Showing Spotlights 1 - 8 of 44 in category All (newest first):
 A novel tunable microcavity deterministically coupled to single quantum dots achieves highly efficient, pure and indistinguishable single photon generation, overcoming key roadblocks to scalable quantum technologies.
A novel tunable microcavity deterministically coupled to single quantum dots achieves highly efficient, pure and indistinguishable single photon generation, overcoming key roadblocks to scalable quantum technologies.
Apr 7th, 2024
 Researchers have developed a method to 3D print complex architectures made of perovskite quantum dot-polymer composites, which could enable sophisticated optoelectronic devices.
Researchers have developed a method to 3D print complex architectures made of perovskite quantum dot-polymer composites, which could enable sophisticated optoelectronic devices.
Mar 25th, 2024
 Researchers report single molecule studies of energy transfer using a quantum dot donor with an organic dye acceptor. They demonstrate that suppression of the blinking of the QD donor minimizes the loss of energy, which is achieved by a simple surface treatment method.
Researchers report single molecule studies of energy transfer using a quantum dot donor with an organic dye acceptor. They demonstrate that suppression of the blinking of the QD donor minimizes the loss of energy, which is achieved by a simple surface treatment method.
Apr 10th, 2023
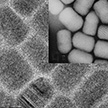 Researchers achieved a milestone in the synthesis of multifunctional photonic nanomaterials. They reported the synthesis of semiconductor 'giant' core-shell CdZnSe/CdS quantum dots with record breaking emissive lifetimes. Furthermore, the lifetimes can be tuned by making a simple alteration to the material's internal structure. These new particles have great efficacy for fundamental biological discovery as they emit at red wavelengths, which minimizes scattering, while the long lifetimes allow for biological imaging to be performed with less background noise.
Researchers achieved a milestone in the synthesis of multifunctional photonic nanomaterials. They reported the synthesis of semiconductor 'giant' core-shell CdZnSe/CdS quantum dots with record breaking emissive lifetimes. Furthermore, the lifetimes can be tuned by making a simple alteration to the material's internal structure. These new particles have great efficacy for fundamental biological discovery as they emit at red wavelengths, which minimizes scattering, while the long lifetimes allow for biological imaging to be performed with less background noise.
Dec 2nd, 2022
 Researchers have have reported the synthesis process and biomedical applications of a novel nanomaterial for in vivo treatment of vasculopathy - a general term used to describe any disease affecting blood vessels. Through their innovative approach using rational design and synthesis strategies, the researchers developed intrinsically immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory tantalum carbide MXene quantum dots. The team is confident that this new nanomaterial could reduce or even avoid the need for anti-rejection drugs for heart transplant patients.
Researchers have have reported the synthesis process and biomedical applications of a novel nanomaterial for in vivo treatment of vasculopathy - a general term used to describe any disease affecting blood vessels. Through their innovative approach using rational design and synthesis strategies, the researchers developed intrinsically immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory tantalum carbide MXene quantum dots. The team is confident that this new nanomaterial could reduce or even avoid the need for anti-rejection drugs for heart transplant patients.
May 9th, 2022
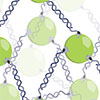 In addition to the plethora of functions such as storage of genetic information and regulation of its expression, DNA and RNA are also highly programmable biomaterials. DNA can be utilized to design short complementary sequences to be used as the linkers which bring together and organize other biological and inorganic materials. Quantum dots are one such inorganic candidate. Researchers now utilized DNA for the precise assembly of QDs into larger three-dimensional scaffolds.
In addition to the plethora of functions such as storage of genetic information and regulation of its expression, DNA and RNA are also highly programmable biomaterials. DNA can be utilized to design short complementary sequences to be used as the linkers which bring together and organize other biological and inorganic materials. Quantum dots are one such inorganic candidate. Researchers now utilized DNA for the precise assembly of QDs into larger three-dimensional scaffolds.
Aug 18th, 2021
 Researchers achieved a milestone in exploring biology using nanotechnology utilizing single-particle tracking to investigate the interaction between human T cells and individual fluorescent nanoparticles of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). The researchers were able to deliver QDs into the cytosol of live T cells by decorating the nanoparticles with a unique cell-penetrating peptide. The study paves the way for improving drug delivery and immunotherapy using novel nanocarriers.
Researchers achieved a milestone in exploring biology using nanotechnology utilizing single-particle tracking to investigate the interaction between human T cells and individual fluorescent nanoparticles of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). The researchers were able to deliver QDs into the cytosol of live T cells by decorating the nanoparticles with a unique cell-penetrating peptide. The study paves the way for improving drug delivery and immunotherapy using novel nanocarriers.
Mar 12th, 2021
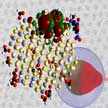 Generally it is believed that core quantum dots (QDs) are good reducing agents and are used for that purpose in solar hydrogen generation and various organic transformations. However, core QDs are very unstable. Core/shell dots are more robust, but the shell minimizes redox activity. Researchers now demonstrate that this isn't perfectly true. In fact, they found that certain core/shell materials are a better reducing agent than the core alone. Most importantly, core/shell QDs are substantially more robust than the core alone.
Generally it is believed that core quantum dots (QDs) are good reducing agents and are used for that purpose in solar hydrogen generation and various organic transformations. However, core QDs are very unstable. Core/shell dots are more robust, but the shell minimizes redox activity. Researchers now demonstrate that this isn't perfectly true. In fact, they found that certain core/shell materials are a better reducing agent than the core alone. Most importantly, core/shell QDs are substantially more robust than the core alone.
Nov 13th, 2020
 A novel tunable microcavity deterministically coupled to single quantum dots achieves highly efficient, pure and indistinguishable single photon generation, overcoming key roadblocks to scalable quantum technologies.
A novel tunable microcavity deterministically coupled to single quantum dots achieves highly efficient, pure and indistinguishable single photon generation, overcoming key roadblocks to scalable quantum technologies.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





