| Posted: Apr 24, 2017 |
Self-assembled nanostructures can be selectively controlled
(Nanowerk News) DNA self-assembly allows the unprecedented control of the optical properties of plasmonic metamolecules.
|
|
Plasmonic nanoparticles exhibit properties based on their geometries and relative positions. Researchers have now developed an easy way to manipulate the optical properties of plasmonic nanostructures that strongly depend on their spatial arrangement.
|
|
The plasmonic nanoparticles can form clusters, plasmonic metamolecules, and then interact with each other. Changing the geometry of the nanoparticles can be used to control the properties of the metamolecules.
|
|
“The challenge is to make the structures change their geometry in a controlled way in response to external stimuli. In this study, structures were programmed to modify their shape by altering the pH,” tells Assistant Professor Anton Kuzyk from Aalto University.
|
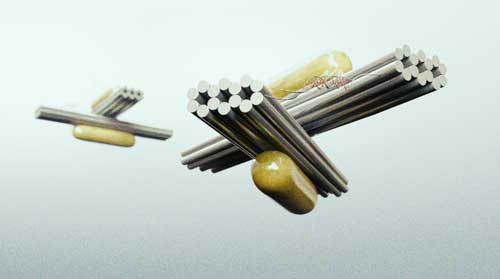 |
| Plasmonic metamolecule schematics. (Image: Marco Tripodi)
|
Utilization of programmable DNA locks
|
|
In this study (Science Advances, "Selective control of reconfigurable chiral plasmonic metamolecules") plasmonic metamolecules were functionalized with pH-sensitive DNA locks. DNA locks can be easily programmed to operate at a specific pH range. Metamolecules can be either in a “locked” state at low pH or in relaxed state at high pH. Both states have very distinct optical responses. This in fact allows creating assemblies of several types of plasmonic metamolecules, with each type designed to switch at different a pH value.
|
|
The ability to program nanostructures to perform a specific function only within a certain pH window could have applications in the field of nanomachines and smart nanomaterials with tailored optical functionalities.
|
|
This active control of plasmonic metamolecules is promising for the development of sensors, optical switches, transducers and phase shifters at different wavelengths. In the future, pH-responsive nanostructures could also be useful in the development of controlled drug delivery.
|
|
The study was carried out by Anton Kuzyk from Aalto University, Maximilian Urban and Na Liu from Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems and the Heidelberg University, and Andrea Idili and Francesco Ricci from the University of Rome Tor Vergata.
|

