| Dec 13, 2022 |
Discovery overturns major assumptions in crystal photochemistry
(Nanowerk News) Photochemical reactions were thought to occur uniformly so that when light shines on crystals evenly, they change color evenly. But a research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has discovered that a photomechanical molecular crystal, 2,5-distyrylpyrazine (DSP), undergoes photochemical reactions differently, with the color change spreading from the crystal’s edges and propagating to its center.
|
|
Stimuli-responsive materials, whose physical properties change in response to external stimuli such as light and heat, are being widely studied as next-generation functional materials. Especially, photo-responsive materials are attracting much attention because their physicochemical properties can be modulated remotely without any physical contact. As one of the photo-responsive materials, photomechanical molecular crystals, which consist of molecules that undergo photochemical reactions upon light irradiation, are being intensively investigated because of their unique photoresponsive behaviors.
|
|
Unlike in solutions where molecules exist independently, the molecules are arranged densely and regularly in crystals, so the unique photoreaction dynamics in crystals must be considered. However, previous studies on photoreactive molecular crystal materials have usually assumed that photoreactions in crystals proceed like those in solutions and follow classical photoreaction kinetics. So, understanding of physicochemical property changes based on the photochemical reaction kinetics in crystals has been an issue for further development of this research field.
|
|
A research group led by Kohei Morimoto, a third-year doctoral student at the Osaka City University Graduate School of Engineering, and Dr. Daichi Kitagawa and Professor Seiya Kobatake at the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering has discovered that photoreactions in 2,5-distyrylpyrazine (DSP) crystals propagate from each of the crystal’s edges to its center. The research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition ("Edge-to-Center Propagation of Photochemical Reaction during Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Photomechanical Transformation of 2,5-Distyrylpyrazine Crystals").
|
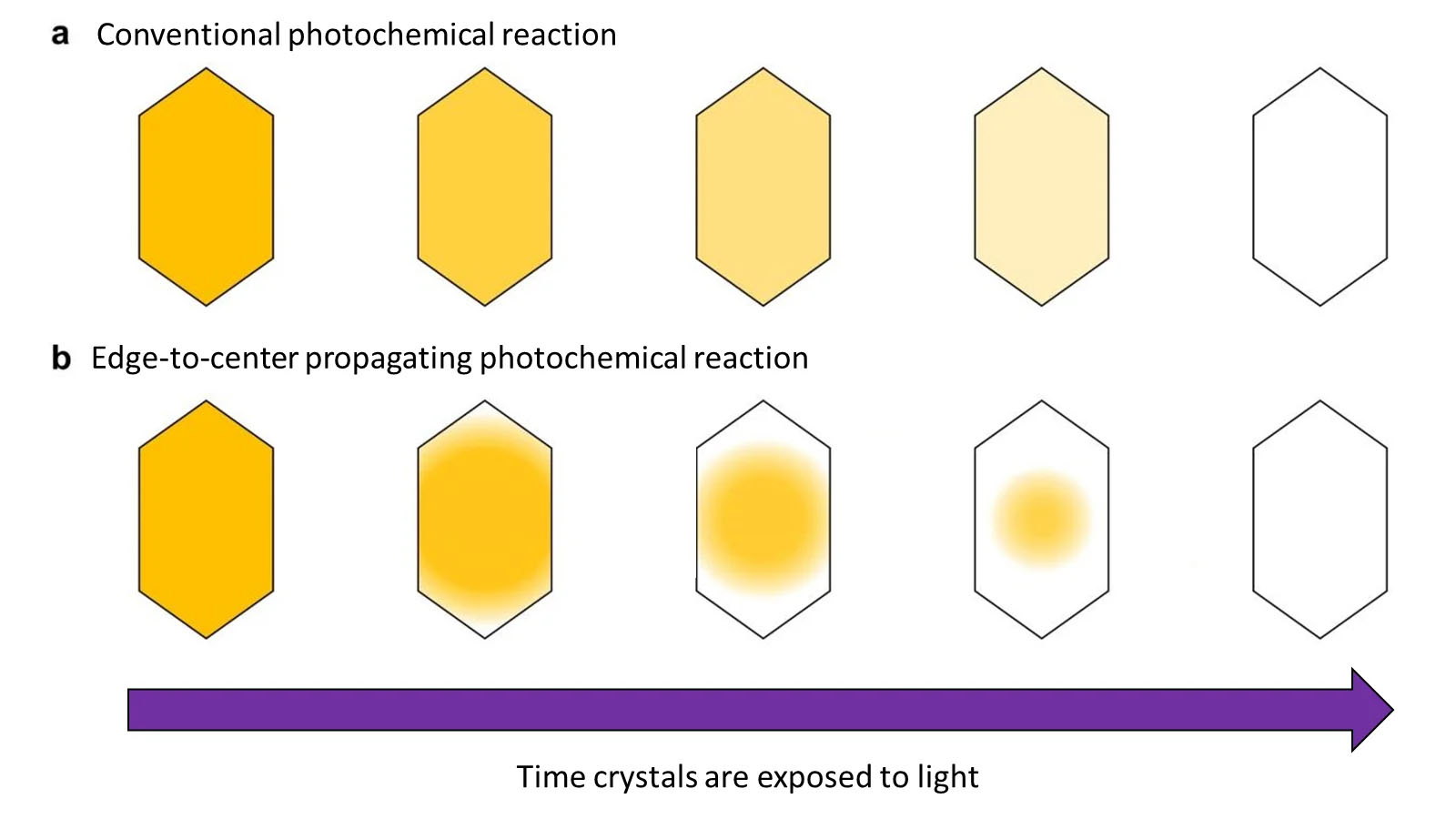 |
| Photochemical reactions were thought to occur uniformly so that when light shines on crystals evenly, they change color evenly. But a research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has discovered that a photomechanical molecular crystal, 2,5-distyrylpyrazine (DSP), undergoes photochemical reactions differently, with the color change spreading from the crystal’s edges and propagating to its center. (Image: Daichi Kitagawa, Osaka Metropolitan University)
|
|
Normally, when light shines evenly on a crystal, the color change caused by the photoreaction also proceeds evenly. However, the research group found that in DSP crystals, the color change started at the crystal’s edge and proceeded to its center, propagating the photoreaction like a wave. The research group determined that this edge-to-center propagation of the color change happens for two reasons: a surface effect, which makes reactivity extremely high at the edges of the crystal, and a cooperative effect, which also elevates reactivity for molecules whose neighbors have already changed color.
|
|
“This phenomenon, which deviates from the conventional conception of photochemistry, is hugely significant for how we understand the basic fundamental science of photoreactions,” said Dr. Kitagawa. “In the future, we would like to clarify the conditions necessary for this unique photoreaction to occur and explore how they can be used to create new functional materials that take advantage of this phenomenon.”
|

