Showing Spotlights 33 - 40 of 152 in category All (newest first):
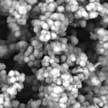 Carbon nano-onions (CNOs), a less studied morphology of carbon nanomaterials, are exotic structures with extraordinary properties and numerous applications. These applications have been largely ignored due to their high synthesis cost. Researchers now have produced inexpensive, stable carbon-nano onions directly from carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide reactant replaces nano-diamonds as the reactant to form the nano-onions. The source of CO2 to produce these CNOs can be the consumption of industrial flue gas or CO2 directly captured from the air.
Carbon nano-onions (CNOs), a less studied morphology of carbon nanomaterials, are exotic structures with extraordinary properties and numerous applications. These applications have been largely ignored due to their high synthesis cost. Researchers now have produced inexpensive, stable carbon-nano onions directly from carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide reactant replaces nano-diamonds as the reactant to form the nano-onions. The source of CO2 to produce these CNOs can be the consumption of industrial flue gas or CO2 directly captured from the air.
Jul 19th, 2019
 Bagasse is a waste plant matter obtained by food industry processes with major potential for several high-value products. An innovative idea of utilizing bagasse is for production of nanocellulose and testing this for wound dressing devices, manufactured by 3D printing. The next step in the development of wound dressings is the personalized aspect of the biomaterials, i.e. wound dressings that are structured and composed of constituents specially selected for a specific wound and wound treatment. Furthermore, sensors could be integrated into wound dressings and thus monitor various aspects of wound development, e.g. moisture and exudates in chronic wounds.
Bagasse is a waste plant matter obtained by food industry processes with major potential for several high-value products. An innovative idea of utilizing bagasse is for production of nanocellulose and testing this for wound dressing devices, manufactured by 3D printing. The next step in the development of wound dressings is the personalized aspect of the biomaterials, i.e. wound dressings that are structured and composed of constituents specially selected for a specific wound and wound treatment. Furthermore, sensors could be integrated into wound dressings and thus monitor various aspects of wound development, e.g. moisture and exudates in chronic wounds.
Jun 3rd, 2019
 Researchers a new strategy for designing Pickering emulsion based on halloysite nanotubes and exploring chitosan and pectin as thickener additives for the development of cleaning and preservation applications for cultural heritage. This novel and facile strategy to prepare hydrogel containing oil-in-water stable emulsion offers an alternative route to prepare formulations with high performance and based on sustainable materials for the controlled cleaning and preservation of stone-based artworks.
Researchers a new strategy for designing Pickering emulsion based on halloysite nanotubes and exploring chitosan and pectin as thickener additives for the development of cleaning and preservation applications for cultural heritage. This novel and facile strategy to prepare hydrogel containing oil-in-water stable emulsion offers an alternative route to prepare formulations with high performance and based on sustainable materials for the controlled cleaning and preservation of stone-based artworks.
May 8th, 2019
 To perform a risk assessment of nanomaterials in the environment, information on the exposure, i.e. the amounts that are present in the environment, is essential. In contrast to many other known pollutants, the concentrations of nanomaterials in environmental systems cannot be measured directly. In this situation, exposure modelling is a solution to estimate the environmental exposure with synthetic nanomaterials. In order to predict the amount of a nanomaterial in a certain environmental compartment (environmental exposure) present in a certain area, two basic types of models are required - material flow analysis and environmental behaviour modelling.
To perform a risk assessment of nanomaterials in the environment, information on the exposure, i.e. the amounts that are present in the environment, is essential. In contrast to many other known pollutants, the concentrations of nanomaterials in environmental systems cannot be measured directly. In this situation, exposure modelling is a solution to estimate the environmental exposure with synthetic nanomaterials. In order to predict the amount of a nanomaterial in a certain environmental compartment (environmental exposure) present in a certain area, two basic types of models are required - material flow analysis and environmental behaviour modelling.
Apr 23rd, 2019
 In new work, researchers explore inexpensive, biodegradable and daily-waste eggshell membrane as a novel bio-piezoelectric material for harvesting green energy. The uniqueness of our work lies in the novelty of directly utilizing natural eggshell membranes as efficient piezoelectric material. This simple, innovative approach could provide huge benefits for research in future energy science, especially with regard to in vivo biomedical applications.
In new work, researchers explore inexpensive, biodegradable and daily-waste eggshell membrane as a novel bio-piezoelectric material for harvesting green energy. The uniqueness of our work lies in the novelty of directly utilizing natural eggshell membranes as efficient piezoelectric material. This simple, innovative approach could provide huge benefits for research in future energy science, especially with regard to in vivo biomedical applications.
Jun 12th, 2018
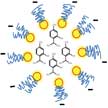 Widespread use of synthetic agrochemicals in crop protection has led to serious concerns of environmental contamination and increased resistance in plant-based pathogenic microbes. In an effort to develop bio-based and non-synthetic alternatives, nanobiotechnology researchers are looking to plants that possess natural antimicrobial properties. In new work, researchers show that nanoscale thymol's antibacterial and antifungal properties not only prevent plant disease but that it also enhances plant growth.
Widespread use of synthetic agrochemicals in crop protection has led to serious concerns of environmental contamination and increased resistance in plant-based pathogenic microbes. In an effort to develop bio-based and non-synthetic alternatives, nanobiotechnology researchers are looking to plants that possess natural antimicrobial properties. In new work, researchers show that nanoscale thymol's antibacterial and antifungal properties not only prevent plant disease but that it also enhances plant growth.
May 4th, 2018
 One of the main challenges for energy efficient technologies is to lower their cost by making cheap energy-efficient materials and devices by preferably using green manufacturing technologies. For example, commercial infrared-blocking windows, both passive and active, are simply too expensive (most of these IR-blocking windows contain an expensive silver coating) and they are not used in the majority of our homes. One approach to this problem involves creating passive infrared-blocking glasses using plasmonic nanocrystals. Researchers have demonstrated that nanocrystals of relatively inexpensive plasmonic materials show an overall good performance as IR-blocking elements.
One of the main challenges for energy efficient technologies is to lower their cost by making cheap energy-efficient materials and devices by preferably using green manufacturing technologies. For example, commercial infrared-blocking windows, both passive and active, are simply too expensive (most of these IR-blocking windows contain an expensive silver coating) and they are not used in the majority of our homes. One approach to this problem involves creating passive infrared-blocking glasses using plasmonic nanocrystals. Researchers have demonstrated that nanocrystals of relatively inexpensive plasmonic materials show an overall good performance as IR-blocking elements.
Apr 27th, 2018
 Carbon nanomaterials, including graphene-based materials, are widely gaining popularity in practical applications of nanomanufacturing. As a result, it becomes more and more likely that the unwanted introduction of such materials into the environment may occur. In particular, aqueous habitats might be severely affected by any accidental carbon nanomaterials exposure. Researching these potential environmental toxicity effects, scientists have found that kaolin, a cheap and abundant clay, can act as a powerful antidote to remediate the toxic effects of graphene oxide.
Carbon nanomaterials, including graphene-based materials, are widely gaining popularity in practical applications of nanomanufacturing. As a result, it becomes more and more likely that the unwanted introduction of such materials into the environment may occur. In particular, aqueous habitats might be severely affected by any accidental carbon nanomaterials exposure. Researching these potential environmental toxicity effects, scientists have found that kaolin, a cheap and abundant clay, can act as a powerful antidote to remediate the toxic effects of graphene oxide.
Apr 25th, 2018
 Carbon nano-onions (CNOs), a less studied morphology of carbon nanomaterials, are exotic structures with extraordinary properties and numerous applications. These applications have been largely ignored due to their high synthesis cost. Researchers now have produced inexpensive, stable carbon-nano onions directly from carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide reactant replaces nano-diamonds as the reactant to form the nano-onions. The source of CO2 to produce these CNOs can be the consumption of industrial flue gas or CO2 directly captured from the air.
Carbon nano-onions (CNOs), a less studied morphology of carbon nanomaterials, are exotic structures with extraordinary properties and numerous applications. These applications have been largely ignored due to their high synthesis cost. Researchers now have produced inexpensive, stable carbon-nano onions directly from carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide reactant replaces nano-diamonds as the reactant to form the nano-onions. The source of CO2 to produce these CNOs can be the consumption of industrial flue gas or CO2 directly captured from the air.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





