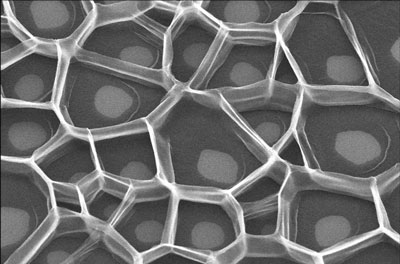
 More than 70 users of ZEISS electron and ion microscopes from all over the world have already submitted their nano masterpieces to the first ever Carl Zeiss Nano Image Contest. The current voting record of the overall competition is held by Peter Nirmalraj from Trinity College Dublin.
More than 70 users of ZEISS electron and ion microscopes from all over the world have already submitted their nano masterpieces to the first ever Carl Zeiss Nano Image Contest. The current voting record of the overall competition is held by Peter Nirmalraj from Trinity College Dublin.
Jul 21st, 2010
Read more
To serve a world bent on gaining autonomous power for wireless sensors, MicroGen Systems LLC, of Ithaca and Cornell University's Energy Materials Center (emc2) have signed a memorandum of understanding to develop 'self-charging' batteries - that use background shaking and stirring for their energy source.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC), the world's leading university-research consortium for semiconductors and related technologies, the National Science Foundation (NSF) and researchers from the University of Connecticut (UConn) and Duke University have found a new way to significantly improve the screening of small delay defects (SDDs) commonly found in semiconductors.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
 Piezo technology specialist PI Ceramic has released a new white paper on the development and test of highly reliable multilayer piezo actuators.
Piezo technology specialist PI Ceramic has released a new white paper on the development and test of highly reliable multilayer piezo actuators.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
 Liverpool scientists have managed to create nanoscale knots in the laboratory by mixing together two simple starting materials - one a rigid aromatic compound and the other a more flexible amine linker.
Liverpool scientists have managed to create nanoscale knots in the laboratory by mixing together two simple starting materials - one a rigid aromatic compound and the other a more flexible amine linker.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
 Electric dipole moment would explain the creation of the universe in the form that we know it.
Electric dipole moment would explain the creation of the universe in the form that we know it.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
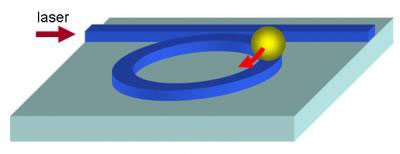 To trap and hold tiny microparticles, engineers at Harvard have 'put a ring on it', using a silicon-based circular resonator to confine particles stably for up to several minutes.
To trap and hold tiny microparticles, engineers at Harvard have 'put a ring on it', using a silicon-based circular resonator to confine particles stably for up to several minutes.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
Dr. Woo Young Lee of the Chemical Engineering and Materials Science department along with Dr. Hongjun Wang of Chemistry, Chemical Biology and Biomedical Engineering at Stevens Institute of Technology have recently received significant NSF funding for their research entitled 'Evaporative Assembly of Drug-Eluting Bioresorbable Nanocomposite Micropatterns'.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
The first-of-its-kind scientific review takes a historical look at the food system, the many challenges ahead, and the crucial role of food science and technology in meeting the needs of the growing population.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
Projects aimed at introducing silicon photonics in innovative products and build a unique value chain taking advantage of Europe's electronics industry.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
New quantum state of matter discovered in Heusler compounds - Researchers from Mainz and Stanford pave the way for spintronics, quantum computing and completely new physical effects.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
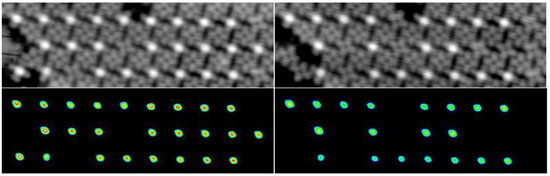 Wissenschaftler haben eine Schrift entwickelt, deren Pixel aus einzelnen Zinn-Atomen bestehen, die sich im Zentrum von Zinn-Phthalocyanin-Molekuelen befinden.
Wissenschaftler haben eine Schrift entwickelt, deren Pixel aus einzelnen Zinn-Atomen bestehen, die sich im Zentrum von Zinn-Phthalocyanin-Molekuelen befinden.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
How do you make a material that has the elasticity of a rubber band and the thermal insulation of a Styrofoam cup? Connect two distinct polymer chains - poly(isoprene) and poly(styrene) - end to end like a series of children's building blocks. The result is an appropriately named 'block copolymer' that boasts the properties of both materials and is commonly used in the tires of automobiles and the soles of athletic shoes.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
CEMMNT, The Centre of Excellence in Metrology for Micro and Nanotechnologies, is set to host a brand new motorsport event on the 21st September 2010 focusing on the application of nanotechnologies in high performance motorsport and automotive engineering.
Jul 20th, 2010
Read more
Physicists in the United States and Germany have discovered a way to use a gallium arsenide nanodevice as a signal processor at terahertz speeds, the first time it's been used for this purpose and an important step forward in the new world of optical communication and computing.
Jul 19th, 2010
Read more
Researchers have found that ivy nanoparticles may protect skin from UV radiation at least four times better than the metal-based sunblocks found on store shelves today.
Jul 19th, 2010
Read more
 More than 70 users of ZEISS electron and ion microscopes from all over the world have already submitted their nano masterpieces to the first ever Carl Zeiss Nano Image Contest. The current voting record of the overall competition is held by Peter Nirmalraj from Trinity College Dublin.
More than 70 users of ZEISS electron and ion microscopes from all over the world have already submitted their nano masterpieces to the first ever Carl Zeiss Nano Image Contest. The current voting record of the overall competition is held by Peter Nirmalraj from Trinity College Dublin.





 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed