Showing Spotlights 17 - 24 of 152 in category All (newest first):
 Combining innovative hydrogel technology and architectural design, these windows offer improved temperature regulation and significant energy savings - a major stride towards a greener future.
Combining innovative hydrogel technology and architectural design, these windows offer improved temperature regulation and significant energy savings - a major stride towards a greener future.
Jun 6th, 2023
 Our society generates staggering amounts of waste in all areas of economic activities. Foremost among them, apart from energy waste, are the food and plastic sectors. However, both food and plastic wastes are potentially valuable sources of carbon. are working on upcycling of waste materials to high-value carbon by combining materials science and nanotechnology approaches to develop functional nanostructures for advanced energy storage, catalysis, water purification, and biosensor applications.
Our society generates staggering amounts of waste in all areas of economic activities. Foremost among them, apart from energy waste, are the food and plastic sectors. However, both food and plastic wastes are potentially valuable sources of carbon. are working on upcycling of waste materials to high-value carbon by combining materials science and nanotechnology approaches to develop functional nanostructures for advanced energy storage, catalysis, water purification, and biosensor applications.
Feb 21st, 2023
 Researchers have made significant strides in developing photodetectors made with tungsten disulfide (WS2) on paper substrates for disposable electronics. This research, which addresses the growing issue of electronic waste, has yielded promising results with WS2 photodetectors on paper substrates reaching photo responses comparable to commercially available silicon photodetectors. The findings have significant implications for ubiquitous electronics and low-performance sensing applications.
Researchers have made significant strides in developing photodetectors made with tungsten disulfide (WS2) on paper substrates for disposable electronics. This research, which addresses the growing issue of electronic waste, has yielded promising results with WS2 photodetectors on paper substrates reaching photo responses comparable to commercially available silicon photodetectors. The findings have significant implications for ubiquitous electronics and low-performance sensing applications.
Feb 20th, 2023
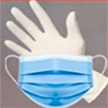 The extensive use of polymer-made, disposable and non-biodegradable COVID-19 pandemic health protectives like surgical face masks, hand gloves and PPE kits, combined with a lack of proper waste recycling systems, considerably increased plastic pollution around the world. Researchers are harnessing a new way to turn these COVID-19 pandemic wastes towards sensor design by fabricating a mask-glove-based contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator (MG-CS TENG).
The extensive use of polymer-made, disposable and non-biodegradable COVID-19 pandemic health protectives like surgical face masks, hand gloves and PPE kits, combined with a lack of proper waste recycling systems, considerably increased plastic pollution around the world. Researchers are harnessing a new way to turn these COVID-19 pandemic wastes towards sensor design by fabricating a mask-glove-based contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator (MG-CS TENG).
Jan 20th, 2023
 With a growing sustainability movement around the globe, the concept of urban farming has gained huge popularity for the development of sustainable communities. Urban farming practices don't necessarily use the same practices as conventional farming; this is especially true for the more high-tech approaches taken in vertical farming and warehouse farming. There is an opportunity and a requirement for smart technologies and the use of novel materials in urban farming, which can contribute to building a higher productivity and more sustainable urban farms.
With a growing sustainability movement around the globe, the concept of urban farming has gained huge popularity for the development of sustainable communities. Urban farming practices don't necessarily use the same practices as conventional farming; this is especially true for the more high-tech approaches taken in vertical farming and warehouse farming. There is an opportunity and a requirement for smart technologies and the use of novel materials in urban farming, which can contribute to building a higher productivity and more sustainable urban farms.
Jun 28th, 2022
 The goal of the electronics industry has always been to build durable devices with stable performance that last a very long time. Self-destructing, transient electronics however, are designed with the exact opposite goal: to dissolve harmlessly into their surroundings after functioning for a predetermined amount of time. Researchers now demonstrate novel biodegradable, recyclable, conductive, flexible, and printable materials that can be applied across many electronic devices to serve as a cornerstone for the development of ecofriendly and recyclable electronics.
The goal of the electronics industry has always been to build durable devices with stable performance that last a very long time. Self-destructing, transient electronics however, are designed with the exact opposite goal: to dissolve harmlessly into their surroundings after functioning for a predetermined amount of time. Researchers now demonstrate novel biodegradable, recyclable, conductive, flexible, and printable materials that can be applied across many electronic devices to serve as a cornerstone for the development of ecofriendly and recyclable electronics.
Jun 22nd, 2022
 Scientists estimate that at any one instant, the Earth's atmosphere contains about 12 900 cubic kilometers of water vapor. Extracting water from the air, that is, atmospheric water harvesting(AWH), becomes a promising alternative technology to produce freshwater. Atmospheric water harvesting can be achieved through three different approaches: fog collection, dew harvesting, and sorbent-based AWH. Here is a review of the recent materials engineering-enabled water management strategies for improving AWH performance at different working conditions (i.e., saturated humidity, dew point, and unsaturated humidity).
Scientists estimate that at any one instant, the Earth's atmosphere contains about 12 900 cubic kilometers of water vapor. Extracting water from the air, that is, atmospheric water harvesting(AWH), becomes a promising alternative technology to produce freshwater. Atmospheric water harvesting can be achieved through three different approaches: fog collection, dew harvesting, and sorbent-based AWH. Here is a review of the recent materials engineering-enabled water management strategies for improving AWH performance at different working conditions (i.e., saturated humidity, dew point, and unsaturated humidity).
Feb 24th, 2022
 BATTERY 2030+ is a large-scale cross-sectoral European research initiative bringing together the most important stakeholders in the field of battery R+D to create a strong battery research and innovation ecosystem community. A goal of the project is to develop a long-term roadmap for battery research in Europe. This roadmap suggests research actions towards breakthrough technologies to radically transform the way to discover, develop, and design ultra-high-performance, durable, safe, sustainable, and affordable batteries for use in real applications.
BATTERY 2030+ is a large-scale cross-sectoral European research initiative bringing together the most important stakeholders in the field of battery R+D to create a strong battery research and innovation ecosystem community. A goal of the project is to develop a long-term roadmap for battery research in Europe. This roadmap suggests research actions towards breakthrough technologies to radically transform the way to discover, develop, and design ultra-high-performance, durable, safe, sustainable, and affordable batteries for use in real applications.
Feb 9th, 2022
 Combining innovative hydrogel technology and architectural design, these windows offer improved temperature regulation and significant energy savings - a major stride towards a greener future.
Combining innovative hydrogel technology and architectural design, these windows offer improved temperature regulation and significant energy savings - a major stride towards a greener future.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





