| Posted: Oct 24, 2014 | |
A nanoparticle-based alternative to Viagra |
|
| (Nanowerk Spotlight) The majority of men who undergo radical prostatectomy for the treatment of prostate cancer will suffer from erectile dysfunction due to disruption of the cavernous nerve. This nerve has been identified as responsible for penile erection. The oral erectogenic PDE5 (phosphodiesterase-5) inhibitors like Viagra rely on the functioning of this nerve to provide the initial burst of nitric oxide (NO) necessary to initiate an erection. Several other patient groups, such as diabetics, where endothelial nitric oxide production is impaired are also refractory to orally administered PDE5 inhibitors. | |
| The precise cause of this neuropraxia – the temporary loss of motor and sensory function due to blockage of nerve conduction – is unclear but it has been hypothesized to include direct trauma during surgery, damage from tissue electrocautery, disruption of the neural vasculature, and generalized local inflammation associated with the procedure. | |
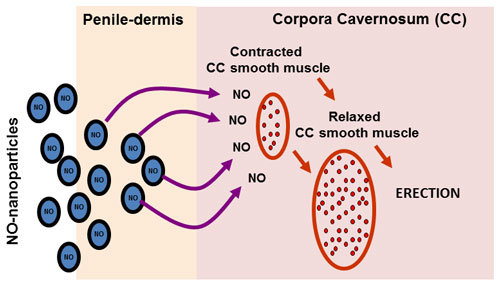
| In this condition nanotechnology – in the form of a nanoparticle delivery system – may come to the rescue by targetting useful therapeutics for penile rehabilitation following radical prostatectomy. | |
| New research recently published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine ("Topically Applied NO-Releasing Nanoparticles Can Increase Intracorporal Pressure and Elicit Spontaneous Erections in a Rat Model of Radical Prostatectomy") from an interdisciplinary team of researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and University of San Diego has demonstrated that nitric oxide nanoparticles (NO-NPs) could make them potentially useful agents in penile rehabilitation. Co-authors include Moses Tar MD , Pedro Cabrales PhD, Mahantesh Navati PhD, Brandon Adler MD, Parimala Nacharaju PhD, Adam J. Friedman MD, Joel Friedman MD, PhD and Kelvin P. Davies PhD. | |
| "Recent research has shown that NO-NPs may have several characteristics desirable for improvement of erectile function following radical prostatectomy," Dr Adam Friedman, Assistant Professor of Dermatology and Director of Dermatologic research at the Montefiore-Albert Einstein College of Medicine, tells Nanowerk. "In our paper we show in real time that NO-NP application in two different vehicles (lipophilic and hydrophilic) increase cutaneous blood flow for 90 minutes as compared to internalized controls." | |
 |
|
| Topically applied NO-NPs induced spontaneous erections and increased basal intracorporal pressure in an animal model of radical prostatectomy. (Image: Kelvin Davies, PhD) | |
| Previously, the same group of researchers published a proof-of-principle article ("Nanoparticles as a novel delivery vehicle for therapeutics targeting erectile dysfunction") demonstrating that topical application of NO-releasing nanoparticles can elicit an erectile response in an aging rat model of erectile dysfunction without stimulation of the cavernous nerve. | |
| The hypothesis of this earlier investigation was that the NO-NPs could topically deliver sufficient nitric oxide to relax corporal smooth muscle tissue and elicit an erection without the need for stimulation of the cavernous nerve. | |
| "In the present study, we further tested this hypothesis to determine if topically applied NO-NPs would elicit an erectile response in an animal model of erectile dysfunction resulting from cavernous nerve transection," Friedman elaborates. "We hypothesized that the prolonged release of nitric oxide from the NO-NPs would lead to an overall increase in intracorporal blood pressure because of increased blood flow into the penis." | |
| In a rodent model of radical prostatectomy, the researchers demonstrated the increase of microvascular blood flow by topical application of NO-NPs in combination with coconut oil or hyaluronic acid. This hydrogel was able to significantly increase blood flow through blood vessels 200 ?m away from the site of NO-NP application to intact skin. The release of nitric oxide from the nanoparticles occurred over a period of seven hours, suggests their physiologic effects could last for at least this duration. | |
| "Several technologies have been proposed for cutaneous delivery of nitric oxide, including but not limited to compressed gas cylinders that deliver it directly to wounds, acidified nitrite cream that releases nitric oxide, and diazeniumdiolates that give off nitric oxide spontaneously from a donor compound," says Friedman. "Unlike these and other nitric oxide delivery platforms, our NO-NPs do not rely on enzymatic conversion or donor compounds for nitric oxide delivery." | |
| In the team's nanoparticle delivery platform, nitric oxide is spontaneously generated through the reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide, facilitated by the rich hydrogen bonding network provided by this unique nanoparticle technology. | |
| Friedman points out that as a result, neither depletion of host thiols nor toxicity as a result of residual parent compound, both of which have been previously reported, are of concern here. | |
| Besides showing the in vivo mechanism of their nanoparticle based system, the team's paper also suggests efficacy of this delivery method for a broad range of diseases resulting from vascular dysfunction (raynauds, distal ulceration in scleroderma). | |
 By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
By
Michael
Berger
– Michael is author of three books by the Royal Society of Chemistry:
Nano-Society: Pushing the Boundaries of Technology,
Nanotechnology: The Future is Tiny, and
Nanoengineering: The Skills and Tools Making Technology Invisible
Copyright ©
Nanowerk LLC
|
|
|
Become a Spotlight guest author! Join our large and growing group of guest contributors. Have you just published a scientific paper or have other exciting developments to share with the nanotechnology community? Here is how to publish on nanowerk.com. |
|
