A potential control over superconductivity
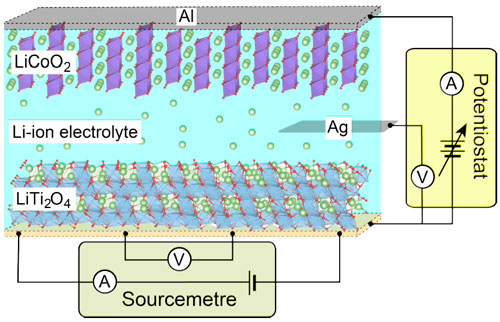 An applied potential can reversibly induce a superconducting-insulator transition in lithium titanate thin films.
An applied potential can reversibly induce a superconducting-insulator transition in lithium titanate thin films.
Nov 7th, 2015
Read more
 An applied potential can reversibly induce a superconducting-insulator transition in lithium titanate thin films.
An applied potential can reversibly induce a superconducting-insulator transition in lithium titanate thin films.
Nov 7th, 2015
Read more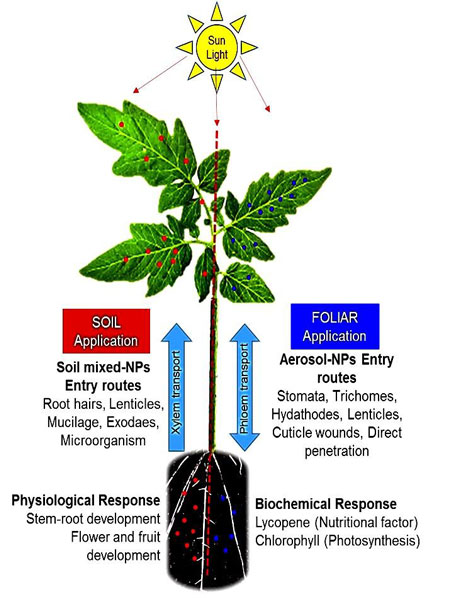 Researchers are using nanoparticles to boost the nutrient content and growth of tomato plants. Taking a clue from their work with solar cells, the team found that by using zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, the tomato plants better absorbed light and minerals, and the fruit had higher antioxidant content.
Researchers are using nanoparticles to boost the nutrient content and growth of tomato plants. Taking a clue from their work with solar cells, the team found that by using zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, the tomato plants better absorbed light and minerals, and the fruit had higher antioxidant content.
Nov 7th, 2015
Read more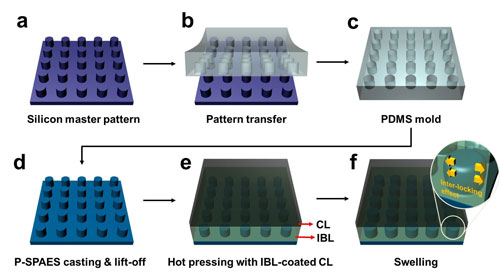 Scientists have developed a new way of making fuel cell membranes using nanoscale fasteners, paving the way for lower-cost, higher-efficiency and more easily manufactured fuel cells.
Scientists have developed a new way of making fuel cell membranes using nanoscale fasteners, paving the way for lower-cost, higher-efficiency and more easily manufactured fuel cells.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more A major showcase of companies developing new technologies from graphene and other two-dimensional materials took place this week at the Cambridge Graphene Centre.
A major showcase of companies developing new technologies from graphene and other two-dimensional materials took place this week at the Cambridge Graphene Centre.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read moreAn international collaboration has produced the first in vitro model of the outer membrane of the bacteria E. coli providing a tool for developing new antibiotics and other drugs.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more New technique using existing technologies allows unprecedented views of cells and other soft materials.
New technique using existing technologies allows unprecedented views of cells and other soft materials.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more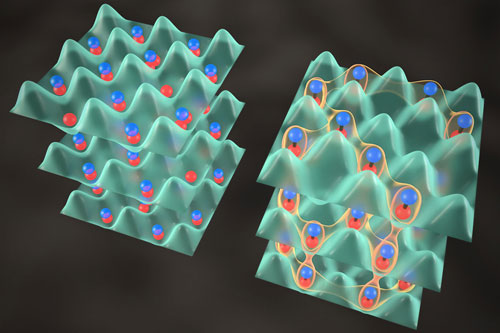 The crystal is useful for studying correlations among the molecules' spins, or rotations, a quantum behavior related to magnetism.
The crystal is useful for studying correlations among the molecules' spins, or rotations, a quantum behavior related to magnetism.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more Chemists devised a new way to detect chemical damage to DNA that sometimes leads to genetic mutations responsible for many diseases, including various cancers and neurological disorders.
Chemists devised a new way to detect chemical damage to DNA that sometimes leads to genetic mutations responsible for many diseases, including various cancers and neurological disorders.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more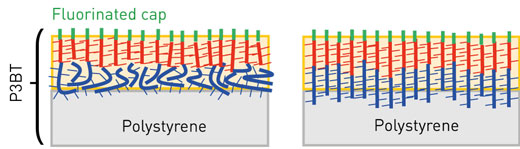 By lining up vertical strands of a polymer, researchers probe the unusual optical properties of thin films.
By lining up vertical strands of a polymer, researchers probe the unusual optical properties of thin films.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more Scientists have developed a nanoparticle delivery system for the antibiotic moxifloxacin that vastly improves the drug's effectiveness against pneumonic tularemia, a type of pneumonia caused by inhalation of the bacterium Francisella tularensis.
Scientists have developed a nanoparticle delivery system for the antibiotic moxifloxacin that vastly improves the drug's effectiveness against pneumonic tularemia, a type of pneumonia caused by inhalation of the bacterium Francisella tularensis.
Nov 6th, 2015
Read more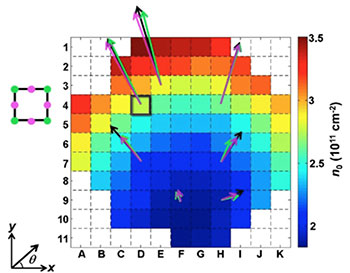 Method analyzes non-uniform conductors with a magnetic field.
Method analyzes non-uniform conductors with a magnetic field.
Nov 5th, 2015
Read more Scientists have found that lithium ion batteries operate longer and faster when their electrodes are treated with hydrogen.
Scientists have found that lithium ion batteries operate longer and faster when their electrodes are treated with hydrogen.
Nov 5th, 2015
Read more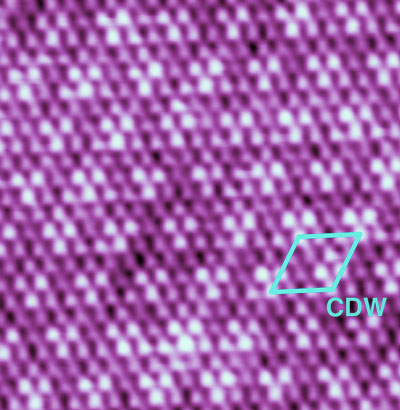 An international team has demonstrated the coexistence of superconductivity and charge density wave order in a single layer of NbSe2, a model transition metal dichalcogenide metal.
An international team has demonstrated the coexistence of superconductivity and charge density wave order in a single layer of NbSe2, a model transition metal dichalcogenide metal.
Nov 5th, 2015
Read more Unique surface structures play a vital role in metamaterials, and scientists have begun looking to nature itself for patterned surfaces from which to draw inspiration. Using a lotus leaf as a template, the new substance is capable of almost total absorption of light across the entire visible spectrum.
Unique surface structures play a vital role in metamaterials, and scientists have begun looking to nature itself for patterned surfaces from which to draw inspiration. Using a lotus leaf as a template, the new substance is capable of almost total absorption of light across the entire visible spectrum.
Nov 5th, 2015
Read more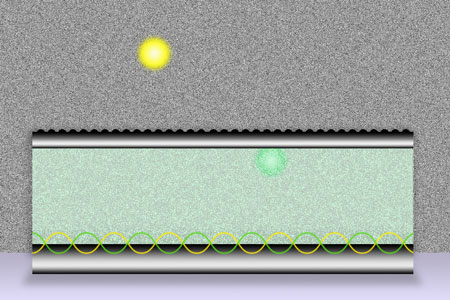 Quantum process increases the number of electrons produced when light strikes a metal-dielectric interface.
Quantum process increases the number of electrons produced when light strikes a metal-dielectric interface.
Nov 5th, 2015
Read more Researchers have shown that it is, in principle, possible to develop materials that are literally allergic to ice and water. To do so, they first taught tiny water droplets how to trampoline.
Researchers have shown that it is, in principle, possible to develop materials that are literally allergic to ice and water. To do so, they first taught tiny water droplets how to trampoline.
Nov 4th, 2015
Read more