 Physicists have developed an attosecond electron microscope that allows them to visualize the dispersion of light in time and space, and observe the motions of electrons in atoms.
Physicists have developed an attosecond electron microscope that allows them to visualize the dispersion of light in time and space, and observe the motions of electrons in atoms.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more
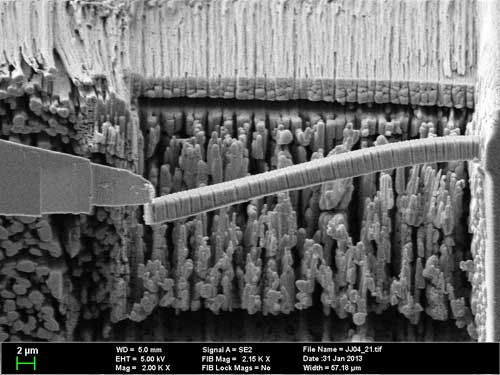 Based on the nanostructure of the sea urchin spines, researchers develop cement that is significantly more fracture-resistant.
Based on the nanostructure of the sea urchin spines, researchers develop cement that is significantly more fracture-resistant.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
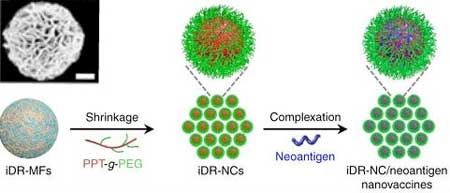 Vaccine stimulates multi-pronged immune attack, inhibits tumor-induced immune suppression.
Vaccine stimulates multi-pronged immune attack, inhibits tumor-induced immune suppression.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
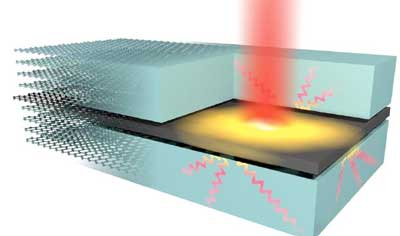 Researchers have recently succeeded in observing and following, in real-time, the way in which heat transport occurs in van der Waals stacks, which consist of graphene encapsulated by the dielectric two-dimensional material hexagonal BN.
Researchers have recently succeeded in observing and following, in real-time, the way in which heat transport occurs in van der Waals stacks, which consist of graphene encapsulated by the dielectric two-dimensional material hexagonal BN.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
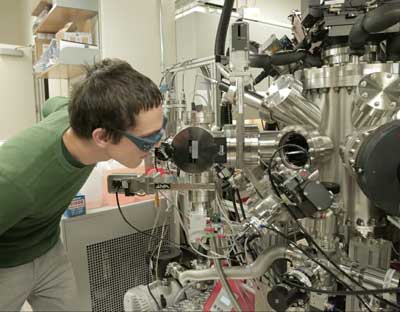 In new research, scientists describe not only their unique process for making a high-quality magnetoelectric material, but exactly how and why it works.
In new research, scientists describe not only their unique process for making a high-quality magnetoelectric material, but exactly how and why it works.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
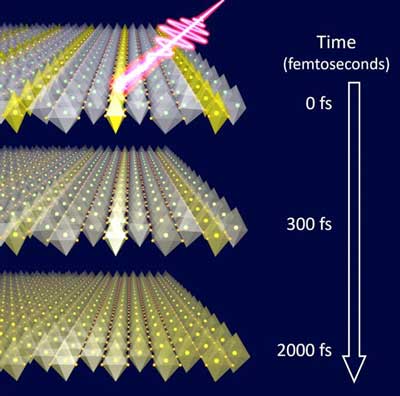 Study uses terahertz laser pulses to reveal ultrafast coupling of atomic-scale patterns.
Study uses terahertz laser pulses to reveal ultrafast coupling of atomic-scale patterns.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
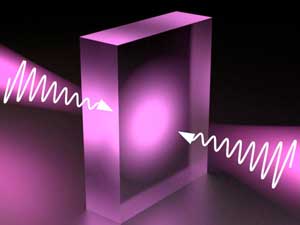 A group of physicists has demonstrated a highly unusual optical effect: They managed to 'virtually' absorb light using a material that has no light-absorbing capacity.
A group of physicists has demonstrated a highly unusual optical effect: They managed to 'virtually' absorb light using a material that has no light-absorbing capacity.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
 Lizards and bark bugs are more similar than they may at first appear: both have unique ways of dealing with water, and this has caught scientists' eyes. The LiNaBioFluid project hopes to replicate both skin systems in organic and inorganic materials for a wide range of applications.
Lizards and bark bugs are more similar than they may at first appear: both have unique ways of dealing with water, and this has caught scientists' eyes. The LiNaBioFluid project hopes to replicate both skin systems in organic and inorganic materials for a wide range of applications.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
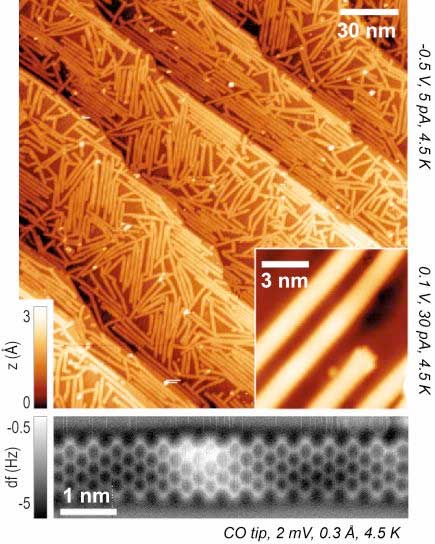 Researchers have succeeded in producing nanotransistors from graphene ribbons that are only a few atoms wide.
Researchers have succeeded in producing nanotransistors from graphene ribbons that are only a few atoms wide.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
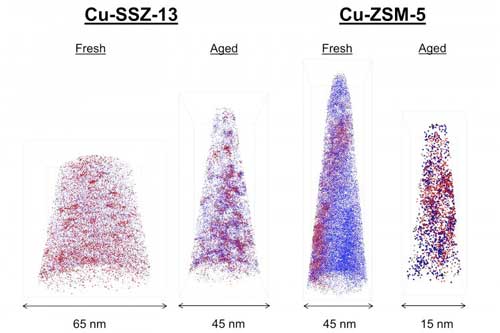 Lower diesel emissions may be possible thanks to a catalyst that 'stays young'.
Lower diesel emissions may be possible thanks to a catalyst that 'stays young'.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
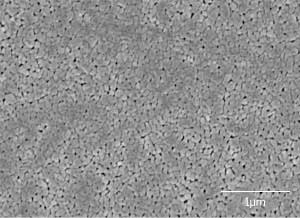 Thin films of a lead-free piezoelectric finally match the performance of the lead-bearing standard.
Thin films of a lead-free piezoelectric finally match the performance of the lead-bearing standard.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
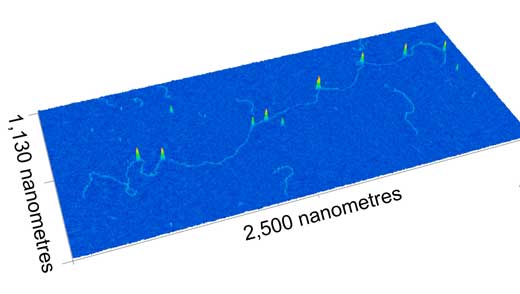 A team of scientists has developed a new nanomapping microscope - powered by the laser and optics found in a typical DVD player.
A team of scientists has developed a new nanomapping microscope - powered by the laser and optics found in a typical DVD player.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
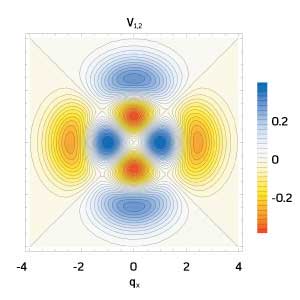 A theoretical model will allow systematic study of a promising class of peculiar quantum states.
A theoretical model will allow systematic study of a promising class of peculiar quantum states.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
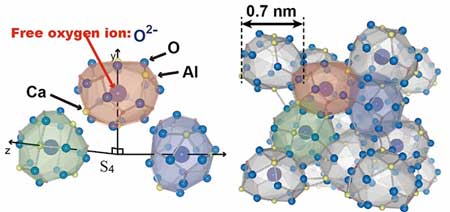 A team of researchers has shown that terahertz rays can be converted to light visible to the human eye. The finding is a breakthrough for functional materials research and could lead to the development of a new kind of terahertz detector.
A team of researchers has shown that terahertz rays can be converted to light visible to the human eye. The finding is a breakthrough for functional materials research and could lead to the development of a new kind of terahertz detector.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
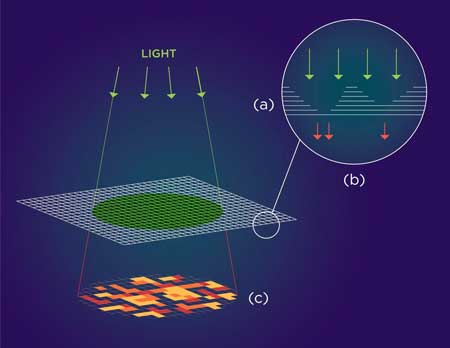 Researchers discover big cryptographic potential in nanomaterial.
Researchers discover big cryptographic potential in nanomaterial.
Nov 29th, 2017
Read more
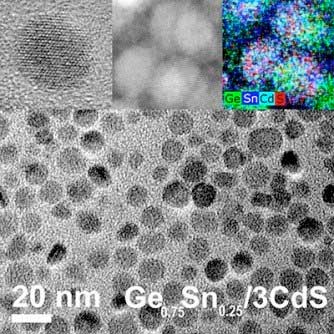 Scientists have developed germanium nanoparticles with improved photoluminescence, making them potentially better materials for solar cells and imaging probes.
Scientists have developed germanium nanoparticles with improved photoluminescence, making them potentially better materials for solar cells and imaging probes.
Nov 28th, 2017
Read more
 Physicists have developed an attosecond electron microscope that allows them to visualize the dispersion of light in time and space, and observe the motions of electrons in atoms.
Physicists have developed an attosecond electron microscope that allows them to visualize the dispersion of light in time and space, and observe the motions of electrons in atoms.















 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed