Simulating physics
 Nature is quantum mechanical, and researchers are ready to study it with a nine-qubit array and the problem of many-body localization.
Nature is quantum mechanical, and researchers are ready to study it with a nine-qubit array and the problem of many-body localization.
Dec 1st, 2017
Read more
 Nature is quantum mechanical, and researchers are ready to study it with a nine-qubit array and the problem of many-body localization.
Nature is quantum mechanical, and researchers are ready to study it with a nine-qubit array and the problem of many-body localization.
Dec 1st, 2017
Read more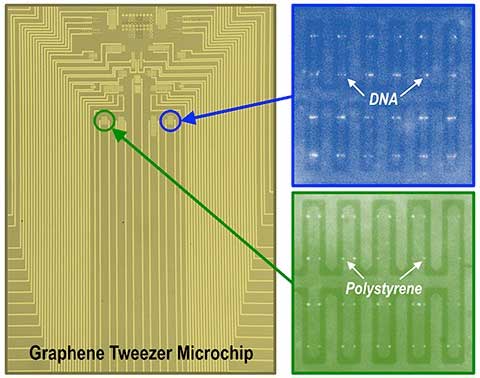 Discovery could lead to revolutionary handheld disease diagnostic system.
Discovery could lead to revolutionary handheld disease diagnostic system.
Dec 1st, 2017
Read more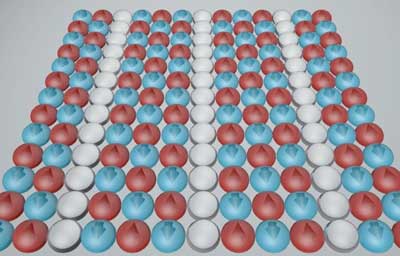 These stripes of electron spin and charge are exciting because of their possible link to a phenomenon that could transform society by making electrical transmission nearly 100 percent efficient.
These stripes of electron spin and charge are exciting because of their possible link to a phenomenon that could transform society by making electrical transmission nearly 100 percent efficient.
Dec 1st, 2017
Read more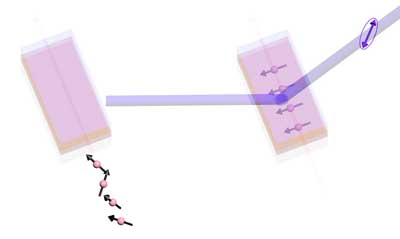 Electric fields produced by structural mismatches between two materials could be harnessed to manage data in spintronic devices.
Electric fields produced by structural mismatches between two materials could be harnessed to manage data in spintronic devices.
Dec 1st, 2017
Read more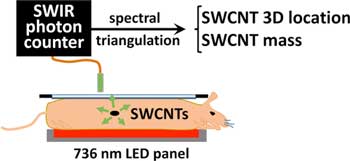 Scientists use fluorescent carbon nanotube probes to achieve first in vivo success.
Scientists use fluorescent carbon nanotube probes to achieve first in vivo success.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more Simple model used to compute elasticity of newly synthesized glassy diamond.
Simple model used to compute elasticity of newly synthesized glassy diamond.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more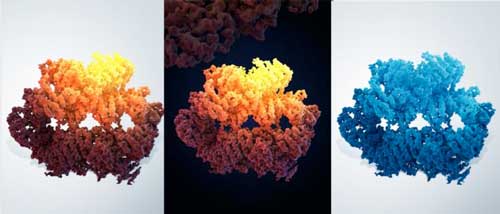 At the first hint of DNA damage, a protein known as an ATR kinase activates the cell's built-in repair system. Scientists have now imaged this protein at unprecedented resolution, and are beginning to understand its response to DNA damage.
At the first hint of DNA damage, a protein known as an ATR kinase activates the cell's built-in repair system. Scientists have now imaged this protein at unprecedented resolution, and are beginning to understand its response to DNA damage.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more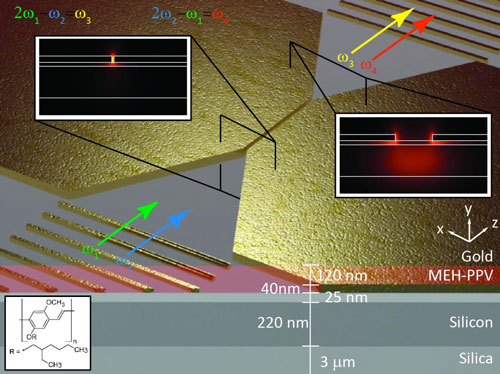 By forcing light to go through a smaller gap than ever before, researchers have paved the way for computers based on light instead of electronics.
By forcing light to go through a smaller gap than ever before, researchers have paved the way for computers based on light instead of electronics.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more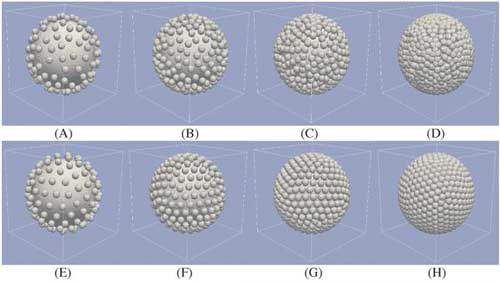 Researcher uses supercomputers to explore optical properties of plasmonic nanovesicles for drug delivery and investigations of molecules in the brain.
Researcher uses supercomputers to explore optical properties of plasmonic nanovesicles for drug delivery and investigations of molecules in the brain.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more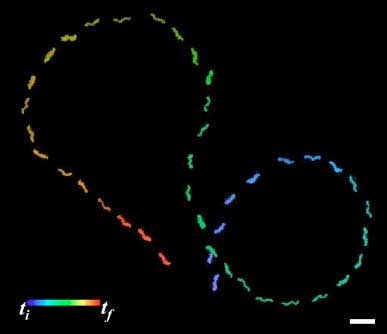 By using bacterial flagella as a template for silica, researchers have demonstrated an easier way to make propulsion systems for nanoscale swimming robots.
By using bacterial flagella as a template for silica, researchers have demonstrated an easier way to make propulsion systems for nanoscale swimming robots.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more Researchers have developed a novel system that enables aggregates composed of magnetised particles to roll along a channel in a combined acoustic and magnetic field.
Researchers have developed a novel system that enables aggregates composed of magnetised particles to roll along a channel in a combined acoustic and magnetic field.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more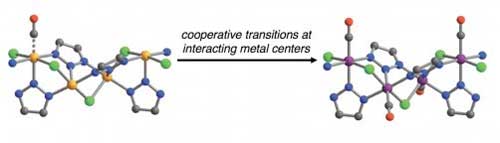 Metal-organic frameworks with chains of iron centers adsorb and release carbon monoxide with very little energy input.
Metal-organic frameworks with chains of iron centers adsorb and release carbon monoxide with very little energy input.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more An entirely human-made architecture produces hydrogen fuel using light, shows promise for transmitting energy in numerous applications.
An entirely human-made architecture produces hydrogen fuel using light, shows promise for transmitting energy in numerous applications.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more Novel defect control in graphene enables direct imaging of trapped electrons that follow Einstein's rules.
Novel defect control in graphene enables direct imaging of trapped electrons that follow Einstein's rules.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more Could the manufacture of the integrated circuits and chips for our everyday electronic devices be made simpler, safer and cheaper simply by being able to switch coloured light on and off?
Could the manufacture of the integrated circuits and chips for our everyday electronic devices be made simpler, safer and cheaper simply by being able to switch coloured light on and off?
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more Researchers report report a general strategy for the high-yield production of MoS2 and WS2 quantum sheets with intrinsic and defect-free characteristics, which was achieved by sequential combination of salt-assisted ball-milling and sonication-assisted solvent exfoliation of the bulk materials.
Researchers report report a general strategy for the high-yield production of MoS2 and WS2 quantum sheets with intrinsic and defect-free characteristics, which was achieved by sequential combination of salt-assisted ball-milling and sonication-assisted solvent exfoliation of the bulk materials.
Nov 30th, 2017
Read more