| Aug 10, 2022 |
A stretchable display without image distortion
(Nanowerk News) Stretchable electronic devices are usually implemented on 2D surfaces of some base elastomeric materials – these devices then deform following the stretching deformation of this base material. As a result, the internal shape of these stretchable devices is distorted from the initial shape under such deformation, which results in the distortion of the displayed images and thereby considerably deteriorating the viewer's experience.
|
|
Auxetic materials have the amazing property of growing wider when stretched. Scientifically, auxetic materials are characterized by a negative Poisson's ratio. Probably the best known and oldest application of unusual Poisson's ratios is the bottle cork, which has a Poisson's ratio of zero. This has the effect that the cork can be put into the thinner neck of the bottle.
|
|
When the Poisson's ratio of the base material is −1, the display can stretch while maintaining the geometric similarity of the original shape, even under uniaxial stretching deformation. This unique stretching behavior occurs because the display expands with the same strain in the perpendicular direction to the stretching direction.
|
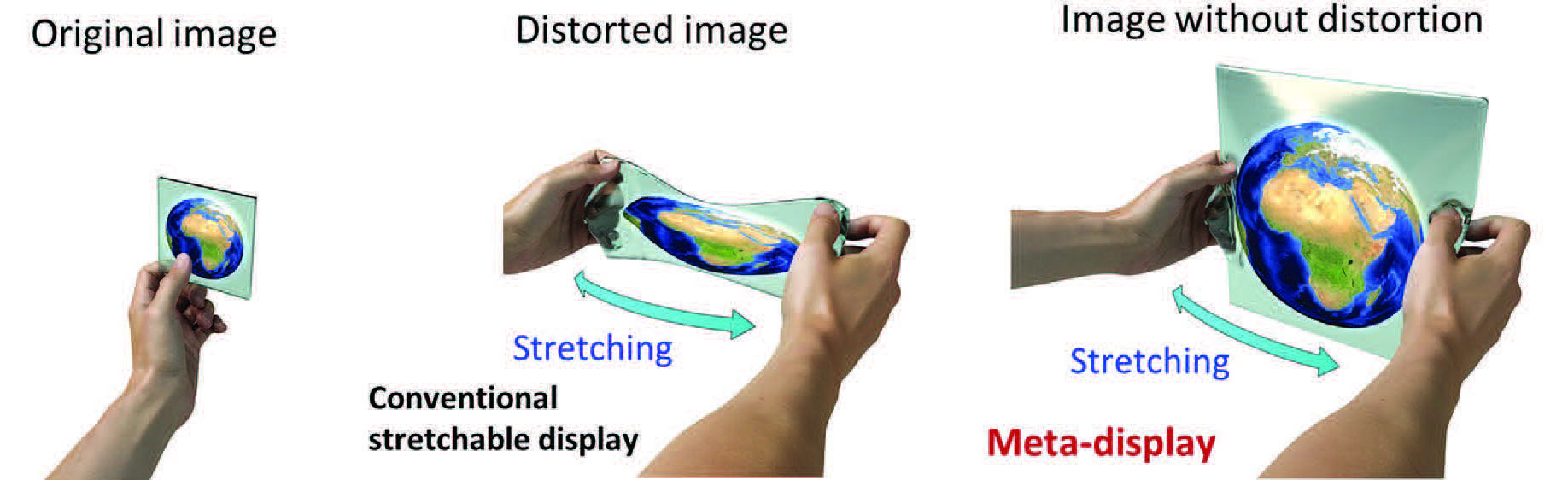 |
| Illustrations of conventional stretchable display with the distorted Earth image and meta-display without image distortion under uniaxial stretching. (Adapted with permission from Wiley-VCH Verlag)
|
|
Natural materials rarely have a negative Poisson's ratio, and there are no known natural materials with a Poisson’s ratio of -1, regardless of the applied strain. Researchers are therefore developing mechanical metamaterials that can serve as a suitable solution for stretchable displays without image distortion by realizing Poisson's ratio of −1.
|
|
The goal is to fabricate a meta-display that can not only stretch but maintain the original shape of the objects. The aspect ratios of the objects displayed on the screen should be kept constant during the stretching action.
|
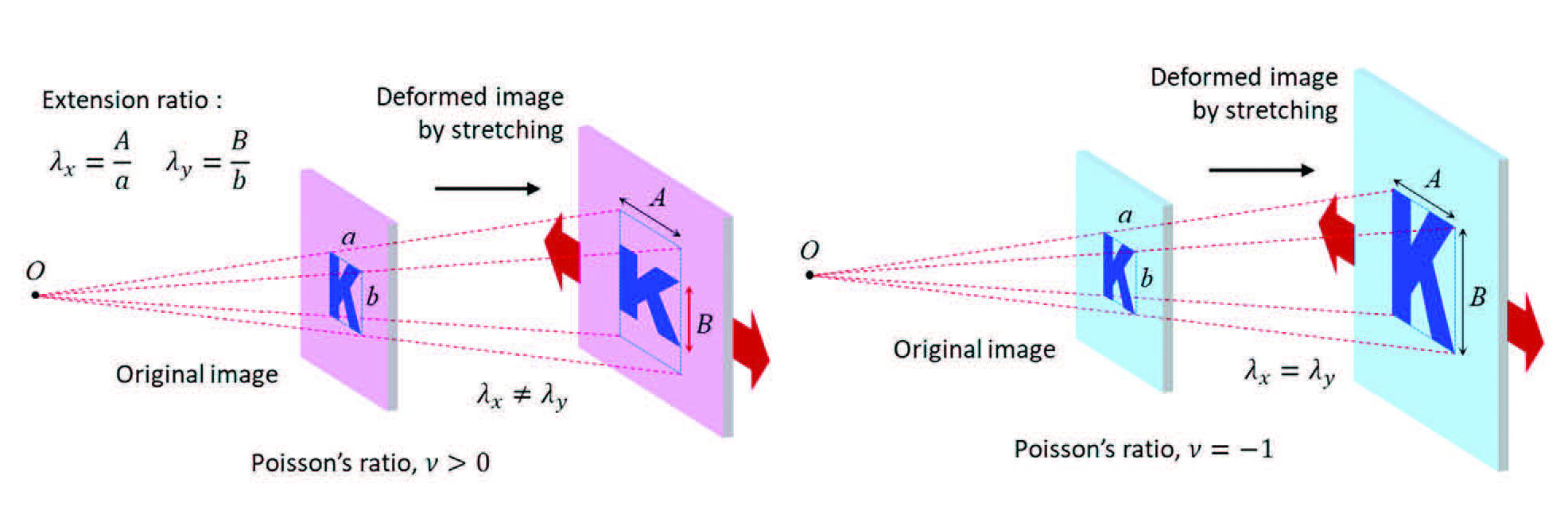 |
| Deformed image by the base material with positive Poisson’s ratio and Poisson’s ratio of −1. (Adapted with permission from Wiley-VCH Verlag)
|
|
For instance, in recent work (Advanced Functional Materials, "Auxetic Meta-Display: Stretchable Display without Image
Distortion"), researchers have developed micro-light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to construct an auxetic meta-display – a distortion-free stretchable display based on auxetic metamaterials.
|
|
In this work, the researchers demonstrate that their auxetic metamaterials enable the display to be stretchable and also suppress image distortion. The meta-printed circuit board, as the substrate for the micro-LEDs, was designed to possess a stretchability of 24.5% and a Poisson’s ratio of −1.
|
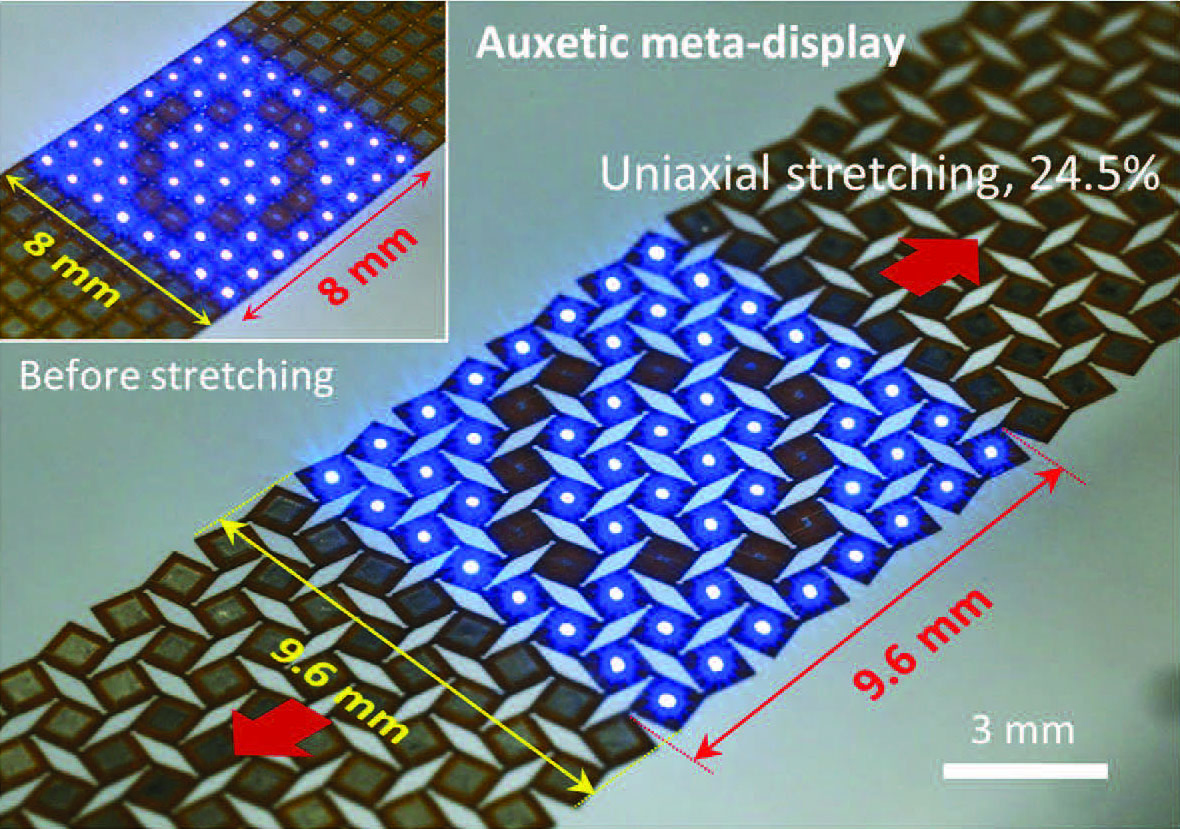 |
| A stretchable micro-LED meta-display with a display resolution of 25 PPI. (Adapted with permission from Wiley-VCH Verlag)
|
|
The authors conclude by noting that the design and fabrication technologies that they developed in this study can broaden the applicability of mechanical metamaterials by tuning their unique mechanical properties.
|



 By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
