Showing Spotlights 833 - 840 of 2785 in category All (newest first):
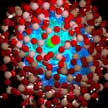 Hybrid nanomaterials (nanohybrids) are composed of two or more components - at least one of which is nanoscale - exhibiting many distinct physicochemical properties and hold great promise for applications in optics, electronics, magnetics, new energy, environment protection, and biomedical engineering. Different types of nanohybrids have been successfully synthesized via microfluidic processes or hybrid microfluidic-batch processes. The synthesis of nanohybrids using microfluidic-based processes can fulfill many challenges present in conventional bottle batch methods.
Hybrid nanomaterials (nanohybrids) are composed of two or more components - at least one of which is nanoscale - exhibiting many distinct physicochemical properties and hold great promise for applications in optics, electronics, magnetics, new energy, environment protection, and biomedical engineering. Different types of nanohybrids have been successfully synthesized via microfluidic processes or hybrid microfluidic-batch processes. The synthesis of nanohybrids using microfluidic-based processes can fulfill many challenges present in conventional bottle batch methods.
May 9th, 2017
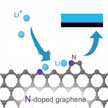 Lithium metal anodes with ultrahigh theoretical specific capacity and the lowest negative electrochemical potential, have been considered the most promising electrode for next-generation rechargeable batteries, including rechargeable Li-S, Li-air batteries, and even Li metal batteries which utilize intercalation compounds as cathodes. Designing a Li plating matrix with a high surface area and lithiophilic surface maybe can help gain a dendrite-free metal anode.
Lithium metal anodes with ultrahigh theoretical specific capacity and the lowest negative electrochemical potential, have been considered the most promising electrode for next-generation rechargeable batteries, including rechargeable Li-S, Li-air batteries, and even Li metal batteries which utilize intercalation compounds as cathodes. Designing a Li plating matrix with a high surface area and lithiophilic surface maybe can help gain a dendrite-free metal anode.
May 5th, 2017
 Immunotherapy has become an important part of treating some types of cancer. It uses certain parts of a person's immune system to fight the cancer. Usually this is done by administering immune system components, such as man-made immune system proteins. In recent years, nanotechnology has played an increasingly important role in pursuing efficient vaccine delivery in cancer immunotherapy. This article discusses vaccine delivery by synthetic nanoparticles or naturally derived nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy has become an important part of treating some types of cancer. It uses certain parts of a person's immune system to fight the cancer. Usually this is done by administering immune system components, such as man-made immune system proteins. In recent years, nanotechnology has played an increasingly important role in pursuing efficient vaccine delivery in cancer immunotherapy. This article discusses vaccine delivery by synthetic nanoparticles or naturally derived nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy.
May 4th, 2017
 Researchers show how spermatozoa can be useful parts of microdevices: As biocompatible propulsion source, but also entailing other functionalities such as their natural destiny for fertilization, their ability to respond to stimuli, or their ability to take up drugs open up fascinating new applications. They demonstrate first examples of using sperm cells as robotic components. The so-called spermbots are also systems that enable biophysical studies, e.g. of sperm motion in confinement.
Researchers show how spermatozoa can be useful parts of microdevices: As biocompatible propulsion source, but also entailing other functionalities such as their natural destiny for fertilization, their ability to respond to stimuli, or their ability to take up drugs open up fascinating new applications. They demonstrate first examples of using sperm cells as robotic components. The so-called spermbots are also systems that enable biophysical studies, e.g. of sperm motion in confinement.
May 3rd, 2017
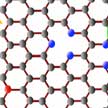 Despite their potential, the practical use of Li-O2 batteries is seriously limited by the corrosion of Li metal by ambient water vapor from air. One way to circumvent this issue is to use an oxygen selective membrane that allows only oxygen into the battery while stopping or slowing water vapor intake. The membrane must be mechanically robust and yet sufficiently thin and light so as to not increase deadweight of the battery. Researchers now have discovered a way to make the thinnest possible oxygen selective membrane using graphene.
Despite their potential, the practical use of Li-O2 batteries is seriously limited by the corrosion of Li metal by ambient water vapor from air. One way to circumvent this issue is to use an oxygen selective membrane that allows only oxygen into the battery while stopping or slowing water vapor intake. The membrane must be mechanically robust and yet sufficiently thin and light so as to not increase deadweight of the battery. Researchers now have discovered a way to make the thinnest possible oxygen selective membrane using graphene.
Apr 25th, 2017
 Researchers have demonstrated an all-stretchable-component sodium-ion full battery, designed and manufactured by integrating stretchable graphene-modified PDMS sponge current collector, sodium-ion conducting gel polymer separator, and elastic PDMS substrate. This first-of-its-kind battery design maintains better mechanical properties compared with most reported designs using one or more rigid components that fail to meet the stretchability requirement for the entire device.
Researchers have demonstrated an all-stretchable-component sodium-ion full battery, designed and manufactured by integrating stretchable graphene-modified PDMS sponge current collector, sodium-ion conducting gel polymer separator, and elastic PDMS substrate. This first-of-its-kind battery design maintains better mechanical properties compared with most reported designs using one or more rigid components that fail to meet the stretchability requirement for the entire device.
Apr 20th, 2017
 In new work, scientists describe a lithium-sulfur battery prototype using commercially viable micron-sized sulfur as cathode materials but with unprecedented cycling life that has never been achieved before. This success in achieving exceptionally long battery life is ascribed to a concept of self-healing. By mimicking a biological self-healing process, fibrinolysis, the team introduced an extrinsic healing agent, polysulfide, to enable the stable operation of sulfur microparticle (SMiP) cathodes.
In new work, scientists describe a lithium-sulfur battery prototype using commercially viable micron-sized sulfur as cathode materials but with unprecedented cycling life that has never been achieved before. This success in achieving exceptionally long battery life is ascribed to a concept of self-healing. By mimicking a biological self-healing process, fibrinolysis, the team introduced an extrinsic healing agent, polysulfide, to enable the stable operation of sulfur microparticle (SMiP) cathodes.
Apr 19th, 2017
 Molecular magnets or single molecule-based magnets are usually anti-ferromagnetic (non-magnetic) at room temperature, which so far has limited their use to laboratory environments. As the first successful molecular magnet in a real-world application, an interdisciplinary research group has reported a new 'exotic' molecular magnet compound - iron salen nanoparticles - which shows intrinsic magnetic nature at room temperature as well as anticancer properties.
Molecular magnets or single molecule-based magnets are usually anti-ferromagnetic (non-magnetic) at room temperature, which so far has limited their use to laboratory environments. As the first successful molecular magnet in a real-world application, an interdisciplinary research group has reported a new 'exotic' molecular magnet compound - iron salen nanoparticles - which shows intrinsic magnetic nature at room temperature as well as anticancer properties.
Apr 13th, 2017
 Hybrid nanomaterials (nanohybrids) are composed of two or more components - at least one of which is nanoscale - exhibiting many distinct physicochemical properties and hold great promise for applications in optics, electronics, magnetics, new energy, environment protection, and biomedical engineering. Different types of nanohybrids have been successfully synthesized via microfluidic processes or hybrid microfluidic-batch processes. The synthesis of nanohybrids using microfluidic-based processes can fulfill many challenges present in conventional bottle batch methods.
Hybrid nanomaterials (nanohybrids) are composed of two or more components - at least one of which is nanoscale - exhibiting many distinct physicochemical properties and hold great promise for applications in optics, electronics, magnetics, new energy, environment protection, and biomedical engineering. Different types of nanohybrids have been successfully synthesized via microfluidic processes or hybrid microfluidic-batch processes. The synthesis of nanohybrids using microfluidic-based processes can fulfill many challenges present in conventional bottle batch methods.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





