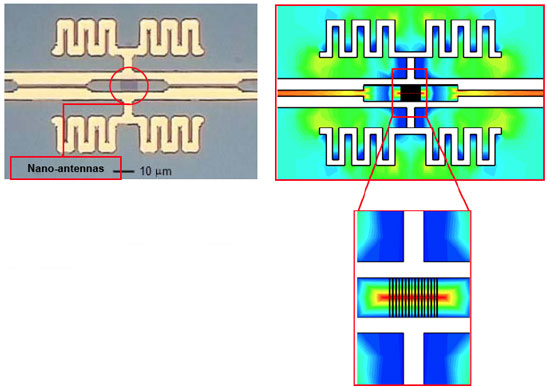
 Scientists who have developed a new way to create a type of radiation known as Terahertz (THz) or T-rays say their new, stronger and more efficient continuous wave T-rays could be used to make better medical scanning gadgets and may one day lead to innovations similar to the "tricorder" scanner used in Star Trek.
Scientists who have developed a new way to create a type of radiation known as Terahertz (THz) or T-rays say their new, stronger and more efficient continuous wave T-rays could be used to make better medical scanning gadgets and may one day lead to innovations similar to the "tricorder" scanner used in Star Trek.
Jan 20th, 2012
Read more
A new class of nanoparticles, synthesized by a UC Davis research team to prevent premature drug release, holds promise for greater accuracy and effectiveness in delivering cancer drugs to tumors.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
Novel technology that reveals lysozymes have jaws could aid in early cancer diagnosis.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
To overcome a built-in mechanism that makes tumors resistant to radiation resistance, researchers have developed a nanoparticle formulation that interferes with the resistance mechanism, and as a result, increases the efficacy of radiation therapy in a mouse model of head and neck cancer.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have developed a strategy for identifying what could be called tumor uptake molecules for use on nanoparticles. This new class of tumor-targeting agents boosts the amount of drug-loaded nanoparticles that get into cancer cells.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
One of the ways in which cancer cells evade anticancer therapy is by producing a protein that pumps drugs out of the cell before these compounds can exert their cell-killing effects. A research team at Northwestern University has found that biocompatible iron oxide-titanium dioxide nanoparticles can bypass this pump and enable DNA-damaging anticancer drugs to reach the cell nucleus.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
Using technologies common to the semiconductor industry, a team of investigators at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Liquidia Technologies has created a polymer nanoparticle that can encapsulate large loads of therapeutic molecules that may have use in treating prostate cancer.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
A collaborative effort between researchers at Stanford University and Xiamen University in China has produced a stable, biocompatible quantum dot that appears to have the desired set of properties needed for biomedical imaging.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
By combining a nanoparticle that is readily visible in X-ray computed tomography (CT) scans with a molecule that targets tumor lymph vessels and other tumor tissues, a research team from the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) and the Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute has developed a new imaging agent that provides high-fidelity CT images of tumors and their edges.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
 It is so small that it cannot be seen by the naked eye - but a tiny Chinese New Year greetings card created by the University of Glasgow represents the huge potential for China to profit from Scottish innovation.
It is so small that it cannot be seen by the naked eye - but a tiny Chinese New Year greetings card created by the University of Glasgow represents the huge potential for China to profit from Scottish innovation.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
 Five scientists from the SUNCAT Center for Interface Science and Catalysis, at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford's Department of Chemical Engineering, have a solution for those who design new chemical catalysts: They made an app.
Five scientists from the SUNCAT Center for Interface Science and Catalysis, at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford's Department of Chemical Engineering, have a solution for those who design new chemical catalysts: They made an app.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
NanoIsrael 2012 (held on March 26th-27th, 2012) to highlight alternative energy, nanomaterials, nanobio, nanomedicine and nanoelectronics.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
Scientists have discovered that a superlattice phase-change film multilayered using germanium-tellurium alloy sub-layers and antimony-tellurium alloy sub-layers with aligned orientation axes has a magnetoresistance effect in excess of 2000% in a temperature range from room temperature to around 150 C.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
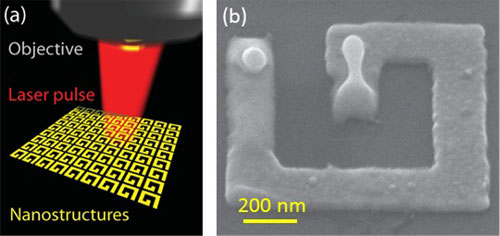 When a pebble is dropped onto the surface of a pond, a droplet of water bounces up from the surface. The same thing happens when a focussed laser-beam strikes the surface of a thin metal film - the metal can be locally melted by the laser light and it can bounce up from the metal surface as a metallic droplet. Researchers now show that this phenomenon can be used to make nanoscale metallic droplets.
When a pebble is dropped onto the surface of a pond, a droplet of water bounces up from the surface. The same thing happens when a focussed laser-beam strikes the surface of a thin metal film - the metal can be locally melted by the laser light and it can bounce up from the metal surface as a metallic droplet. Researchers now show that this phenomenon can be used to make nanoscale metallic droplets.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
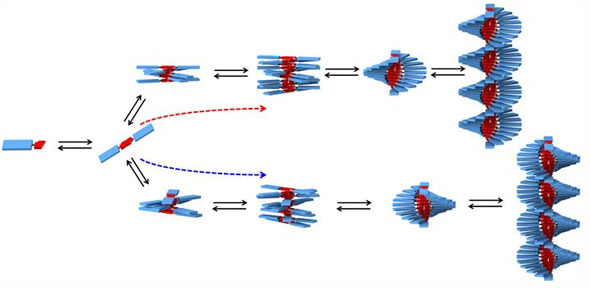 Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) have succeeded in monitoring and controlling a molecular self-assembly process via different pathways. While it was formerly thought that the molecules form the right structure by themselves, this research shows that the assembly process can follow different pathways yielding different structures; in this case polymer chains with left- and right-handed helical directions.
Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) have succeeded in monitoring and controlling a molecular self-assembly process via different pathways. While it was formerly thought that the molecules form the right structure by themselves, this research shows that the assembly process can follow different pathways yielding different structures; in this case polymer chains with left- and right-handed helical directions.
Jan 19th, 2012
Read more
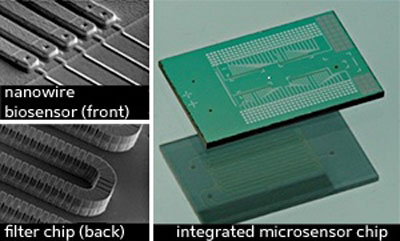 A*STAR researchers have developed an integrated chip device for the rapid analysis of blood samples from cardiac patients.
A*STAR researchers have developed an integrated chip device for the rapid analysis of blood samples from cardiac patients.
Jan 18th, 2012
Read more
 Scientists who have developed a new way to create a type of radiation known as Terahertz (THz) or T-rays say their new, stronger and more efficient continuous wave T-rays could be used to make better medical scanning gadgets and may one day lead to innovations similar to the "tricorder" scanner used in Star Trek.
Scientists who have developed a new way to create a type of radiation known as Terahertz (THz) or T-rays say their new, stronger and more efficient continuous wave T-rays could be used to make better medical scanning gadgets and may one day lead to innovations similar to the "tricorder" scanner used in Star Trek.





 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed