 Hydrogen is considered the fuel of the future. Yet this lightest of the chemical elements can embrittle the metals used in vehicle engineering. The result: components suddenly malfunction and break. A new special laboratory is aiding researchers' search for hydrogen-compatible metals.
Hydrogen is considered the fuel of the future. Yet this lightest of the chemical elements can embrittle the metals used in vehicle engineering. The result: components suddenly malfunction and break. A new special laboratory is aiding researchers' search for hydrogen-compatible metals.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a new way to regulate the uncontrolled growth of blood vessels, a major problem in a broad range of diseases and conditions.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
 The concentrations of toxic nitrogen oxide that are present in German cities regularly exceed the maximum permitted levels. That's now about to change, as innovative paving slabs that will help protect the environment are being introduced. Coated in titanium dioxide nanoparticles, they reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide in the air.
The concentrations of toxic nitrogen oxide that are present in German cities regularly exceed the maximum permitted levels. That's now about to change, as innovative paving slabs that will help protect the environment are being introduced. Coated in titanium dioxide nanoparticles, they reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide in the air.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
The third German-Japanese Micro/Nano Business Forum at the Exhibition Micromachine last Thursday in Tokyo attracted more than 300 Japanese industry representatives.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
Das Internationale Graduiertenkolleg 'Materialien und Konzepte fuer fortschrittliche Metallisierungssysteme' geht in die zweite Runde.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
The conditions experienced by water molecules on Neptune might be simulated in 2015.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
Over 300 delegates expected at the 5th SBE International Conference on Bioengineering and Nanotechnology organized by IBN in Singapore.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
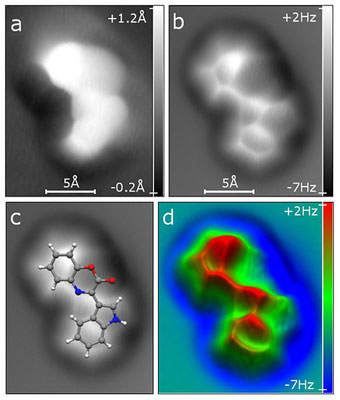 In a pioneering research project, for the first time, scientists at IBM and the University of Aberdeen have collaborated to 'see' the structure of a marine compound from the deepest place on the Earth using an atomic force microscope (AFM). The results of the project open up new possibilities in biological research which could lead to the faster development of new medicines in the future.
In a pioneering research project, for the first time, scientists at IBM and the University of Aberdeen have collaborated to 'see' the structure of a marine compound from the deepest place on the Earth using an atomic force microscope (AFM). The results of the project open up new possibilities in biological research which could lead to the faster development of new medicines in the future.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
 Researchers have found that silicon, the most widely used material for computer chips and solar cells, can exhibit this strange property of 'retrograde melting' when it contains high concentrations of certain metals dissolved in it.
Researchers have found that silicon, the most widely used material for computer chips and solar cells, can exhibit this strange property of 'retrograde melting' when it contains high concentrations of certain metals dissolved in it.
Aug 2nd, 2010
Read more
One Chicago skyline is dazzling enough. Now imagine 15,000 of them. A Northwestern University research team has done just that -- drawing 15,000 identical skylines with tiny beams of light using an innovative nanofabrication technology called beam-pen lithography (BPL).
Aug 1st, 2010
Read more
A new membrane developed at the University of Rochester's Laboratory for Laser Energetics blocks gas from flowing through it when one color of light is shined on its surface, and permits gas to flow through when another color of light is used.
Aug 1st, 2010
Read more
This three-year ENIAC (European Nanoelectronics Initiative Advisory Council) project aims to achieve substantial advances in state-of-the-art medical 3D-imaging platforms by focusing on the diagnosis and therapy of serious diseases of the central nervous system and brain.
Jul 31st, 2010
Read more
Through advancements in nanotechnology, Professor Babak Parviz, from the University of Washington, will explain at a NASA talk how contact lenses have been converted into systems that can complete extraordinary tasks.
Jul 31st, 2010
Read more
MTECH Laboratories receives $150K NSF award to demonstrate the feasibility of its novel, high-efficiency energy distribution system for large buildings.
Jul 31st, 2010
Read more
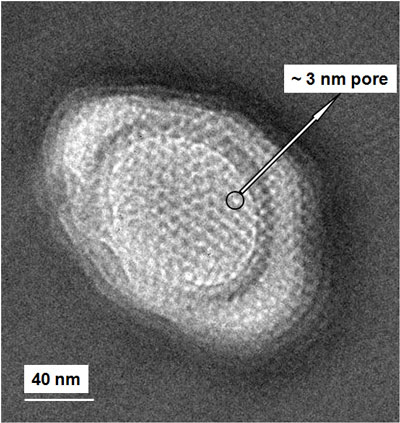 In an innovation critical to improved DNA sequencing, a markedly slower transmission of DNA through nanopores has been achieved by a team led by Sandia National Laboratories researchers.
In an innovation critical to improved DNA sequencing, a markedly slower transmission of DNA through nanopores has been achieved by a team led by Sandia National Laboratories researchers.
Jul 30th, 2010
Read more
 Ultra-strong interaction between light and matter realized.
Ultra-strong interaction between light and matter realized.
Jul 30th, 2010
Read more
 Hydrogen is considered the fuel of the future. Yet this lightest of the chemical elements can embrittle the metals used in vehicle engineering. The result: components suddenly malfunction and break. A new special laboratory is aiding researchers' search for hydrogen-compatible metals.
Hydrogen is considered the fuel of the future. Yet this lightest of the chemical elements can embrittle the metals used in vehicle engineering. The result: components suddenly malfunction and break. A new special laboratory is aiding researchers' search for hydrogen-compatible metals.





 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed