Showing Spotlights 241 - 248 of 2786 in category All (newest first):
 Nanotechnology has the ability to completely transform the health care sector, particularly in developing countries like South Africa, where access to effective healthcare is still a challenge for millions of people living in poverty-stricken environments. Many African countries, despite having policies and strategies in place, struggle to allocate sufficient resources for research in nanomedicine. Most of the research conducted on the subject in Africa is focused on academic interests, rather than practical applications.
Nanotechnology has the ability to completely transform the health care sector, particularly in developing countries like South Africa, where access to effective healthcare is still a challenge for millions of people living in poverty-stricken environments. Many African countries, despite having policies and strategies in place, struggle to allocate sufficient resources for research in nanomedicine. Most of the research conducted on the subject in Africa is focused on academic interests, rather than practical applications.
Jan 15th, 2023
 Blockchain technology can be used in various ways to improve the transparency, integrity, and security of data in scientific research. For example, it can be used to create a tamper-evident record of research data, facilitate collaborations between researchers, protect intellectual property, fund scientific projects, and track the movement of materials throughout the supply chain. By using blockchain, researchers can ensure that their work is properly credited and cited, and that the data they collect is accurately recorded and preserved for future use.
Blockchain technology can be used in various ways to improve the transparency, integrity, and security of data in scientific research. For example, it can be used to create a tamper-evident record of research data, facilitate collaborations between researchers, protect intellectual property, fund scientific projects, and track the movement of materials throughout the supply chain. By using blockchain, researchers can ensure that their work is properly credited and cited, and that the data they collect is accurately recorded and preserved for future use.
Jan 11th, 2023
 Key components that are essential to the functioning of the Internet of Things include sensors and devices, network connectivity, data storage and processing, user interfaces, and security. Many aspects of these elements can be enhanced by nanotechnologies. Nanotechnology can enhance the performance and capabilities of IoT devices by enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient, and more versatile sensors, antennas, and processors. These improvements can lead to greater accuracy, energy efficiency, and versatility in a variety of applications, including healthcare, industrial monitoring, and environmental sensing.
Key components that are essential to the functioning of the Internet of Things include sensors and devices, network connectivity, data storage and processing, user interfaces, and security. Many aspects of these elements can be enhanced by nanotechnologies. Nanotechnology can enhance the performance and capabilities of IoT devices by enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient, and more versatile sensors, antennas, and processors. These improvements can lead to greater accuracy, energy efficiency, and versatility in a variety of applications, including healthcare, industrial monitoring, and environmental sensing.
Jan 9th, 2023
 A new motorized three-point-bending apparatus has been developed that is capable of automating strain engineering experiments on two-dimensional (2D) materials. The setup can be used to apply precise, uniform strain to 2D materials such as MoS2, allowing researchers to study the effects of strain on the electrical and optical properties of these materials. The system can also be used to study straintronic devices, devices whose output characteristics can be adjusted by means of applied strain.
A new motorized three-point-bending apparatus has been developed that is capable of automating strain engineering experiments on two-dimensional (2D) materials. The setup can be used to apply precise, uniform strain to 2D materials such as MoS2, allowing researchers to study the effects of strain on the electrical and optical properties of these materials. The system can also be used to study straintronic devices, devices whose output characteristics can be adjusted by means of applied strain.
Dec 16th, 2022
 By mimicking a biological cell plasma membrane, i.e. the membrane that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment, researchers have demonstrated that a 2D reduced graphene oxide membrane can regulate complex polysulfide chemistry in lithium-sulfur batteries. The efficiency of this separator in controlling the polysulfide chemistry and its sub-micron thickness allows to minimize the amount of electrolyte needed, which enables lightweight, high energy density batteries.
By mimicking a biological cell plasma membrane, i.e. the membrane that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment, researchers have demonstrated that a 2D reduced graphene oxide membrane can regulate complex polysulfide chemistry in lithium-sulfur batteries. The efficiency of this separator in controlling the polysulfide chemistry and its sub-micron thickness allows to minimize the amount of electrolyte needed, which enables lightweight, high energy density batteries.
Dec 16th, 2022
 Magnetism at atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials is of essential interest to scientists and engineers since it has the potential to revolutionize modern information technology enabling ultra-fast and ultra-small novel electronic and magnetic devices. However, most of the experimentally demonstrated 2D magnets possess a Curie point far below the room temperature, limiting their application in the real world. In new work, researchers developed an end-to-end computational pipeline that can predict the Curie temperature accurately from the first principles-based quantum mechanical calculations.
Magnetism at atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials is of essential interest to scientists and engineers since it has the potential to revolutionize modern information technology enabling ultra-fast and ultra-small novel electronic and magnetic devices. However, most of the experimentally demonstrated 2D magnets possess a Curie point far below the room temperature, limiting their application in the real world. In new work, researchers developed an end-to-end computational pipeline that can predict the Curie temperature accurately from the first principles-based quantum mechanical calculations.
Dec 12th, 2022
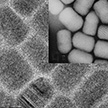 Researchers achieved a milestone in the synthesis of multifunctional photonic nanomaterials. They reported the synthesis of semiconductor 'giant' core-shell CdZnSe/CdS quantum dots with record breaking emissive lifetimes. Furthermore, the lifetimes can be tuned by making a simple alteration to the material's internal structure. These new particles have great efficacy for fundamental biological discovery as they emit at red wavelengths, which minimizes scattering, while the long lifetimes allow for biological imaging to be performed with less background noise.
Researchers achieved a milestone in the synthesis of multifunctional photonic nanomaterials. They reported the synthesis of semiconductor 'giant' core-shell CdZnSe/CdS quantum dots with record breaking emissive lifetimes. Furthermore, the lifetimes can be tuned by making a simple alteration to the material's internal structure. These new particles have great efficacy for fundamental biological discovery as they emit at red wavelengths, which minimizes scattering, while the long lifetimes allow for biological imaging to be performed with less background noise.
Dec 2nd, 2022
 Recent investigations suggest that topological semimetals reveal unique properties that can enable unprecedented functionalities for future electronics. New research results shed light on the specifics of electron transport in quasi-one-dimensional topological Weyl semimetals and can be important for their proposed applications as downscaled interconnects. The results obtained in this work can be used for developing assessment methodologies for the reliability of topological semimetals.
Recent investigations suggest that topological semimetals reveal unique properties that can enable unprecedented functionalities for future electronics. New research results shed light on the specifics of electron transport in quasi-one-dimensional topological Weyl semimetals and can be important for their proposed applications as downscaled interconnects. The results obtained in this work can be used for developing assessment methodologies for the reliability of topological semimetals.
Nov 22nd, 2022
 Nanotechnology has the ability to completely transform the health care sector, particularly in developing countries like South Africa, where access to effective healthcare is still a challenge for millions of people living in poverty-stricken environments. Many African countries, despite having policies and strategies in place, struggle to allocate sufficient resources for research in nanomedicine. Most of the research conducted on the subject in Africa is focused on academic interests, rather than practical applications.
Nanotechnology has the ability to completely transform the health care sector, particularly in developing countries like South Africa, where access to effective healthcare is still a challenge for millions of people living in poverty-stricken environments. Many African countries, despite having policies and strategies in place, struggle to allocate sufficient resources for research in nanomedicine. Most of the research conducted on the subject in Africa is focused on academic interests, rather than practical applications.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





