Showing Spotlights 25 - 32 of 77 in category All (newest first):
 The development of perovskite solar cells, first reported in 2009 (and with a record power conversion efficiency of 20.1 percent so far), is a possible route towards high efficiency photovoltaics that are also cost-effectiveness, owing to to their easy-processing from solution. Question marks have however remained on their stability. Now, researchers report the world's first nanorod-based perovskite solar module. In addition to high efficiency, these perovskite solar modules also show remarkable and improved shelf life.
The development of perovskite solar cells, first reported in 2009 (and with a record power conversion efficiency of 20.1 percent so far), is a possible route towards high efficiency photovoltaics that are also cost-effectiveness, owing to to their easy-processing from solution. Question marks have however remained on their stability. Now, researchers report the world's first nanorod-based perovskite solar module. In addition to high efficiency, these perovskite solar modules also show remarkable and improved shelf life.
Aug 7th, 2015
 Researchers have integrated a biocompatible silk fibroin with a mesh of silver nanowires to achieve a flexible, transparent, and biodegradable substrate for efficient plastic solar cell. The most common flexible substrates used for flexible solar cells so far have been synthetic polymers such as PET and PEN. However, if organic solar cells are to be applied onto clothes and other soft surfaces, some of which come into direct contact with skin, they are required to be human-compatible, non-toxic and non-irritable.
Researchers have integrated a biocompatible silk fibroin with a mesh of silver nanowires to achieve a flexible, transparent, and biodegradable substrate for efficient plastic solar cell. The most common flexible substrates used for flexible solar cells so far have been synthetic polymers such as PET and PEN. However, if organic solar cells are to be applied onto clothes and other soft surfaces, some of which come into direct contact with skin, they are required to be human-compatible, non-toxic and non-irritable.
Dec 30th, 2014
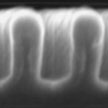 In recent years, polymer solar cells have drawn considerable research interest due to their attractive features including flexibility, semi-transparency, and manufacturability using cost-effective continuous printing processes. However, one challenge limiting their commercialization is the relatively low power conversion efficiency when compared to inorganic solar cells. New work shows that low bandgap polymer solar cells with high efficiency of 5.5% can be fabricated using nanoimprint lithography.
In recent years, polymer solar cells have drawn considerable research interest due to their attractive features including flexibility, semi-transparency, and manufacturability using cost-effective continuous printing processes. However, one challenge limiting their commercialization is the relatively low power conversion efficiency when compared to inorganic solar cells. New work shows that low bandgap polymer solar cells with high efficiency of 5.5% can be fabricated using nanoimprint lithography.
Nov 12th, 2014
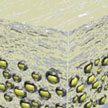 A large part of low-energy photons, such as in the deep-red and infrared, are lost during conventional photovoltaic or photochemical processes. However, about half of all the solar energy reaching the Earth's surface can be found in these wavelengths.
Harvesting this light more efficiently is possible thanks to a process called photon energy upconversion. Researchers now have successfully synthesized a bioinspired upconverting solid-state-like film using nanocellulose.
A large part of low-energy photons, such as in the deep-red and infrared, are lost during conventional photovoltaic or photochemical processes. However, about half of all the solar energy reaching the Earth's surface can be found in these wavelengths.
Harvesting this light more efficiently is possible thanks to a process called photon energy upconversion. Researchers now have successfully synthesized a bioinspired upconverting solid-state-like film using nanocellulose.
Aug 14th, 2014
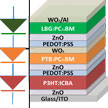 Researchers present an efficient design for a triple-junction organic tandem solar cell featuring a configuration of bandgap energies designed to maximize the tandem photocurrent output. The key innovation in this study is the demonstration of organic materials being able to mimic the record-setting efficiency of triple-junction structures in III-V solar cells. The team set out to determine a practical combination of bandgap energies for triple junctions to develop an efficient organic tandem solar cell structure.
Researchers present an efficient design for a triple-junction organic tandem solar cell featuring a configuration of bandgap energies designed to maximize the tandem photocurrent output. The key innovation in this study is the demonstration of organic materials being able to mimic the record-setting efficiency of triple-junction structures in III-V solar cells. The team set out to determine a practical combination of bandgap energies for triple junctions to develop an efficient organic tandem solar cell structure.
Jul 31st, 2014
 Ever since its discovery in 2004, graphene has been considered a relatively stable, high surface area platform to anchor nanostructured catalyst materials for various electrochemical and photocatalytic applications. The emergence of solution-based graphene in the form of graphene oxide has enabled new wet-chemistry approaches to the creation of graphene-based nanocomposites. A new study raises questions about the long-term stability of reduced graphene oxide in an aqueous environment where hydroxyl radicals can be present as part of the photocatalytic reaction cycle.
Ever since its discovery in 2004, graphene has been considered a relatively stable, high surface area platform to anchor nanostructured catalyst materials for various electrochemical and photocatalytic applications. The emergence of solution-based graphene in the form of graphene oxide has enabled new wet-chemistry approaches to the creation of graphene-based nanocomposites. A new study raises questions about the long-term stability of reduced graphene oxide in an aqueous environment where hydroxyl radicals can be present as part of the photocatalytic reaction cycle.
Jul 28th, 2014
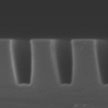 Conjugated polymer based organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices have been the subject of increasing research interest over the past years due to their potential of being light weight, mechanically flexible, semitransparent. To increase the efficiency of OPV, it is necessary to achieve a precisely controlled donor-acceptor phase separation within the short exciton diffusion length without dead ends, as well as a high hole mobility within the polymer. Now, researchers have demonstrated the effects of nanostructure geometry on the nanoimprint induced P3HT chain alignment and the performance of nanoimprinted photovoltaic devices.
Conjugated polymer based organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices have been the subject of increasing research interest over the past years due to their potential of being light weight, mechanically flexible, semitransparent. To increase the efficiency of OPV, it is necessary to achieve a precisely controlled donor-acceptor phase separation within the short exciton diffusion length without dead ends, as well as a high hole mobility within the polymer. Now, researchers have demonstrated the effects of nanostructure geometry on the nanoimprint induced P3HT chain alignment and the performance of nanoimprinted photovoltaic devices.
Jul 22nd, 2014
 Researchers report for the first time the fabrication and measurement of all-inkjet-printed, all-air-processed organic solar cells. Organic photovoltaic technologies have the potential to become a thin-film alternative to inorganic silicon photovoltaics due to their intrinsic potential for low-cost print processing from solution - high-speed and at low temperature. Organic solar cells can be integrated into building facades and windows because they are optically translucent and can be manufactured on large areas at high throughput.
Researchers report for the first time the fabrication and measurement of all-inkjet-printed, all-air-processed organic solar cells. Organic photovoltaic technologies have the potential to become a thin-film alternative to inorganic silicon photovoltaics due to their intrinsic potential for low-cost print processing from solution - high-speed and at low temperature. Organic solar cells can be integrated into building facades and windows because they are optically translucent and can be manufactured on large areas at high throughput.
Jun 16th, 2014
 The development of perovskite solar cells, first reported in 2009 (and with a record power conversion efficiency of 20.1 percent so far), is a possible route towards high efficiency photovoltaics that are also cost-effectiveness, owing to to their easy-processing from solution. Question marks have however remained on their stability. Now, researchers report the world's first nanorod-based perovskite solar module. In addition to high efficiency, these perovskite solar modules also show remarkable and improved shelf life.
The development of perovskite solar cells, first reported in 2009 (and with a record power conversion efficiency of 20.1 percent so far), is a possible route towards high efficiency photovoltaics that are also cost-effectiveness, owing to to their easy-processing from solution. Question marks have however remained on their stability. Now, researchers report the world's first nanorod-based perovskite solar module. In addition to high efficiency, these perovskite solar modules also show remarkable and improved shelf life.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





