NASA, the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), the U.S. State Department and Nike have issued a challenge to identify 10 game-changing innovations that could enable fabric systems to enhance global economic growth, drive human prosperity and replenish the planet's resources.
Apr 29th, 2013
Read more
 ESA's Herschel space observatory has exhausted its supply of liquid helium coolant, ending more than three years of pioneering observations of the cool Universe.
ESA's Herschel space observatory has exhausted its supply of liquid helium coolant, ending more than three years of pioneering observations of the cool Universe.
Apr 29th, 2013
Read more
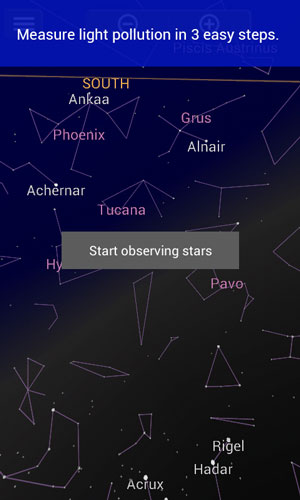 Researchers from the German 'Loss of the Night' project have developed an app for Android smart phones, which counts the number of visible stars in the sky. The data from the app will be used by scientists to understand light pollution on a world wide scale.
Researchers from the German 'Loss of the Night' project have developed an app for Android smart phones, which counts the number of visible stars in the sky. The data from the app will be used by scientists to understand light pollution on a world wide scale.
Apr 29th, 2013
Read more
A University of Washington astronomer is using Earth's interstellar neighbors to learn the nature of certain stars too far away to be directly measured or observed, and the planets they may host.
Apr 26th, 2013
Read more
 An international team of astronomers and an exotic pair of binary stars have proved that Albert Einstein's theory of relativity is still right, even in the most extreme conditions tested yet.
An international team of astronomers and an exotic pair of binary stars have proved that Albert Einstein's theory of relativity is still right, even in the most extreme conditions tested yet.
Apr 26th, 2013
Read more
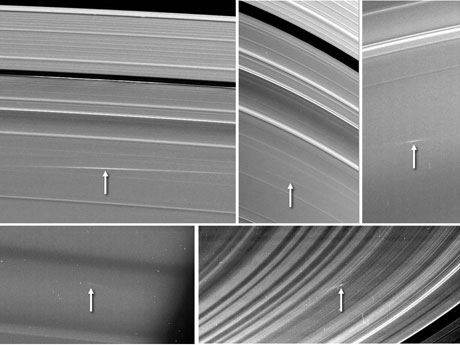 Scientists have been searching for years to find proof of small meteors that they believe have been smashing into Saturn's rings. Cornell researchers and their colleagues announced today that they now have evidence of these collisions, thanks to images of Saturn's rings taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
Scientists have been searching for years to find proof of small meteors that they believe have been smashing into Saturn's rings. Cornell researchers and their colleagues announced today that they now have evidence of these collisions, thanks to images of Saturn's rings taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
Apr 25th, 2013
Read more
 When galaxies form new stars, they sometimes do so in frantic episodes of activity known as starbursts. During these bursts, hundreds of millions of stars are born, and their combined effect can drive a powerful wind that travels out of the galaxy. These winds were known to affect their host galaxy - but this new research now shows that they have a significantly greater effect than previously thought.
When galaxies form new stars, they sometimes do so in frantic episodes of activity known as starbursts. During these bursts, hundreds of millions of stars are born, and their combined effect can drive a powerful wind that travels out of the galaxy. These winds were known to affect their host galaxy - but this new research now shows that they have a significantly greater effect than previously thought.
Apr 25th, 2013
Read more
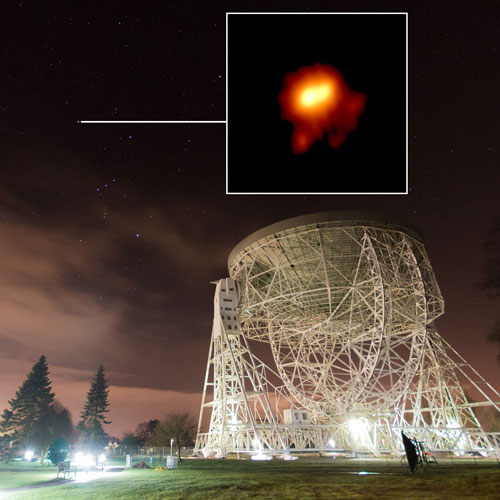 Astronomers have released a new image of the outer atmosphere of Betelgeuse - one of the nearest red supergiants to Earth - revealing the detailed structure of the matter being thrown off the star.
Astronomers have released a new image of the outer atmosphere of Betelgeuse - one of the nearest red supergiants to Earth - revealing the detailed structure of the matter being thrown off the star.
Apr 25th, 2013
Read more
Because it has no source of energy, a dead star - known as a white dwarf - will eventually cool down and fade away. But circumstantial evidence suggests that white dwarfs can still support habitable planets.
Apr 25th, 2013
Read more
 Astronomers have found a galaxy turning gas into stars with almost 100 percent efficiency, a rare phase of galaxy evolution that is the most extreme yet observed. The findings come from the IRAM Plateau de Bure interferometer in the French Alps, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
Astronomers have found a galaxy turning gas into stars with almost 100 percent efficiency, a rare phase of galaxy evolution that is the most extreme yet observed. The findings come from the IRAM Plateau de Bure interferometer in the French Alps, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
Apr 23rd, 2013
Read more
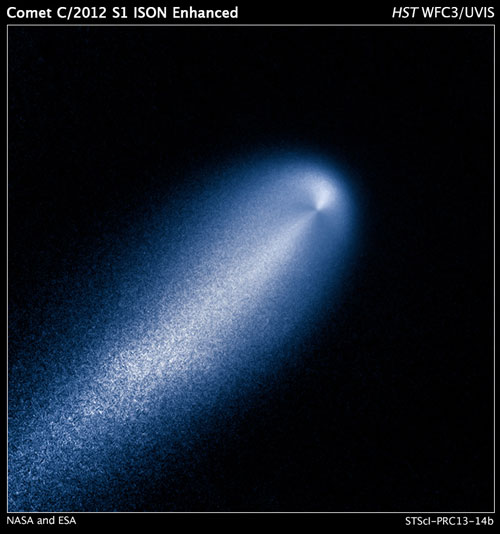 Hubble photographed a jet blasting dust particles off the sunward-facing side of the comet's nucleus. Preliminary measurements suggest that ISON's nucleus is no larger than three or four miles across.
Hubble photographed a jet blasting dust particles off the sunward-facing side of the comet's nucleus. Preliminary measurements suggest that ISON's nucleus is no larger than three or four miles across.
Apr 23rd, 2013
Read more
Many collisions occur between asteroids and other objects in our solar system, but scientists are not always able to detect or track these impacts from Earth. The 'rogue debris' created by such collisions can sometimes catch us by surprise. UCLA space scientists have now devised a way to monitor these types of collisions in interplanetary space by using a new method to determine the mass of magnetic clouds that result from the impacts.
Apr 23rd, 2013
Read more
 Without hi-tech magnetic sensors, rovers wouldn't be able to roam around Mars. These same sensors will soon boost terrestrial travel by improving the machinery that moulds parts for cars and aircraft here on Earth.
Without hi-tech magnetic sensors, rovers wouldn't be able to roam around Mars. These same sensors will soon boost terrestrial travel by improving the machinery that moulds parts for cars and aircraft here on Earth.
Apr 23rd, 2013
Read more
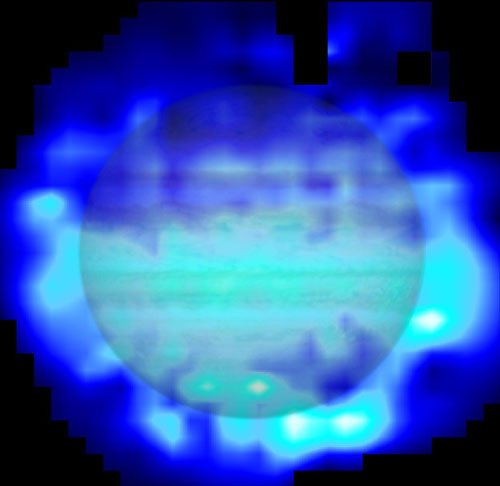 ESA's Herschel space observatory has solved a long-standing mystery as to the origin of water in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter, finding conclusive evidence that it was delivered by the dramatic impact of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 in July 1994.
ESA's Herschel space observatory has solved a long-standing mystery as to the origin of water in the upper atmosphere of Jupiter, finding conclusive evidence that it was delivered by the dramatic impact of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 in July 1994.
Apr 23rd, 2013
Read more
Cells sent up on final flight of shuttle program may help answer important questions about the effects of microgravity on the human body.
Apr 22nd, 2013
Read more
 Scientists working at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered two tiny grains of silica (the most common constituent of sand) in meteorites that fell to earth in Antarctica. Because of their isotopic composition these two grains are thought to be pure samples from a massive star that exploded before the birth of the solar system, perhaps the supernova whose explosion is thought to have triggered the collapse of a giant molecular cloud, giving birth to the Sun.
Scientists working at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered two tiny grains of silica (the most common constituent of sand) in meteorites that fell to earth in Antarctica. Because of their isotopic composition these two grains are thought to be pure samples from a massive star that exploded before the birth of the solar system, perhaps the supernova whose explosion is thought to have triggered the collapse of a giant molecular cloud, giving birth to the Sun.
Apr 22nd, 2013
Read more
Prof. Hagai Netzer of Tel Aviv University has developed a method that uses black holes to measure distances of billions of light years with a high degree of accuracy. The ability to measure these distances will allow scientists to see further into the past of the universe than ever before.
Apr 22nd, 2013
Read more
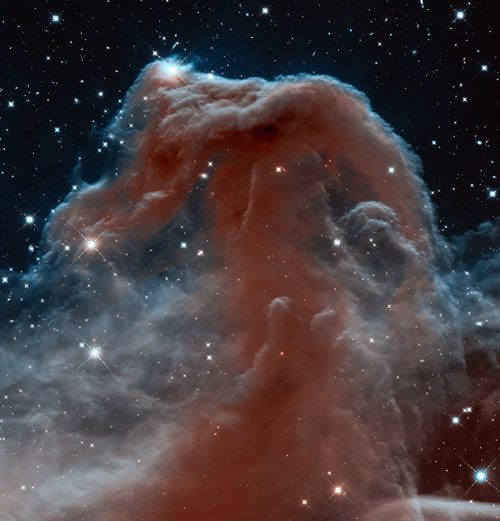 Astronomers have used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to photograph the iconic Horsehead Nebula in a new, infrared light to mark the 23rd anniversary of the famous observatory's launch aboard the space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990.
Astronomers have used NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to photograph the iconic Horsehead Nebula in a new, infrared light to mark the 23rd anniversary of the famous observatory's launch aboard the space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990.
Apr 19th, 2013
Read more

 Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed
Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed










