 ETH-Zurich spin-off Climeworks is looking to filter carbon dioxide out of the ambient air and sell it to major customers such as greenhouses at competitive prices. The first pilot plant is up and running and the equipment is expected to filter up to 1,000 tons of carbon dioxide out of the air a year by 2014.
ETH-Zurich spin-off Climeworks is looking to filter carbon dioxide out of the ambient air and sell it to major customers such as greenhouses at competitive prices. The first pilot plant is up and running and the equipment is expected to filter up to 1,000 tons of carbon dioxide out of the air a year by 2014.
Jul 5th, 2013
Read more
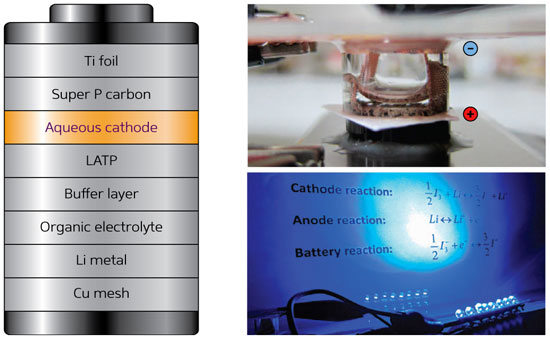 An innovative iodine-based aqueous cathode doubles the energy density of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
An innovative iodine-based aqueous cathode doubles the energy density of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Jul 5th, 2013
Read more
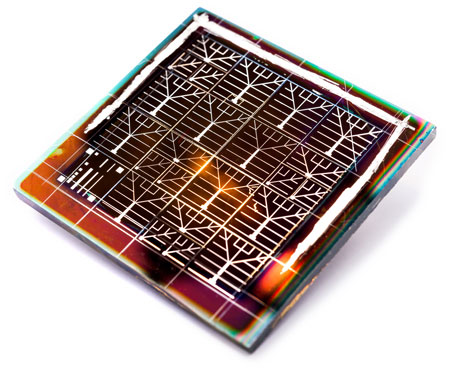 At next week's Intersolar conference in San Francisco, imomec, imec's associated lab at the Hasselt University, and Solliance, the European consortium that focuses on thin-film photovoltaic solar energy, will present a CZTSe-based solar cell with 9.7 percent efficiency.
At next week's Intersolar conference in San Francisco, imomec, imec's associated lab at the Hasselt University, and Solliance, the European consortium that focuses on thin-film photovoltaic solar energy, will present a CZTSe-based solar cell with 9.7 percent efficiency.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
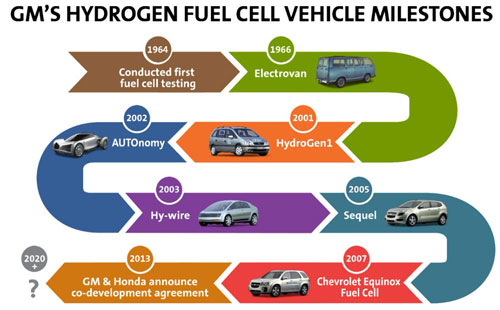 General Motors and Honda announced a long-term, definitive master agreement to co-develop next-generation fuel cell system and hydrogen storage technologies, aiming for the 2020 time frame. The collaboration expects to succeed by sharing expertise, economies of scale and common sourcing strategies.
General Motors and Honda announced a long-term, definitive master agreement to co-develop next-generation fuel cell system and hydrogen storage technologies, aiming for the 2020 time frame. The collaboration expects to succeed by sharing expertise, economies of scale and common sourcing strategies.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
South Carolina's leading automotive research center and premier technology and aviation business park have partnered to study next-generation vehicle technology.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
A Centre for Power Electronics that will focus on delivering the underpinning science and engineering behind many low carbon technologies from electric vehicles to renewable energy generation and distribution has been launched thanks to funding of GBP18 million by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
 Scientists have discovered for the first time that temperature determines where key soil microbes can thrive - microbes that are critical to forming topsoil crusts in arid lands.
Scientists have discovered for the first time that temperature determines where key soil microbes can thrive - microbes that are critical to forming topsoil crusts in arid lands.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
The DESERTEC Foundation announced the termination of its membership with Dii GmbH.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
Study shows the atmospheric CO2 has big consequences for the tiny bacteria that are the foundation of most of the life in the sea.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
Since 2005, the European Union has co-financed 22 projects in 58 cities in the scope of the EU CONCERTO initiative. The objective of these projects is to build and renovate buildings in an energy efficient manner and to utilise renewable energy sources in an intelligent mix. This is a commitment that pays off, as was demonstrated in Brussels at the EU Sustainable Energy Week.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
 Researchers built and tested the prototype of a device to harness energy from ocean currents able to work in deep water.
Researchers built and tested the prototype of a device to harness energy from ocean currents able to work in deep water.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
Until now, scientists have assumed that keeping livestock on large steppe grassland contributes to the constantly growing nitrous oxide concentration in the atmosphere and thus to global warming. But now the opposite has been proved: Klaus Butterbach-Bahl's team of five from the Karlsruher Institute of Technology (KIT) have shown that animals grazing on steppe and prairie areas can actually reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
 Bicyclean, a 2012 thesis project that helps recycle e-waste in developing nations, wins silver at Acer Incredible Green Contest.
Bicyclean, a 2012 thesis project that helps recycle e-waste in developing nations, wins silver at Acer Incredible Green Contest.
Jul 1st, 2013
Read more
What do the cities of the future look like? What role do they play for global climate change? What influence does the German energy transformation have worldwide? These questions are in the centre of the 2nd Global Sustainability Summer School on 'COMPLEX(C)ITY - Urbanization and energy transition in a changing climate' taking place from 1 to 12 July.
Jul 1st, 2013
Read more
In the world, there are a lot of small molecules people would like to get rid of, or at least convert to something useful, according to University of Wisconsin-Madison chemist Robert J. Hamers.
Jun 30th, 2013
Read more
Scientists from the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) are using ultrasound to reduce the amount of energy needed to harvest microalgae.
Jun 28th, 2013
Read more
The search for thermoelectrics, exotic materials that convert heat directly into electricity, has received a boost from researchers at the California Institute of Technology and the University of Tokyo, who have found the best way to identify them.
Jun 27th, 2013
Read more
For the first time ever, scientists and stakeholders from all over the world come together this week to have a look at the big impacts picture. They assemble at the 'Impacts World 2013' conference in Potsdam, Germany, aiming at developing a new scientific agenda to systematically address knowledge gaps and to start bridging them.
Jun 27th, 2013
Read more
 ETH-Zurich spin-off Climeworks is looking to filter carbon dioxide out of the ambient air and sell it to major customers such as greenhouses at competitive prices. The first pilot plant is up and running and the equipment is expected to filter up to 1,000 tons of carbon dioxide out of the air a year by 2014.
ETH-Zurich spin-off Climeworks is looking to filter carbon dioxide out of the ambient air and sell it to major customers such as greenhouses at competitive prices. The first pilot plant is up and running and the equipment is expected to filter up to 1,000 tons of carbon dioxide out of the air a year by 2014.
 Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed
Subscribe to our Cleantech News feed




