| Dec 16, 2020 |
Changing graphene properties one bond at a time
(Nanowerk News) An international research team has demonstrated a novel process to modify the structure and properties of graphene. This chemical reaction, known as photocycloaddition, modifies the bonds between atoms using ultraviolet (UV) light.
|
|
The results of the study were recently published in the prestigious journal Nature Chemistry ("Long-range ordered and atomic-scale control of graphene hybridization by photocycloaddition").
|
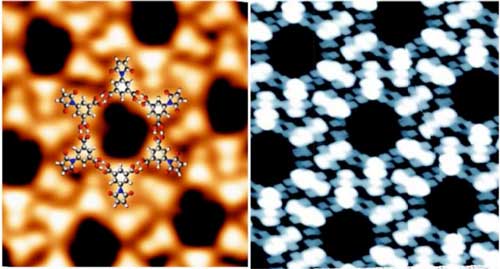 |
| Magnified experimental and simulated scanning tunnelling microscopy images of the molecule used (maleimide derivative-BCM) network on graphene. (Image: INRS)
|
|
Graphene has outstanding physical, optical and mechanical properties. For instance, it is commonly used in the manufacture of transparent touch screens, in aerospace, and in biomedicine. This material, however, has limited use in electronics.
|
|
"No other material has properties similar to graphene, yet unlike semiconductors used in electronics, it lacks a band gap. In electronics, this gap is a space in which there are no energy levels that can be occupied by electrons. Yet it is essential for interacting with light," explains Professor Federico Rosei of INRS's Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre.
|
|
"The multidisciplinary group of researchers from Canada, China, Denmark, France and the United Kingdom succeeded in modifying graphene so as to create a band gap. Current research is rather fundamental but could have repercussions over the next few years in optoelectronics, such as in the fabrication of photodetectors or in the field of solar energy. These include the manufacture of high-performance photovoltaic cells for converting solar energy into electricity, or the field of nanoelectronics, for the extreme miniaturisation of devices," emphasizes Professor Rosei.
|
|
This breakthrough is complementary to the results published in Nature Materials ("Synthesis of mesoscale ordered two-dimensional π-conjugated polymers with semiconducting properties"), by an Italian-Canadian team of researchers under the supervision of Professor Rosei.
|
|
Professor Rosei's research has been recognized numerous times by national and international awards and distinctions. These include the recent Brimacombe Medal from the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS), the Royal Society of Chemistry, which identified him as one of the 5% most cited authors for its journals in 2019, and the Stanford list of the 2% most cited researchers in the world.
|

