| Jan 24, 2024 |
Organic electronics lead to new ways to sense light
(Nanowerk News) The past few decades have seen astonishing advances in imaging technology, from high-speed optical sensors that process over two million frames per second to tiny lensless cameras that record images using a single pixel.
|
|
In a study recently published in Advanced Materials ("Ultraflexible Wireless Imager Integrated with Organic Circuits for Broadband Infrared Thermal Analysis"), researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research), at Osaka University have developed an optical sensor on an ultrathin, flexible sheet that can be bent without breaking. In fact, this sensor is so flexible, it will work even after it has been crumpled into a ball.
|
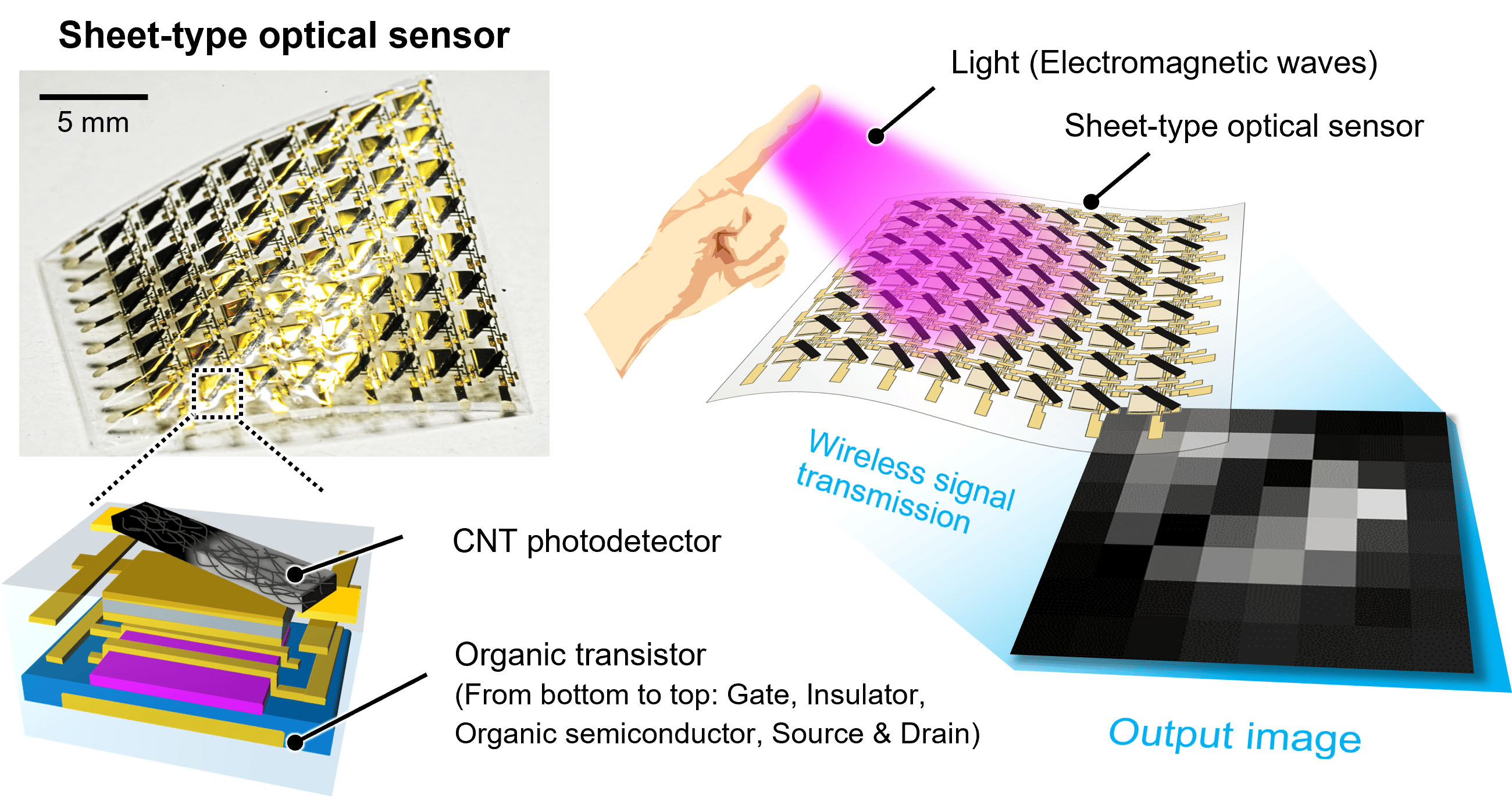 |
| Sheet-type optical sensor integrated with a carbon nanotube photodetector and an organic transistor. (Reprinted with permission from Advanced Materials, CC BY 4.0)
|
|
In a camera, the optical sensor is the device that senses the light that has passed through a lens, similar to the retina inside a human eye.
|
|
“Conventional optical sensors are built using inorganic semiconductors and ferroelectric materials,” says Rei Kawabata, lead author of the study. “This makes the sensors stiff and unable to bend. To avoid this problem, we looked at a different way to detect light.”
|
|
Instead of traditional light sensors, the researchers use an array of tiny carbon nanotube photodetectors printed on an ultra-thin polymer substrate (less than 5 µm). When exposed to light, the carbon nanotubes heat up, creating a thermal gradient that then generates a voltage signal. Doping the nanotubes with chemical carriers during printing further increases their sensitivity. Using these nanotubes, visible light as well as infrared light such as those related to heat or molecules can be measured.
|
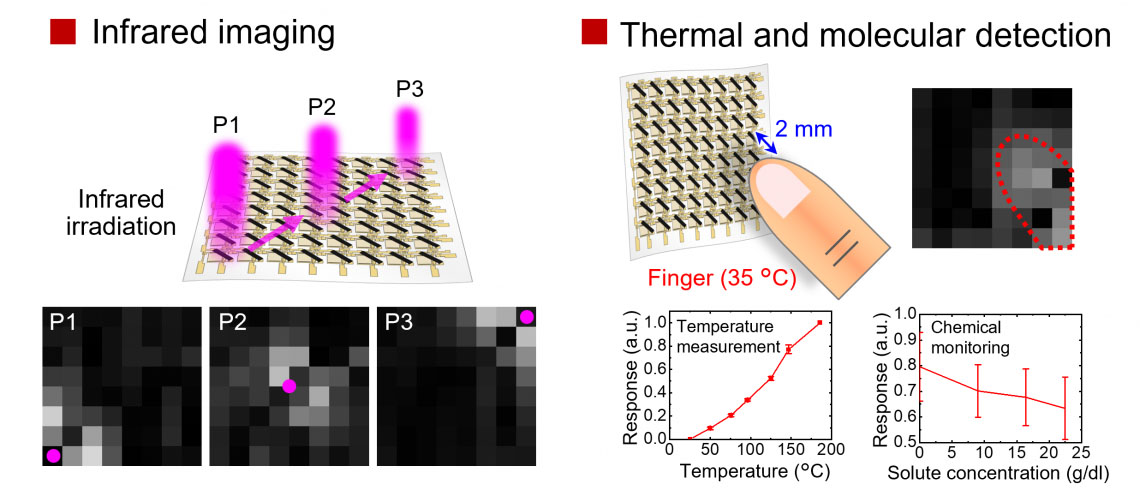 |
| Detection and imaging of light, heat, and molecules using sheet-type optical sensors. (Reprinted with permission from Advanced Materials, CC BY 4.0)
|
|
Along with the carbon nanotube sensors, organic transistors are also printed on the polymer substrate to organize the voltage signals into an image signal. To read this signal, a computer does not need to be physically connected by wires to the sensor. Instead, a wireless Bluetooth module is used.
|
|
“Together with this wireless system, our imager can attach soft and curved objects to analyse their surfaces or insides without damaging them,” says Teppei Araki, senior author of the study.
|
|
The researchers built a prototype of the sheet-type optical sensor and tested its ability to sense heat from objects like human fingers or wires as well as glucose flowing through tubes. They found the optical sensor has high sensitivity over a wide range of wavelengths. Moreover, at room temperature and atmospheric conditions, tests showed it has high bending durability and worked even after it was crumpled.
|
|
The unique advantages of this wireless measurement system and sheet-type optical sensor will lead to new and simpler ways to perform many tasks such as evaluating the quality of liquid without needing to sample it. The researchers believe it holds high promise in many applications such as non-destructive imaging, wearable devices, and soft robotics.
|


