X-ray tomography on a living frog embryo
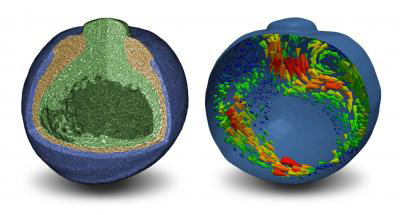 Motion of individual cells within developing frog embryos resolved/X-ray tomography based on diffraction rather than absorption/new methods for developmental biology.
Motion of individual cells within developing frog embryos resolved/X-ray tomography based on diffraction rather than absorption/new methods for developmental biology.
May 16th, 2013
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
 Motion of individual cells within developing frog embryos resolved/X-ray tomography based on diffraction rather than absorption/new methods for developmental biology.
Motion of individual cells within developing frog embryos resolved/X-ray tomography based on diffraction rather than absorption/new methods for developmental biology.
May 16th, 2013
Read more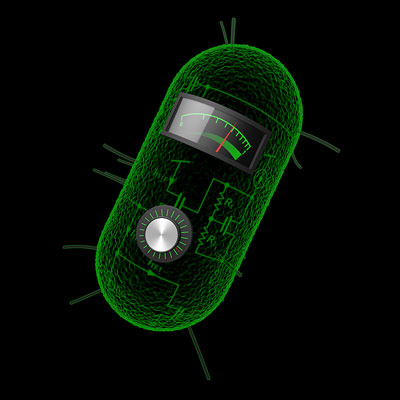 Using analog computation circuits, MIT engineers design cells that can compute logarithms, divide and take square roots.
Using analog computation circuits, MIT engineers design cells that can compute logarithms, divide and take square roots.
May 16th, 2013
Read moreBBSRC, with input from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), has published a document outlining the impacts that their 2010 'Synthetic Biology Dialogue' has had in informing continued discussions around synthetic biology.
May 15th, 2013
Read more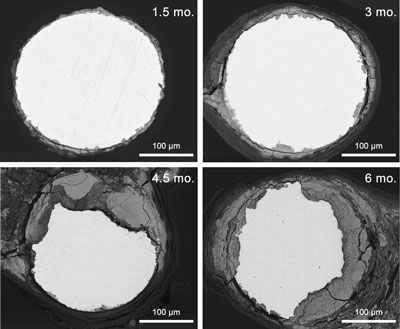 Some materials dissolve too quickly, before cardiac arteries can fully heal, and some hang around forever. Zinc, however, may be just right.
Some materials dissolve too quickly, before cardiac arteries can fully heal, and some hang around forever. Zinc, however, may be just right.
May 14th, 2013
Read more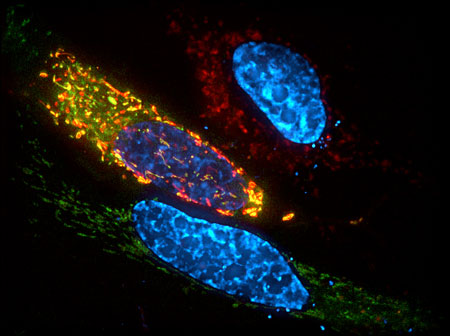 Findings may offer a new way to kill cancer cells by forcing them into an alternative programmed-death pathway.
Findings may offer a new way to kill cancer cells by forcing them into an alternative programmed-death pathway.
May 14th, 2013
Read more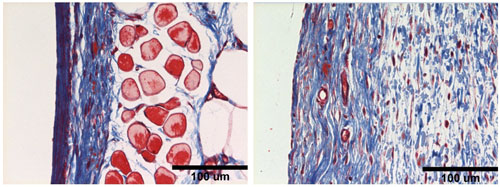 Expensive, state-of-the-art medical devices and surgeries often are thwarted by the body's natural response to attack something in the tissue that appears foreign. Now, University of Washington engineers have demonstrated in mice a way to prevent this sort of response.
Expensive, state-of-the-art medical devices and surgeries often are thwarted by the body's natural response to attack something in the tissue that appears foreign. Now, University of Washington engineers have demonstrated in mice a way to prevent this sort of response.
May 14th, 2013
Read moreA team of Tel Aviv University researchers, led by Dr. Shimon Rochkind and Prof. Zvi Nevo, has invented a method for repairing damaged peripheral nerves using a biodegradable implant along with a newly-developed gel that increases nerve growth and healing, ultimately restoring function to a torn or damaged nerve. The therapy is only a few years away from clinical use, say the researchers.
May 13th, 2013
Read more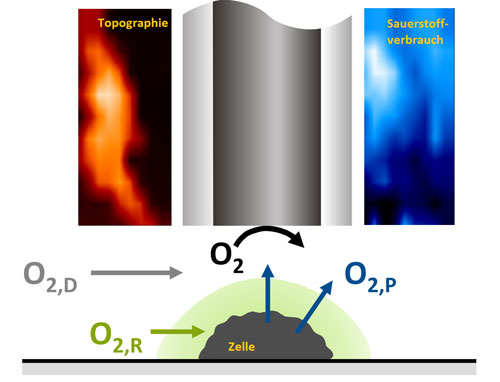 How active a living cell is can be seen by its oxygen consumption. The method for determining this consumption has now been significantly improved by chemists in Bochum.
How active a living cell is can be seen by its oxygen consumption. The method for determining this consumption has now been significantly improved by chemists in Bochum.
May 13th, 2013
Read moreThe Synthetic Biology ERA-NET (ERASynBio) has announced its 1st joint call for transnational research projects in Synthetic Biology. The call will be open until 26 August 2013 and represents a unique opportunity for Europe and the USA to build Synthetic Biology capacity through innovative transnational projects.
May 13th, 2013
Read more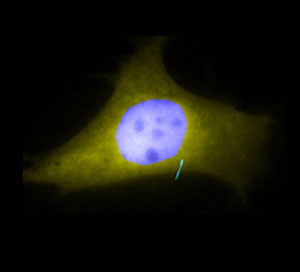 Experiments at Johns Hopkins have unearthed clues about which protein signaling molecules are allowed into hollow, hair-like 'antennae', called cilia, that alert cells to critical changes in their environments.
Experiments at Johns Hopkins have unearthed clues about which protein signaling molecules are allowed into hollow, hair-like 'antennae', called cilia, that alert cells to critical changes in their environments.
May 13th, 2013
Read more Researchers have made a significant first step with newly engineered biomaterials for cell transplantation that could help lead to a possible cure for Type 1 diabetes, which affects about 3 million Americans.
Researchers have made a significant first step with newly engineered biomaterials for cell transplantation that could help lead to a possible cure for Type 1 diabetes, which affects about 3 million Americans.
May 9th, 2013
Read more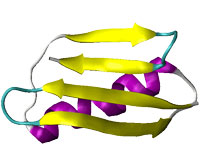 A team of researchers of the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) of Trieste and of University of Cambridge have devised a method to reduce the time used to simulate how proteins take on their signature three-dimensional shape. Such important information to comprehend their function is usually obtained using often very costly experimental techniques.
A team of researchers of the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) of Trieste and of University of Cambridge have devised a method to reduce the time used to simulate how proteins take on their signature three-dimensional shape. Such important information to comprehend their function is usually obtained using often very costly experimental techniques.
May 8th, 2013
Read moreOver 20 million people in Europe suffer from osteoarthritis which can lead to extensive damage to the knee and hip cartilage. Stem cells offer a promising way forward but a key challenge has been to design a 'smart material' that is biologically effective for cartilage tissue regeneration. Now researchers have identified a blend of naturally occurring fibers such as cellulose and silk that makes progress towards affordable and effective cell-based therapy for cartilage repair a step closer.
May 7th, 2013
Read moreDuke University biomedical engineers have grown three-dimensional human heart muscle that acts just like natural tissue. This advancement could be important in treating heart attack patients or in serving as a platform for testing new heart disease medicines.
May 6th, 2013
Read more Take a swab of saliva from your mouth and within minutes your DNA could be ready for analysis and genome sequencing with the help of a new device.
Take a swab of saliva from your mouth and within minutes your DNA could be ready for analysis and genome sequencing with the help of a new device.
May 6th, 2013
Read more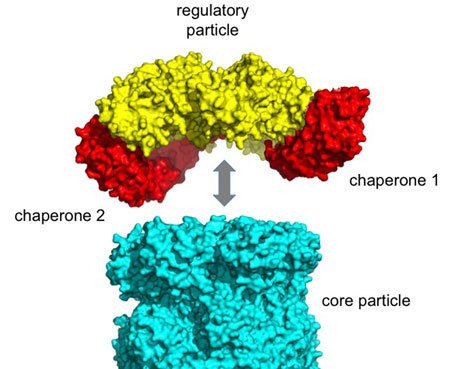 Kansas State University scientists helped discover new details about an intricate process in cells. Their finding may advance treatments for cancer and neurological diseases.
Kansas State University scientists helped discover new details about an intricate process in cells. Their finding may advance treatments for cancer and neurological diseases.
May 6th, 2013
Read more Australian scientists are at the forefront of a medical revolution using 3D printing to reproduce human body parts.
Australian scientists are at the forefront of a medical revolution using 3D printing to reproduce human body parts.
May 6th, 2013
Read moreA collaboration between the DOE JGI, Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and the University of Washington has resulted in an improved workflow for genome assembly that the team describes as a fully automated process from DNA sample preparation to the determination of the finished genome.
May 5th, 2013
Read more