The EU Parliament drew attention to the gap in knowledge of potential risks associated with nanotechnology, saying that the permitted limits for an additive in nanoparticle form should not be the same as when it is in traditional form.
Jul 12th, 2007
Read more
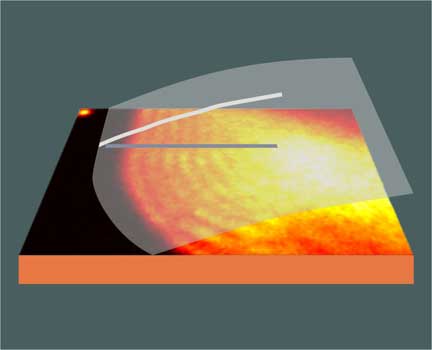 Physicists describe a new way to view three-dimensional structures in real time. Although they haven't yet published 3-D movies, they managed to reconstruct the heights of tiny droplets using still images from 2-D movies.
Physicists describe a new way to view three-dimensional structures in real time. Although they haven't yet published 3-D movies, they managed to reconstruct the heights of tiny droplets using still images from 2-D movies.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
 A newly released report from the Swiss Re Centre for Global Dialogue: "The Risk Governance of Nanotechnology: Recommendations for Managing a Global Issue".
A newly released report from the Swiss Re Centre for Global Dialogue: "The Risk Governance of Nanotechnology: Recommendations for Managing a Global Issue".
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
In its continuing efforts to better understand the potential risks and benefits of nanotechnology, EPA, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, is inviting the public to comment on the agency's proposed approach to developing a Nanoscale Materials Stewardship Program (NMSP).
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
A discovery, known as acoustic plasmon, could have applications in the design of ultra-high velocity electronic devices for data storage, for use in nano-optics or biomaterials, as well as in the creation of new materials for medical applications.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
EPA, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, invites you to exchange ideas and information on using nanotechnology to develop new ways to prevent pollution at their conference "Pollution Prevention through Nanotechnology Conference" on September 25-26, 2007 in Arlington, Virginia.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
Investing in Medical Nanotechnologies II.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
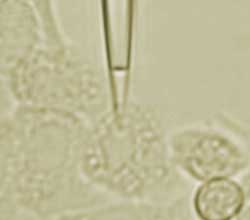 US electrochemists have given hope to biologists who want to inject precise and tiny volumes of fluids into living cells. They have developed a syringe that delivers attolitre volumes.
US electrochemists have given hope to biologists who want to inject precise and tiny volumes of fluids into living cells. They have developed a syringe that delivers attolitre volumes.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
A new targeted drug delivery method uses ultrasound to image tumors, while also releasing the drug from "nanobubbles" into the tumor.
Jul 11th, 2007
Read more
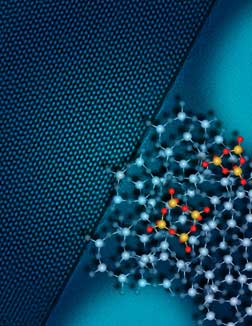 New research shows that nanoscale materials self-assembled in artificially determined patterns can improve upon nature�??s designs.
New research shows that nanoscale materials self-assembled in artificially determined patterns can improve upon nature�??s designs.
Jul 10th, 2007
Read more
The EU launched its very own YouTube platform on June 29 - complete with some of Europe's leading nanotechnology research and European film's best sex scenes.
Jul 10th, 2007
Read more
The electronics industry believes that when it comes to circuits, smaller is better - and many foresee a future where electrical switches and circuits will be as tiny as single molecules.
Jul 10th, 2007
Read more
Scientists have applied a nanoscale imaging method to a biological system, helping to clear up an old puzzle of the global carbon and nitrogen cycle.
Jul 10th, 2007
Read more
The winning work was "Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of Nanomaterials in Aquatic Species".
Jul 9th, 2007
Read more
Researchers have discovered how to make polymeric micro- and nanoparticles in a wide variety of different shapes and sizes using commonly-available lab chemicals and equipment.
Jul 9th, 2007
Read more
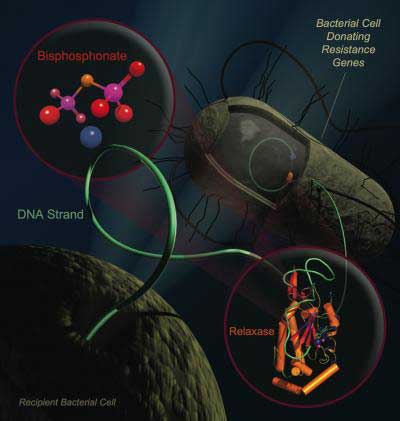 Putting bacteria on birth control could stop the spread of drug-resistant microbes.
Putting bacteria on birth control could stop the spread of drug-resistant microbes.
Jul 9th, 2007
Read more






 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed