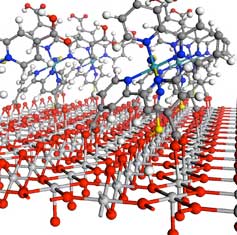 An international research team has found a way to understand and manipulate the transition of charges in molecular junctions.
An international research team has found a way to understand and manipulate the transition of charges in molecular junctions.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
 Engineers have built a bright-light emitting device that is millimeters wide and fully transparent when turned off. The light emitting material in this device is a monolayer semiconductor, which is just three atoms thick.
Engineers have built a bright-light emitting device that is millimeters wide and fully transparent when turned off. The light emitting material in this device is a monolayer semiconductor, which is just three atoms thick.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
 Hybrid plasmonic and pyroelectric harvesting of light fluctuations.
Hybrid plasmonic and pyroelectric harvesting of light fluctuations.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
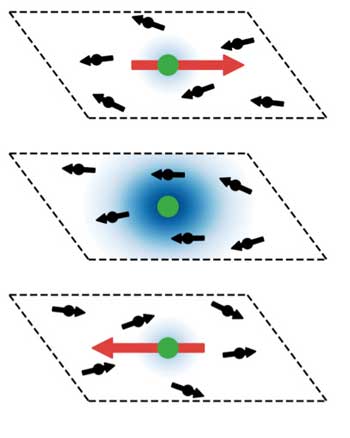 Highly adaptive electronics could be created using quantum features.
Highly adaptive electronics could be created using quantum features.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
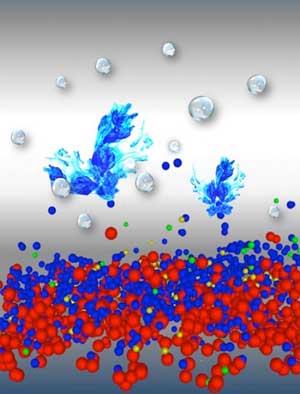 Scientists found out that the topmost atomic layers of electrocatalysts contain chemical species, which determine their efficiency and reveal how they can be influenced to speed-up water splitting.
Scientists found out that the topmost atomic layers of electrocatalysts contain chemical species, which determine their efficiency and reveal how they can be influenced to speed-up water splitting.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
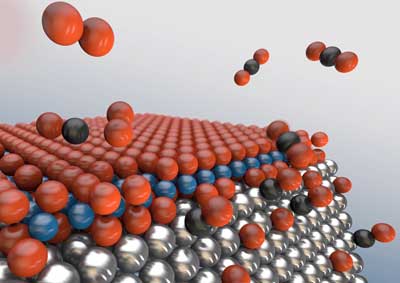 X-rays reveal oxide islands on noble metal nanoparticles.
X-rays reveal oxide islands on noble metal nanoparticles.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
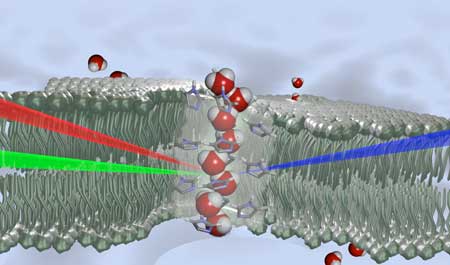 Inspired by cellular proteins, researchers have developed membranes with asymmetric artificial channels in the interior, from which they were able to observe 'chiral' water.
Inspired by cellular proteins, researchers have developed membranes with asymmetric artificial channels in the interior, from which they were able to observe 'chiral' water.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
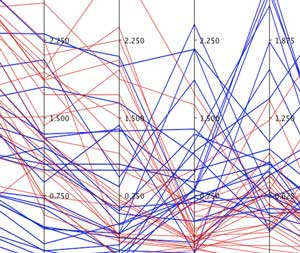 New application of data analysis, visualization techniques achieves better representation of multidimensional materials data.
New application of data analysis, visualization techniques achieves better representation of multidimensional materials data.
Mar 26th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers discover that nanometer-thick tin selenide crafted in thin films of connected ?nanoflakes? shows promise for thermoelectric energy conversion.
Researchers discover that nanometer-thick tin selenide crafted in thin films of connected ?nanoflakes? shows promise for thermoelectric energy conversion.














 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed