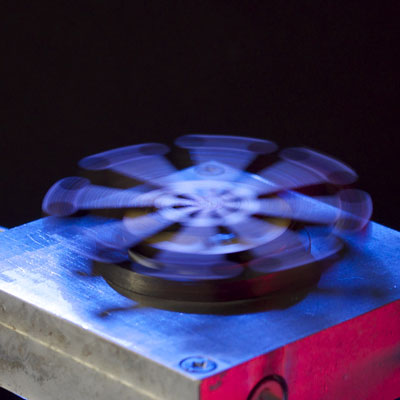
 Martian colonists could use an innovative new technique to harvest energy from carbon dioxide thanks to research that proposes a new kind of engine for producing energy based on the Leidenfrost effect - a phenomenon which happens when a liquid comes into near contact with a surface much hotter than its boiling point.
Martian colonists could use an innovative new technique to harvest energy from carbon dioxide thanks to research that proposes a new kind of engine for producing energy based on the Leidenfrost effect - a phenomenon which happens when a liquid comes into near contact with a surface much hotter than its boiling point.
Mar 5th, 2015
Read more
 Study explains why galaxies don't churn out as many stars as they should.
Study explains why galaxies don't churn out as many stars as they should.
Mar 5th, 2015
Read more
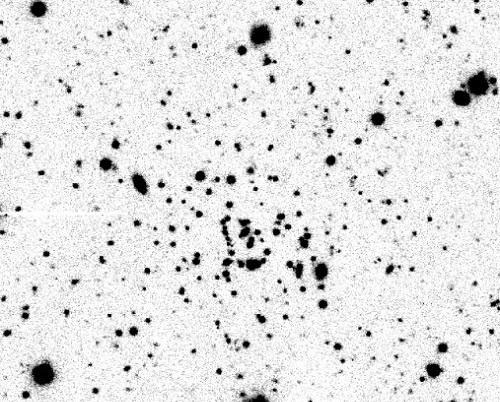 Like the lost little puppy that wanders too far from home, astronomers have found an unusually small and distant group of stars that seems oddly out of place. The cluster, made of only a handful of stars, is located far away, in the Milky Way's 'suburbs'. It is located where astronomers have never spotted such a small cluster of stars before.
Like the lost little puppy that wanders too far from home, astronomers have found an unusually small and distant group of stars that seems oddly out of place. The cluster, made of only a handful of stars, is located far away, in the Milky Way's 'suburbs'. It is located where astronomers have never spotted such a small cluster of stars before.
Mar 3rd, 2015
Read more
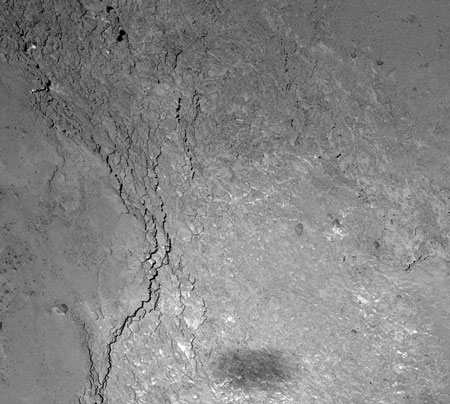 On 14 February 2015, the Optical, Spectroscopic and Infrared Remote Imaging System (OSIRIS) on the Rosetta spacecraft observed the surface of comet 67P Churyumov-Gerasimenko with the Sun directly behind it, so the only shadow seen in the image is that of the photographer, the orbiter itself.
On 14 February 2015, the Optical, Spectroscopic and Infrared Remote Imaging System (OSIRIS) on the Rosetta spacecraft observed the surface of comet 67P Churyumov-Gerasimenko with the Sun directly behind it, so the only shadow seen in the image is that of the photographer, the orbiter itself.
Mar 3rd, 2015
Read more
 Team describes use of method to determine properties of clouds surrounding the exoplanet Kepler-7b.
Team describes use of method to determine properties of clouds surrounding the exoplanet Kepler-7b.
Mar 3rd, 2015
Read more
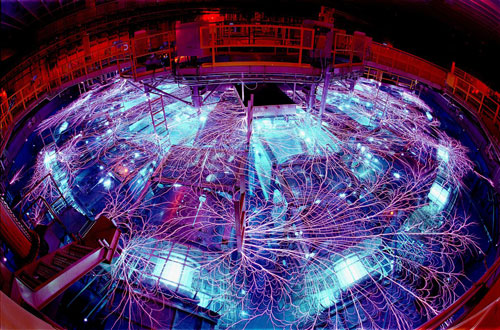 Recreating the violent conditions of Earth's formation, scientists are learning more about how iron vaporizes and how this iron rain affected the formation of the Earth and Moon.
Recreating the violent conditions of Earth's formation, scientists are learning more about how iron vaporizes and how this iron rain affected the formation of the Earth and Moon.
Mar 2nd, 2015
Read more
 Astronomers have discovered a dust-filled galaxy from the very early universe. The discovery demonstrates that galaxies were very quickly enriched with dust particles containing elements such as carbon and oxygen, which could form planets.
Astronomers have discovered a dust-filled galaxy from the very early universe. The discovery demonstrates that galaxies were very quickly enriched with dust particles containing elements such as carbon and oxygen, which could form planets.
Mar 2nd, 2015
Read more
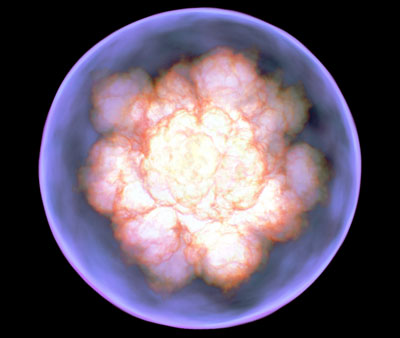 A new astrophysics research group aims to find out how supernova explosions proceed.
A new astrophysics research group aims to find out how supernova explosions proceed.
Mar 2nd, 2015
Read more
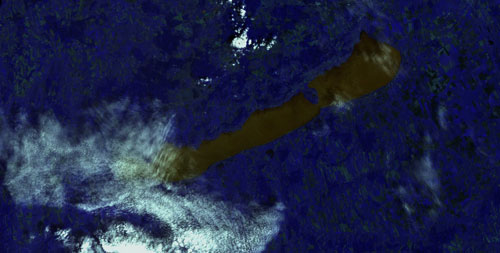 An international team of researchers has demonstrated a way to assess the quality of water on Earth from space by using satellite technology that can visualise pollution levels otherwise invisible to the human eye through 'Superhero vision'.
An international team of researchers has demonstrated a way to assess the quality of water on Earth from space by using satellite technology that can visualise pollution levels otherwise invisible to the human eye through 'Superhero vision'.
Mar 2nd, 2015
Read more
 Taking a simultaneously imaginative and rigidly scientific view, Cornell chemical engineers and astronomers offer a template for life that could thrive in a harsh, cold world - specifically Titan, the giant moon of Saturn.
Taking a simultaneously imaginative and rigidly scientific view, Cornell chemical engineers and astronomers offer a template for life that could thrive in a harsh, cold world - specifically Titan, the giant moon of Saturn.
Feb 27th, 2015
Read more
 An article published this week confirms the existence of methane fluctuations in the atmosphere of Mars, as a result of the detailed analysis of data sent during 605 soles or Martian days.
An article published this week confirms the existence of methane fluctuations in the atmosphere of Mars, as a result of the detailed analysis of data sent during 605 soles or Martian days.
Feb 27th, 2015
Read more
 New research by an astrophysicist provides revelations about the most energetic event in the universe - the merging of two spinning, orbiting black holes into a much larger black hole.
New research by an astrophysicist provides revelations about the most energetic event in the universe - the merging of two spinning, orbiting black holes into a much larger black hole.
Feb 26th, 2015
Read more
 The MUSE instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope has given astronomers the best ever three-dimensional view of the deep Universe. After staring at the Hubble Deep Field South region for only 27 hours, the new observations reveal the distances, motions and other properties of far more galaxies than ever before in this tiny piece of the sky. They also go beyond Hubble and reveal previously invisible objects.
The MUSE instrument on ESO's Very Large Telescope has given astronomers the best ever three-dimensional view of the deep Universe. After staring at the Hubble Deep Field South region for only 27 hours, the new observations reveal the distances, motions and other properties of far more galaxies than ever before in this tiny piece of the sky. They also go beyond Hubble and reveal previously invisible objects.
Feb 26th, 2015
Read more
 Astronomers have found a huge black hole which was powering the brightest object in the early universe. The black hole's mass is 12 billion solar masses, and the surrounding quasar pumped out 10^15 times the sun's energy.
Astronomers have found a huge black hole which was powering the brightest object in the early universe. The black hole's mass is 12 billion solar masses, and the surrounding quasar pumped out 10^15 times the sun's energy.
Feb 25th, 2015
Read more
Most of the laws of nature treat particles and antiparticles equally, but stars and planets are made of particles, or matter, and not antiparticles, or antimatter. That asymmetry, which favors matter to a very small degree, has puzzled scientists for many years. New research offers a possible solution to the mystery of the origin of matter in the universe.
Feb 25th, 2015
Read more
HAKUTO, the only Japanese team competing for the $30 million Google Lunar XPRIZE, has announced a contract with fellow competitor, Astrobotic, based in Pittsburgh, Pa., to carry a pair of rovers to the moon.
Feb 23rd, 2015
Read more
 By looking at the speed of ambient gas spewing out from a well-known quasar, astronomers are gaining insight into how black holes and their host galaxies might have evolved at the same time.
By looking at the speed of ambient gas spewing out from a well-known quasar, astronomers are gaining insight into how black holes and their host galaxies might have evolved at the same time.
Feb 20th, 2015
Read more
 NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution has completed the first of five deep-dip maneuvers designed to gather measurements closer to the lower end of the Martian upper atmosphere.
NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution has completed the first of five deep-dip maneuvers designed to gather measurements closer to the lower end of the Martian upper atmosphere.
Feb 20th, 2015
Read more
 Martian colonists could use an innovative new technique to harvest energy from carbon dioxide thanks to research that proposes a new kind of engine for producing energy based on the Leidenfrost effect - a phenomenon which happens when a liquid comes into near contact with a surface much hotter than its boiling point.
Martian colonists could use an innovative new technique to harvest energy from carbon dioxide thanks to research that proposes a new kind of engine for producing energy based on the Leidenfrost effect - a phenomenon which happens when a liquid comes into near contact with a surface much hotter than its boiling point.
 Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed
Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed













