 A new microfluidic method for evaluating drugs commonly used for preventing heart attacks has found that while aspirin can prevent dangerous blood clots in some at-risk patients, it may not be effective in all patients with narrowed arteries. The study, which involved 14 human subjects, used a device that simulated blood flowing through narrowed coronary arteries to assess effects of anti-clotting drugs.
A new microfluidic method for evaluating drugs commonly used for preventing heart attacks has found that while aspirin can prevent dangerous blood clots in some at-risk patients, it may not be effective in all patients with narrowed arteries. The study, which involved 14 human subjects, used a device that simulated blood flowing through narrowed coronary arteries to assess effects of anti-clotting drugs.
Mar 24th, 2014
Read more
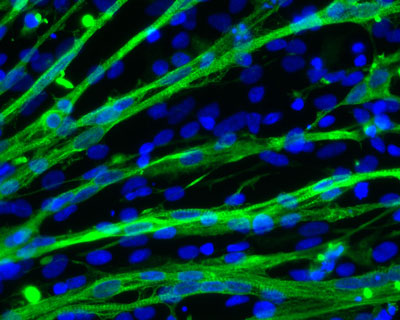 As stem cells continue their gradual transition from the lab to the clinic, a research group at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has discovered a new way to make large concentrations of skeletal muscle cells and muscle progenitors from human stem cells.
As stem cells continue their gradual transition from the lab to the clinic, a research group at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has discovered a new way to make large concentrations of skeletal muscle cells and muscle progenitors from human stem cells.
Mar 21st, 2014
Read more
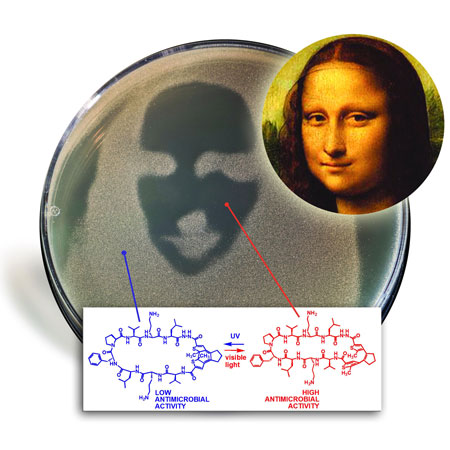 Scientists have produced an antibiotic, whose biological activity can be controlled with light. Thanks to the robust diarylethene photoswitch, the antimicrobial effect of the peptide mimetic can be applied in a spatially and temporally specific manner.
Scientists have produced an antibiotic, whose biological activity can be controlled with light. Thanks to the robust diarylethene photoswitch, the antimicrobial effect of the peptide mimetic can be applied in a spatially and temporally specific manner.
Mar 21st, 2014
Read more
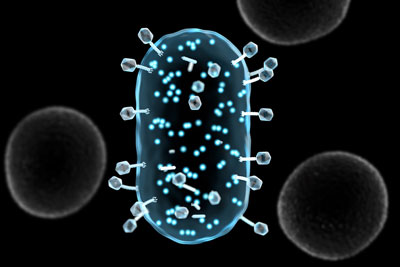 An advanced assay quickly illuminates bacteria for more rapid, accurate detection.
An advanced assay quickly illuminates bacteria for more rapid, accurate detection.
Mar 20th, 2014
Read more
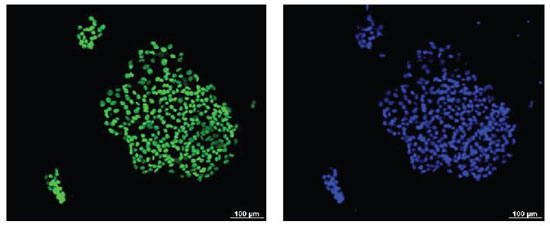 The DIY finger-prick technique opens door for extensive stem cell banking.
The DIY finger-prick technique opens door for extensive stem cell banking.
Mar 20th, 2014
Read more
 The compound uses natural enzymes instead of the traditional chemical reagents, is biodegradable, and involves no environmental impact. Most important, it is easily applicable in the production process and requires no additional investment.
The compound uses natural enzymes instead of the traditional chemical reagents, is biodegradable, and involves no environmental impact. Most important, it is easily applicable in the production process and requires no additional investment.
Mar 19th, 2014
Read more
University of Adelaide mathematicians have devised a method for identifying how cell clusters have formed by analysing an image of the cluster.
Mar 19th, 2014
Read more
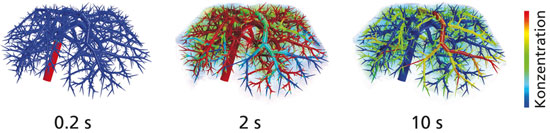 A new computer technique can realistically simulate how medicine affects the liver.
A new computer technique can realistically simulate how medicine affects the liver.
Mar 19th, 2014
Read more
When a heart gets damaged, such as during a major heart attack, there's no easy fix. But scientists working on a way to repair the vital organ have now engineered tissue that closely mimics natural heart muscle that beats, not only in a lab dish but also when implanted into animals.
Mar 18th, 2014
Read more
As some countries and companies roll out new rules to limit animal testing in pharmaceutical products designed for people, scientists are stepping in with a new way to test therapeutic drug candidates and determine drug safety and drug interactions - without using animals.
Mar 18th, 2014
Read more
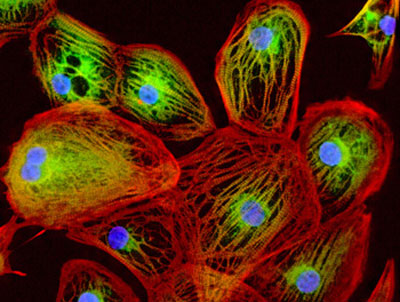 The University of California, Berkeley, and UC San Francisco are launching the Innovative Genomics Initiative (to lead a revolution in genetic engineering based on a new technology already generating novel strategies for gene therapy and the genetic study of disease.
The University of California, Berkeley, and UC San Francisco are launching the Innovative Genomics Initiative (to lead a revolution in genetic engineering based on a new technology already generating novel strategies for gene therapy and the genetic study of disease.
Mar 18th, 2014
Read more
In response to drug-resistant superbugs that send millions of people to hospitals around the world, scientists are building tiny, 'molecular drill bits' that kill bacteria by bursting through their protective cell walls.
Mar 17th, 2014
Read more
Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
Mar 14th, 2014
Read more
 Researchers have used a computer-aided design tool to create genetic languages to guide the design of biological systems.
Researchers have used a computer-aided design tool to create genetic languages to guide the design of biological systems.
Mar 13th, 2014
Read more
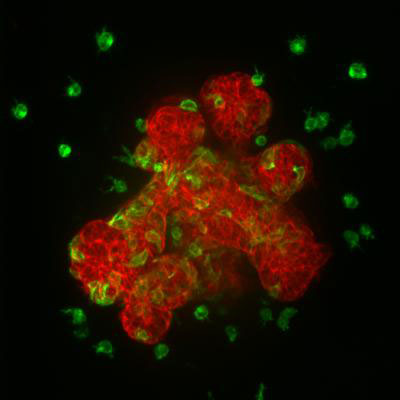 Studying epithelial cells, the cell type that most commonly turns cancerous, Johns Hopkins researchers have identified a protein that causes cells to release from their neighbors and migrate away from healthy mammary, or breast, tissue in mice. They also found that deletion of a cellular 'Velcro protein' does not cause the single-celled migration expected. Their results, they say, help clarify the molecular changes required for cancer cells to metastasize.
Studying epithelial cells, the cell type that most commonly turns cancerous, Johns Hopkins researchers have identified a protein that causes cells to release from their neighbors and migrate away from healthy mammary, or breast, tissue in mice. They also found that deletion of a cellular 'Velcro protein' does not cause the single-celled migration expected. Their results, they say, help clarify the molecular changes required for cancer cells to metastasize.
Mar 13th, 2014
Read more
From genetic and genomic testing to new techniques in human assisted reproduction, various technologies are providing parents with more of a say about the children they have and 'stirring the pot of designer baby concerns', writes Thomas H. Murray, President Emeritus of The Hastings Center, in a commentary in Science.
Mar 13th, 2014
Read more
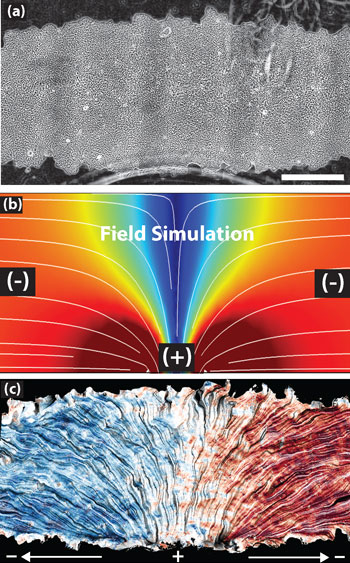 Engineers have found that an electrical current can be used to orchestrate the flow of a group of cells. This achievement sets the stage for more controlled forms of tissue engineering and for potential applications such as 'smart bandages' that use electrical stimulation to help heal wounds.
Engineers have found that an electrical current can be used to orchestrate the flow of a group of cells. This achievement sets the stage for more controlled forms of tissue engineering and for potential applications such as 'smart bandages' that use electrical stimulation to help heal wounds.
Mar 11th, 2014
Read more
Bacteria may be the key to produce useful bioplastics from the gasification of urban waste.
Mar 11th, 2014
Read more
 A new microfluidic method for evaluating drugs commonly used for preventing heart attacks has found that while aspirin can prevent dangerous blood clots in some at-risk patients, it may not be effective in all patients with narrowed arteries. The study, which involved 14 human subjects, used a device that simulated blood flowing through narrowed coronary arteries to assess effects of anti-clotting drugs.
A new microfluidic method for evaluating drugs commonly used for preventing heart attacks has found that while aspirin can prevent dangerous blood clots in some at-risk patients, it may not be effective in all patients with narrowed arteries. The study, which involved 14 human subjects, used a device that simulated blood flowing through narrowed coronary arteries to assess effects of anti-clotting drugs.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed








