Showing Spotlights 2561 - 2568 of 2851 in category All (newest first):
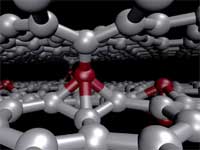 Research into the subject of radiation damage in graphite began in the early 1940s as a part of the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power. Some designs of nuclear power reactors, such as the Chernobyl reactors, use graphite as moderator (the material which slows down the neutrons released from fission so that they cause more fission). The damage to the graphite moderators caused by radiation has been one of the major concerns of the nuclear power industry and radiation defects, i.e. structural irregularities, in graphite produced upon irradiation, their structure, properties and formation mechanisms, have been subject of intense research. Several years ago, defects in carbon materials became a hot topic again but now in the context of carbon layered nanostructures, such as multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, which closely resemble graphite in their structure. The formation of irradiation-induced defects in graphite like layered carbon nanostructures, multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, nanoonions, etc. changes their mechanical and electronic properties and may even trigger dramatic structural changes. While the terms "radiation damage" and "defect" are perceived negatively by people, the nanoengineering research community is trying to make use of defect structures for the deliberate modification of carbon nanomaterials, which can eventually be used in the manufacturing of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS). This process is sometimes called "defect-assisted engineering."
Research into the subject of radiation damage in graphite began in the early 1940s as a part of the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power. Some designs of nuclear power reactors, such as the Chernobyl reactors, use graphite as moderator (the material which slows down the neutrons released from fission so that they cause more fission). The damage to the graphite moderators caused by radiation has been one of the major concerns of the nuclear power industry and radiation defects, i.e. structural irregularities, in graphite produced upon irradiation, their structure, properties and formation mechanisms, have been subject of intense research. Several years ago, defects in carbon materials became a hot topic again but now in the context of carbon layered nanostructures, such as multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, which closely resemble graphite in their structure. The formation of irradiation-induced defects in graphite like layered carbon nanostructures, multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, nanoonions, etc. changes their mechanical and electronic properties and may even trigger dramatic structural changes. While the terms "radiation damage" and "defect" are perceived negatively by people, the nanoengineering research community is trying to make use of defect structures for the deliberate modification of carbon nanomaterials, which can eventually be used in the manufacturing of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS). This process is sometimes called "defect-assisted engineering."
Apr 13th, 2007
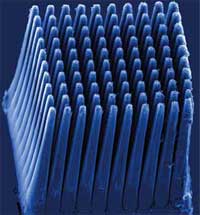 For computer chips, 'smaller and faster' just isn't good enough anymore. Power and heat have become the biggest issues for chip manufacturers and companies integrating these chips in everyday devices such as cell phones and laptops. The computing power of today's computer chips is provided mostly by operations switching at ever higher frequency. This physically induced power dissipation represents the limiting factor to a further increase of the capability of integrated circuits. Heat dissipation of the latest Intel processors has become a widely discussed issue. By the end of the decade, you might as well be feeling a rocket nozzle than touching a chip. And soon after 2010, computer chips could feel like the bubbly hot surface of the sun itself. As the electronics industry continues to churn out smaller and slimmer portable devices, manufacturers have been challenged to find new ways to combat the persistent problem of thermal management. New research suggests that the integration of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as heat sinks into electronic devices might provide a solution to this problem.
For computer chips, 'smaller and faster' just isn't good enough anymore. Power and heat have become the biggest issues for chip manufacturers and companies integrating these chips in everyday devices such as cell phones and laptops. The computing power of today's computer chips is provided mostly by operations switching at ever higher frequency. This physically induced power dissipation represents the limiting factor to a further increase of the capability of integrated circuits. Heat dissipation of the latest Intel processors has become a widely discussed issue. By the end of the decade, you might as well be feeling a rocket nozzle than touching a chip. And soon after 2010, computer chips could feel like the bubbly hot surface of the sun itself. As the electronics industry continues to churn out smaller and slimmer portable devices, manufacturers have been challenged to find new ways to combat the persistent problem of thermal management. New research suggests that the integration of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as heat sinks into electronic devices might provide a solution to this problem.
Apr 12th, 2007
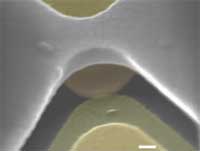 Organic materials offer new electronic functionality not available in inorganic devices. Promising examples of novel characteristics in organic devices range from the memory effects observed in monolayers and polymer films to negative differential resistance devices. However, the integration of organic compounds within nanoscale electronic circuitry poses considerable challenges for materials physics and chemistry, and a detailed understanding of the conduction mechanisms, switching and memory is still lacking. With increasing research into very different material systems such as oxides, solid-state electrolytes, phase-change memory materials, it is becoming clear that electronic switching on the smallest length scale cannot be purely electronic phenomena. Rather, a motion of heavier constituents has to be involved that will in turn change the electronic properties. New work conducted at Bell Labs demonstrates the success of such a line of thought in molecular systems. The Bell scientists demonstrated a novel approach to creating and chemically modifying conducting electronic states in nanoscale molecular devices.
Organic materials offer new electronic functionality not available in inorganic devices. Promising examples of novel characteristics in organic devices range from the memory effects observed in monolayers and polymer films to negative differential resistance devices. However, the integration of organic compounds within nanoscale electronic circuitry poses considerable challenges for materials physics and chemistry, and a detailed understanding of the conduction mechanisms, switching and memory is still lacking. With increasing research into very different material systems such as oxides, solid-state electrolytes, phase-change memory materials, it is becoming clear that electronic switching on the smallest length scale cannot be purely electronic phenomena. Rather, a motion of heavier constituents has to be involved that will in turn change the electronic properties. New work conducted at Bell Labs demonstrates the success of such a line of thought in molecular systems. The Bell scientists demonstrated a novel approach to creating and chemically modifying conducting electronic states in nanoscale molecular devices.
Apr 11th, 2007
 Polystyrene (PS), also known under its trademark name styrofoam, is found in your home, office, local grocery, fast food outlet and in the cafeteria. It comes in many shapes and forms, from foam egg cartons and meat trays, plates and salad boxes, from coffee cups and utensils to CD jewel boxes, and from produce trays to those foam peanuts used in packing and the lightweight foam pieces that cushion new appliances and electronics. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Municipal Solid Waste statistics (the things we read at Nanowerk to bring you interesting stories...), solid waste in the U.S. in 2005 contained almost 2.6 million tons of PS - a material that takes hundreds of years to break down and which is not recovered in recycling. PS is also a principle component of marine debris. Motivated by this problem of 'white pollution', a group of researchers in China developed a nanocomposite material that not only has superabsorbent capabilities but also utilizes waste PS foam. If commercially successful, this and similar methods of recycling waste PS into new products could go along way in reducing the worldwide harmful effects of white pollution.
Polystyrene (PS), also known under its trademark name styrofoam, is found in your home, office, local grocery, fast food outlet and in the cafeteria. It comes in many shapes and forms, from foam egg cartons and meat trays, plates and salad boxes, from coffee cups and utensils to CD jewel boxes, and from produce trays to those foam peanuts used in packing and the lightweight foam pieces that cushion new appliances and electronics. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Municipal Solid Waste statistics (the things we read at Nanowerk to bring you interesting stories...), solid waste in the U.S. in 2005 contained almost 2.6 million tons of PS - a material that takes hundreds of years to break down and which is not recovered in recycling. PS is also a principle component of marine debris. Motivated by this problem of 'white pollution', a group of researchers in China developed a nanocomposite material that not only has superabsorbent capabilities but also utilizes waste PS foam. If commercially successful, this and similar methods of recycling waste PS into new products could go along way in reducing the worldwide harmful effects of white pollution.
Apr 10th, 2007
 Science fiction style robots like Star Wars' R2-D2 or the NS-5 model in I, Robot firmly belong into the realm of Hollywood - and so do "nanobots" a la Michael Crichton's Prey. Staying with both feet firmly on scientific ground, robotics can be defined as the theory and application of robots, a completely self-contained electronic, electric, or mechanical device, to such activities as manufacturing. Scale that robot down to a few billionth of a meter and you are talking nanotechnology robotics; nanorobotics in short. The field of nanorobotics brings together several disciplines, including nanofabrication processes used for producing nanoscale robots, nanoactuators, nanosensors, and physical modeling at nanoscales. Nanorobotic manipulation technologies, including the assembly of nanometer-sized parts, the manipulation of biological cells or molecules, and the types of robots used to perform these tasks also form a component of nanorobotics. Nanorobotics might one day even lead to the holy grail of nanotechnology where automated and self-contained molecular assemblers not only are capable of building complex molecules but build copies of themselves - "self-replication" - or even complete everyday products (this vision is nicely illustrated in the clip "Productive Nanosystems: From Molecules to Superproducts"). Whether this will ever happen is hotly debated - to understand where both sides stand, read the famous 2003 debate where Drexler and Smalley make the case for and against molecular assemblers. Today's nanorobotics research deals with more mundane issues such as how to build nanoscale motors and simple nanomanipulators.
Science fiction style robots like Star Wars' R2-D2 or the NS-5 model in I, Robot firmly belong into the realm of Hollywood - and so do "nanobots" a la Michael Crichton's Prey. Staying with both feet firmly on scientific ground, robotics can be defined as the theory and application of robots, a completely self-contained electronic, electric, or mechanical device, to such activities as manufacturing. Scale that robot down to a few billionth of a meter and you are talking nanotechnology robotics; nanorobotics in short. The field of nanorobotics brings together several disciplines, including nanofabrication processes used for producing nanoscale robots, nanoactuators, nanosensors, and physical modeling at nanoscales. Nanorobotic manipulation technologies, including the assembly of nanometer-sized parts, the manipulation of biological cells or molecules, and the types of robots used to perform these tasks also form a component of nanorobotics. Nanorobotics might one day even lead to the holy grail of nanotechnology where automated and self-contained molecular assemblers not only are capable of building complex molecules but build copies of themselves - "self-replication" - or even complete everyday products (this vision is nicely illustrated in the clip "Productive Nanosystems: From Molecules to Superproducts"). Whether this will ever happen is hotly debated - to understand where both sides stand, read the famous 2003 debate where Drexler and Smalley make the case for and against molecular assemblers. Today's nanorobotics research deals with more mundane issues such as how to build nanoscale motors and simple nanomanipulators.
Apr 5th, 2007
 In the future, wearable electronics will go far beyond just very small electronic devices. Not only will such devices be embedded on textile substrates, but an electronics device or system could become the fabric itself. Electronics textiles will allow the design and production of a new generation of garments with distributed sensors and electronic functions. Such e-textiles will have the revolutionary ability to sense, act, store, emit, and move (think biomedical monitoring functions or new man-machine interfaces) while leveraging an existing low-cost textile manufacturing infrastructure. Reporting a novel approach through the construction of all-organic wire electrochemical transistor devices (WECT) , researchers in Sweden show that textile monofilaments can be coated with continuous thin films of a conducting polymer and used to create microscale WECTs on single fibers. They also demonstrate inverters and multiplexers for digital logic. This opens an avenue for three-dimensional polymer micro-electronics, where large-scale circuits can be designed and integrated directly into the three-dimensional structure of woven fibers.
In the future, wearable electronics will go far beyond just very small electronic devices. Not only will such devices be embedded on textile substrates, but an electronics device or system could become the fabric itself. Electronics textiles will allow the design and production of a new generation of garments with distributed sensors and electronic functions. Such e-textiles will have the revolutionary ability to sense, act, store, emit, and move (think biomedical monitoring functions or new man-machine interfaces) while leveraging an existing low-cost textile manufacturing infrastructure. Reporting a novel approach through the construction of all-organic wire electrochemical transistor devices (WECT) , researchers in Sweden show that textile monofilaments can be coated with continuous thin films of a conducting polymer and used to create microscale WECTs on single fibers. They also demonstrate inverters and multiplexers for digital logic. This opens an avenue for three-dimensional polymer micro-electronics, where large-scale circuits can be designed and integrated directly into the three-dimensional structure of woven fibers.
Apr 4th, 2007
 Super-tough materials with exceptional mechanical properties are in critical need for applications under extreme conditions such as jet engines, power turbines, catalytic heat exchangers, military armors, aircrafts, and spacecrafts. Researchers involved in improving man-made composite materials are trying to understand how some of the amazing high-performance materials found in Nature can be copied or even improved upon. Nature has evolved complex bottom-up methods for fabricating ordered nanostructured materials that often have extraordinary mechanical strength and toughness. One of the best examples is nacre, the pearly internal layer of many mollusc shells. It has evolved through millions of years to a level of optimization currently achieved in very few engineered composites. In a novel approach, scientists have prepared a high-performing nanocomposite material that takes advantage of two different exceptional natural materials - layered nacre and the marine adhesive of mussels. The resulting nanostructured composite film exhibits high strength exceeding that of even nacre.
Super-tough materials with exceptional mechanical properties are in critical need for applications under extreme conditions such as jet engines, power turbines, catalytic heat exchangers, military armors, aircrafts, and spacecrafts. Researchers involved in improving man-made composite materials are trying to understand how some of the amazing high-performance materials found in Nature can be copied or even improved upon. Nature has evolved complex bottom-up methods for fabricating ordered nanostructured materials that often have extraordinary mechanical strength and toughness. One of the best examples is nacre, the pearly internal layer of many mollusc shells. It has evolved through millions of years to a level of optimization currently achieved in very few engineered composites. In a novel approach, scientists have prepared a high-performing nanocomposite material that takes advantage of two different exceptional natural materials - layered nacre and the marine adhesive of mussels. The resulting nanostructured composite film exhibits high strength exceeding that of even nacre.
Apr 3rd, 2007
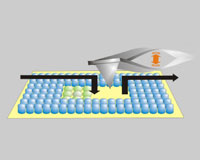 Proteins are very specific about which other proteins or biochemicals they will interact with and therefore are of great use for biosensing applications. For instance, if a malignant cancer develops in the human body, the cancer cells produce certain types of proteins. Identifying such proteins enables early detection of cancer. One of the goals of nanobiotechnology is to develop protein chips that are sensitively responsive to a very tiny amount of specific proteins in order to enable such early stage diagnosis. For example, a protein that is known to bind to a protein produced by a cancer cell could be attached to a biochip. If this particular cancer cell protein were present in a sample passed over the chip, it would bind to the protein on the chip, causing a detectable change in the electrical signal passing through the chip. This change in the electrical signal would be registered by the device, confirming the presence of the protein in the sample. While this sounds very promising for the future of diagnostic systems, with the promise of protein chips capable of single-molecule resolution, the controlled assembly of proteins into bioactive nanostructures still is a key challenge in nanobiotechnology. Researchers in Germany took a further step towards this goal by developing a native protein nanolithography technique that allows for the nanostructured assembly of even fragile proteins.
Proteins are very specific about which other proteins or biochemicals they will interact with and therefore are of great use for biosensing applications. For instance, if a malignant cancer develops in the human body, the cancer cells produce certain types of proteins. Identifying such proteins enables early detection of cancer. One of the goals of nanobiotechnology is to develop protein chips that are sensitively responsive to a very tiny amount of specific proteins in order to enable such early stage diagnosis. For example, a protein that is known to bind to a protein produced by a cancer cell could be attached to a biochip. If this particular cancer cell protein were present in a sample passed over the chip, it would bind to the protein on the chip, causing a detectable change in the electrical signal passing through the chip. This change in the electrical signal would be registered by the device, confirming the presence of the protein in the sample. While this sounds very promising for the future of diagnostic systems, with the promise of protein chips capable of single-molecule resolution, the controlled assembly of proteins into bioactive nanostructures still is a key challenge in nanobiotechnology. Researchers in Germany took a further step towards this goal by developing a native protein nanolithography technique that allows for the nanostructured assembly of even fragile proteins.
Apr 2nd, 2007
 Research into the subject of radiation damage in graphite began in the early 1940s as a part of the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power. Some designs of nuclear power reactors, such as the Chernobyl reactors, use graphite as moderator (the material which slows down the neutrons released from fission so that they cause more fission). The damage to the graphite moderators caused by radiation has been one of the major concerns of the nuclear power industry and radiation defects, i.e. structural irregularities, in graphite produced upon irradiation, their structure, properties and formation mechanisms, have been subject of intense research. Several years ago, defects in carbon materials became a hot topic again but now in the context of carbon layered nanostructures, such as multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, which closely resemble graphite in their structure. The formation of irradiation-induced defects in graphite like layered carbon nanostructures, multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, nanoonions, etc. changes their mechanical and electronic properties and may even trigger dramatic structural changes. While the terms "radiation damage" and "defect" are perceived negatively by people, the nanoengineering research community is trying to make use of defect structures for the deliberate modification of carbon nanomaterials, which can eventually be used in the manufacturing of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS). This process is sometimes called "defect-assisted engineering."
Research into the subject of radiation damage in graphite began in the early 1940s as a part of the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power. Some designs of nuclear power reactors, such as the Chernobyl reactors, use graphite as moderator (the material which slows down the neutrons released from fission so that they cause more fission). The damage to the graphite moderators caused by radiation has been one of the major concerns of the nuclear power industry and radiation defects, i.e. structural irregularities, in graphite produced upon irradiation, their structure, properties and formation mechanisms, have been subject of intense research. Several years ago, defects in carbon materials became a hot topic again but now in the context of carbon layered nanostructures, such as multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, which closely resemble graphite in their structure. The formation of irradiation-induced defects in graphite like layered carbon nanostructures, multiwalled and bundled carbon nanotubes, nanoonions, etc. changes their mechanical and electronic properties and may even trigger dramatic structural changes. While the terms "radiation damage" and "defect" are perceived negatively by people, the nanoengineering research community is trying to make use of defect structures for the deliberate modification of carbon nanomaterials, which can eventually be used in the manufacturing of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS). This process is sometimes called "defect-assisted engineering."
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





