Shaping the future of biomedical applications
 Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more
 Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Bio-compatible electrostrictive materials will play a leading role in the future generation of medical micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS).
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more The findings of this new research may change views about what limits the performance of organic solar cells, photodetectors and OLEDs.
The findings of this new research may change views about what limits the performance of organic solar cells, photodetectors and OLEDs.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more Researchers use electrically charged polymers to detect biomarkers in body fluids. Not just one layer of this, but dozens. In this way they manage reaching a 25 times higher sensitivity.
Researchers use electrically charged polymers to detect biomarkers in body fluids. Not just one layer of this, but dozens. In this way they manage reaching a 25 times higher sensitivity.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more The instrument could bring powerful sensing and imaging capabilities out of the lab and into hospitals, airports, or other settings.
The instrument could bring powerful sensing and imaging capabilities out of the lab and into hospitals, airports, or other settings.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more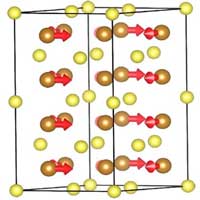 This discovery provides a new route to design materials with tunable electrical and magnetic behaviors for potential applications in information storage and spintronics computing.
This discovery provides a new route to design materials with tunable electrical and magnetic behaviors for potential applications in information storage and spintronics computing.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more Researchers develop silicon nanoresonators that can control the scattering of light when excited by another laser. This research may lead to faster and completely optical computer switches and circuits.
Researchers develop silicon nanoresonators that can control the scattering of light when excited by another laser. This research may lead to faster and completely optical computer switches and circuits.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more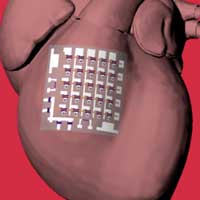 Researchers have developed a patch made from fully rubbery electronics that can be placed directly on the heart to collect electrophysiological activity, temperature, heartbeat and other indicators, all at the same time.
Researchers have developed a patch made from fully rubbery electronics that can be placed directly on the heart to collect electrophysiological activity, temperature, heartbeat and other indicators, all at the same time.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more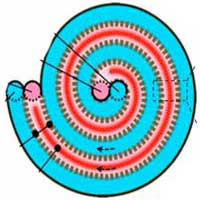 A thin coating of the 2D nanomaterial hexagonal boron nitride is the key ingredient in a cost-effective technology for desalinating industrial-strength brine.
A thin coating of the 2D nanomaterial hexagonal boron nitride is the key ingredient in a cost-effective technology for desalinating industrial-strength brine.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more A new study shows that it is possible to jet inks, containing tiny flakes of 2D materials such as graphene, to build up and mesh together the different layers of complex, customised electronic structures.
A new study shows that it is possible to jet inks, containing tiny flakes of 2D materials such as graphene, to build up and mesh together the different layers of complex, customised electronic structures.
Nov 4th, 2020
Read more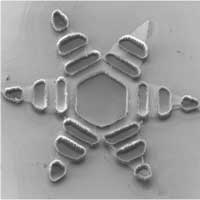 'Theragrippers' are inspired by a parasitic worm that clamps onto its host's intestines.
'Theragrippers' are inspired by a parasitic worm that clamps onto its host's intestines.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more This study is the first to demonstrate electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing for microsupercapacitor fabrication.
This study is the first to demonstrate electrohydrodynamic (EHD) jet printing for microsupercapacitor fabrication.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more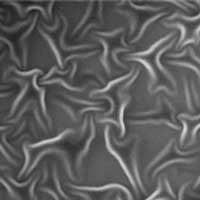 Researchers have synthesized a film composed of densely packed diamond-like carbon nanofibers.
Researchers have synthesized a film composed of densely packed diamond-like carbon nanofibers.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more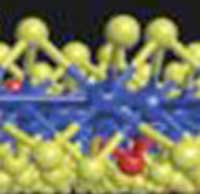 A recent study has unveiled 2D material-based ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensor by synthesizing uniform large-area 2D films.
A recent study has unveiled 2D material-based ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensor by synthesizing uniform large-area 2D films.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more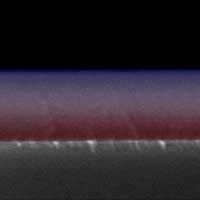 Materials that simultaneously have contrasting properties - for example, they are soft on the one hand and hard on the other, the transition is gradual - could enable completely new applications like gradual anti-reflective lenses.
Materials that simultaneously have contrasting properties - for example, they are soft on the one hand and hard on the other, the transition is gradual - could enable completely new applications like gradual anti-reflective lenses.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more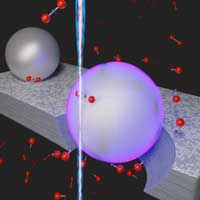 New method could potentially reduce carbon dioxide emission into the atmosphere and slash costs of chemical manufacturing.
New method could potentially reduce carbon dioxide emission into the atmosphere and slash costs of chemical manufacturing.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more Scientists have put forth an innovative design for the development of a high-power transparent solar cell.
Scientists have put forth an innovative design for the development of a high-power transparent solar cell.
Nov 3rd, 2020
Read more