| Posted: Jul 06, 2015 |
Transition from 3 to 2 dimensions increases conduction
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Scientists from the MIPT Department of Molecular and Chemical Physics have for the first time described the behavior of electrons in a previously unstudied analogue of graphene, two-dimensional niobium telluride, and, in the process, uncovered the nature of two-dimensionality effects on conducting properties. These findings will help in the creation of future flat and flexible electronic devices.
|
|
In recent decades, physicists have been actively studying so-called two-dimensional materials. Andrei Geim and Konstantin Novoselov received the Nobel Prize for their research on graphene, the most well-known among them. The properties of such materials, which can be described as "sheets" with a thickness of a few atoms, strongly differ from their three-dimensional analogues. For example, graphene is transparent, conducts current better than copper and has good thermal conductivity. Scientists believe that other types of two-dimensional materials may possess even more exotic properties.
|
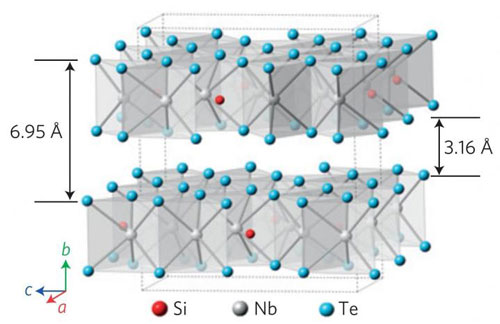 |
| This is the crystal structure of Nb3SiTe6.
|
|
A group of scientists from Russia and the USA, including Pavel Sorokin and Liubov Antipina from MIPT, recently conducted research on the properties of the crystals of one such material,Nb3SiTe6, a compound of niobium telluride (Nature Physics, "Enhanced electron coherence in atomically thin Nb3SiTe6"). In their structure, the crystals resemble sandwiches with a thickness of three atoms (around 4 angstroms): a layer of tellurium, a layer of niobium mixed with silicon atoms and then another layer of tellurium. This substance belongs to a class of materials known as dichalcogenides, which many scientists view as promising two-dimensional semiconductors.
|
|
The scientists synthesized Nb3SiTe6 crystals in a laboratory at Tulane University (New Orleans). They then separated them into two-dimensional layers, taking samples for further analysis by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray crystal analysis and other methods. The goal of the researchers was to investigate electron-phonon interaction changes in two-dimensional substances.
|
|
Quasi particles, quanta of crystal lattice oscillations, are called phonons. Physicists introduced the concept of phonons because it helped simplify the description of processes in crystals, and tracking of electron-phonon interaction is fundamentally important for description of the different conducting properties in matter.
|
|
"We developed a theory that predicts that electron-phonon interaction is suppressed due to dimensional effects in two-dimensional material. In other words, these materials obstruct the flow of electrons to a lesser extent," says Pavel Sorokin, a co-author of the study, doctor of physical and mathematical sciences, and lecturer at the MIPT Section of the Physics and Chemistry of Nanostructures (DMCP).
|
|
American colleagues confirmed this predictioninrelatedexperiments. "They conducted measurements where the same effectwas observed. Our calculations allowed the ruling out of other explanations; we managed to prove that changes in electron-phonon interaction occur specifically because of the two-dimensionality of the membrane," Sorokin adds.
|

