Fast-moving electrons create current in organic solar cells
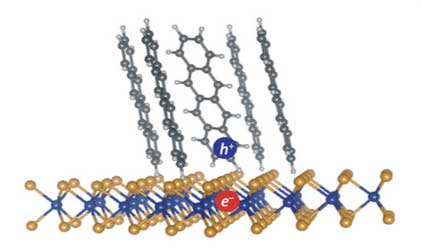 Researchers have identified the mechanism that allows organic solar cells to create a charge, solving a longstanding puzzle in physics.
Researchers have identified the mechanism that allows organic solar cells to create a charge, solving a longstanding puzzle in physics.
Jan 13th, 2018
Read more
 Researchers have identified the mechanism that allows organic solar cells to create a charge, solving a longstanding puzzle in physics.
Researchers have identified the mechanism that allows organic solar cells to create a charge, solving a longstanding puzzle in physics.
Jan 13th, 2018
Read more Electronic states at the edge of topological insulators are promising as carriers of quantum information.
Electronic states at the edge of topological insulators are promising as carriers of quantum information.
Jan 12th, 2018
Read more A new material measures temperatures in the range of 80-750 kelvin and could be used in manufacturing and biological processes.
A new material measures temperatures in the range of 80-750 kelvin and could be used in manufacturing and biological processes.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more Lab makes short nanotube samples by hand to dramatically cut production time.
Lab makes short nanotube samples by hand to dramatically cut production time.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more The magnetic noise caused by adsorbed oxygen molecules is 'eating at' the phase stability of quantum bits, mitigating the noise is vital for future quantum computers.
The magnetic noise caused by adsorbed oxygen molecules is 'eating at' the phase stability of quantum bits, mitigating the noise is vital for future quantum computers.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more Study shows 2-D layers of boron nitride could aid strength, toughness and thermal conductivity of ceramics.
Study shows 2-D layers of boron nitride could aid strength, toughness and thermal conductivity of ceramics.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more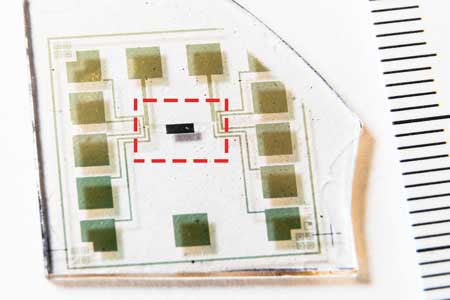 Researchers have developed the world's first complementary electrochemical logic circuits that can function stably for long periods in water.
Researchers have developed the world's first complementary electrochemical logic circuits that can function stably for long periods in water.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more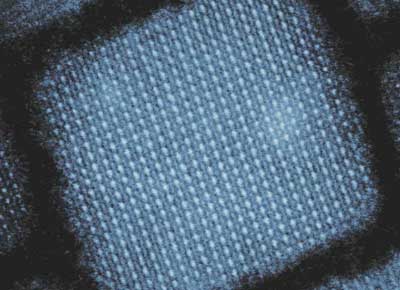 A type of quantum dot that has been intensively studied in recent years can reproduce light in every colour and is very bright. An international research team has now discovered why this is the case.
A type of quantum dot that has been intensively studied in recent years can reproduce light in every colour and is very bright. An international research team has now discovered why this is the case.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more Researchers have show for the first time the use of plants as self-powered light sources using exclusive nanotechnology approaches.
Researchers have show for the first time the use of plants as self-powered light sources using exclusive nanotechnology approaches.
Jan 11th, 2018
Read more Researchers analyzed how organic solar cells' crystal structures develop as they are produced under different conditions.
Researchers analyzed how organic solar cells' crystal structures develop as they are produced under different conditions.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more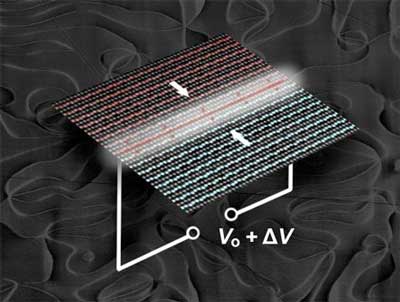 An electric field switches the conductivity on and off in atomic-scale channels, which could allow for upgrades at will.
An electric field switches the conductivity on and off in atomic-scale channels, which could allow for upgrades at will.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more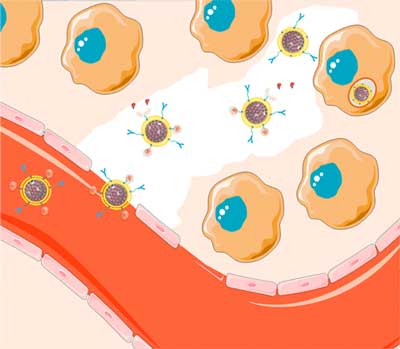 Scientists show that, by cloaking anti-cancer drugs in a specially designed particle, they could target and destroy tumor cells deep inside a malignant mass in vitro.
Scientists show that, by cloaking anti-cancer drugs in a specially designed particle, they could target and destroy tumor cells deep inside a malignant mass in vitro.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more Researchers integrated oxide two-dimensional electron gases with gallium arsenide and paved the way toward new opto-electrical devices.
Researchers integrated oxide two-dimensional electron gases with gallium arsenide and paved the way toward new opto-electrical devices.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more Water passes through human-made straws faster than the 'gold standard' protein, allowing to filter seawater.
Water passes through human-made straws faster than the 'gold standard' protein, allowing to filter seawater.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more Researchers have demonstrated that a simple sheet of standalone graphene foam can act as efficient solar thermal capture and conversion device.
Researchers have demonstrated that a simple sheet of standalone graphene foam can act as efficient solar thermal capture and conversion device.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more A team of researchers have disclosed in which location self-healing occurs for the future solar cells through the use of Photoconductive Atomic Force Microscope.
A team of researchers have disclosed in which location self-healing occurs for the future solar cells through the use of Photoconductive Atomic Force Microscope.
Jan 10th, 2018
Read more