Showing Spotlights 169 - 176 of 203 in category All (newest first):
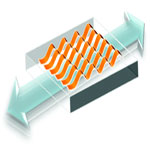 Previous research has shown that high performance piezoelectric ceramics PZT (lead zirconate titanate) could be printed as nanoribbons onto biocompatible and flexible substrates for applications such as harvesting energy from human motion like walking or breathing. While some motions, such as walking, only require flexibility, others, such as breathing, require that the materials be not just flexible but also stretchable. However, the PZT ribbons cannot stand stretching operation modes due to their brittle nature, which leads to cracking. The research team therefore has been looking to overcome this difficulty by fashioning the piezoelectric ribbons into wavy shapes, and integrating them with stretchable silicone rubber, such that the composite material can withstand large amounts of elastic strain.
Previous research has shown that high performance piezoelectric ceramics PZT (lead zirconate titanate) could be printed as nanoribbons onto biocompatible and flexible substrates for applications such as harvesting energy from human motion like walking or breathing. While some motions, such as walking, only require flexibility, others, such as breathing, require that the materials be not just flexible but also stretchable. However, the PZT ribbons cannot stand stretching operation modes due to their brittle nature, which leads to cracking. The research team therefore has been looking to overcome this difficulty by fashioning the piezoelectric ribbons into wavy shapes, and integrating them with stretchable silicone rubber, such that the composite material can withstand large amounts of elastic strain.
Feb 18th, 2011
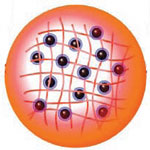 The particular physical properties that result from their unusual state of matter - they combine the properties of solids and fluids - make hydrogels ideal candidates for a number of applications. Nanoscale colloidally stable particles made from hydrogels are referred to as nanogels and these material systems have many general advantages, such as high transparency, high diffusion rates, high surface area, high dispersion stability, and monodispersity. Researchers in Japan have now proposed a novel photochemical application toward artificial photosynthesis using nanogels as nanogenerators, which evolve hydrogen gas from the internal water induced by irradiation with visible light. Actually, these nanogel systems generated hydrogen gas more efficiently than conventional solution systems.
The particular physical properties that result from their unusual state of matter - they combine the properties of solids and fluids - make hydrogels ideal candidates for a number of applications. Nanoscale colloidally stable particles made from hydrogels are referred to as nanogels and these material systems have many general advantages, such as high transparency, high diffusion rates, high surface area, high dispersion stability, and monodispersity. Researchers in Japan have now proposed a novel photochemical application toward artificial photosynthesis using nanogels as nanogenerators, which evolve hydrogen gas from the internal water induced by irradiation with visible light. Actually, these nanogel systems generated hydrogen gas more efficiently than conventional solution systems.
Feb 17th, 2011
 Traditional anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, like graphite, have a fairly low storage capacity and release rate, so finding alternatives is key to making batteries that last longer and produce more power. Titanium dioxide is regarded as one of the ideal candidates for high-rate anode materials, owing not only to its structural characteristics and special surface activity, but also to its low cost, safety, and relatively low environmental impact. Researchers in Singapore have developed a facile system to fabricate sandwich-like carbon-supported stacked titanium dioxide nanosheets, in which carbon pillars create open channels for fast lithium ion diffusion and the ultrathin framework renders the storage of lithium almost exclusively on the surface. This work provides a new route to design the electrode materials for quick-charging lithium ion batteries.
Traditional anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, like graphite, have a fairly low storage capacity and release rate, so finding alternatives is key to making batteries that last longer and produce more power. Titanium dioxide is regarded as one of the ideal candidates for high-rate anode materials, owing not only to its structural characteristics and special surface activity, but also to its low cost, safety, and relatively low environmental impact. Researchers in Singapore have developed a facile system to fabricate sandwich-like carbon-supported stacked titanium dioxide nanosheets, in which carbon pillars create open channels for fast lithium ion diffusion and the ultrathin framework renders the storage of lithium almost exclusively on the surface. This work provides a new route to design the electrode materials for quick-charging lithium ion batteries.
Jan 21st, 2011
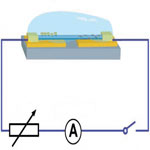 Nanotechnology researchers working on self-powered nanodevices - nanoscale systems that scavenge energy from their surrounding environment - have been experimenting with various power sources ranging from piezoelectric systems to sound. However, the most abundant energy available in biosystems is chemical and biochemical energy, such as glucose. Researchers in China have now reported a nanowire-based biofuel cell based on a single proton conductive polymer nanowire for converting chemical energy from biofluids into electricity, using glucose oxidase and laccase as catalyst. The output of this biofuel cell is sufficient to drive pH, glucose or photon sensors. The high output power, low cost and easy fabrication process, large-scale manufacturability, high 'on-chip' integrability and stability demonstrates its great potential for in vivo biosensing.
Nanotechnology researchers working on self-powered nanodevices - nanoscale systems that scavenge energy from their surrounding environment - have been experimenting with various power sources ranging from piezoelectric systems to sound. However, the most abundant energy available in biosystems is chemical and biochemical energy, such as glucose. Researchers in China have now reported a nanowire-based biofuel cell based on a single proton conductive polymer nanowire for converting chemical energy from biofluids into electricity, using glucose oxidase and laccase as catalyst. The output of this biofuel cell is sufficient to drive pH, glucose or photon sensors. The high output power, low cost and easy fabrication process, large-scale manufacturability, high 'on-chip' integrability and stability demonstrates its great potential for in vivo biosensing.
Jan 3rd, 2011
 Traditionally, battery materials have been studied with bulk quantities in a complex environment with both active electrode components and many other supporting materials such as polymer binders and conductive additives. Although nanomaterials have been found to be able to improve battery performance, the complexity has made it hard to tell clearly about their advantages. Moreover, it is difficult to know whether fast capacity fading is due to the intrinsic nature of the transport property changes of active nanomaterials or an extrinsic reason from their interactions with the supporting materials, if all of them are studied together. The goal to understand the intrinsic reason of active material capacity fading has motivated a group of researchers to design single nanowire electrochemical devices as an extremely simplified model system to push the fundamental limits of the nanowire materials for energy storage applications. The result is a powerful and effective diagnostic tool for property degradation of lithium ion based energy storage devices.
Traditionally, battery materials have been studied with bulk quantities in a complex environment with both active electrode components and many other supporting materials such as polymer binders and conductive additives. Although nanomaterials have been found to be able to improve battery performance, the complexity has made it hard to tell clearly about their advantages. Moreover, it is difficult to know whether fast capacity fading is due to the intrinsic nature of the transport property changes of active nanomaterials or an extrinsic reason from their interactions with the supporting materials, if all of them are studied together. The goal to understand the intrinsic reason of active material capacity fading has motivated a group of researchers to design single nanowire electrochemical devices as an extremely simplified model system to push the fundamental limits of the nanowire materials for energy storage applications. The result is a powerful and effective diagnostic tool for property degradation of lithium ion based energy storage devices.
Sep 27th, 2010
 Imagine cellular phones that can be charged during conversations and sound-insulating walls near highways that generate electricity from the sound of passing vehicles. A number of approaches for self-powering systems by scavenging energy from environments using photovoltaic, thermoelectric, and piezoelectric phenomena have been intensively explored. Among them, very recent innovative research has been intensively carried out to convert external mechanical stimuli such as body movements, heartbeat, blood flow, and ultrasonic wave into electricity, resulting in piezoelectric power-driven wireless self-powered systems. Such a piezoelectric power generation aims to capture the normally wasted energy surrounding a system and converts it into usable energy for operating electrical devices. New work by a nanotechnology research team in Korea has now demonstrated that it is possible to use sound as a power source to drive nanogenerators based on piezoelectric nanowires.
Imagine cellular phones that can be charged during conversations and sound-insulating walls near highways that generate electricity from the sound of passing vehicles. A number of approaches for self-powering systems by scavenging energy from environments using photovoltaic, thermoelectric, and piezoelectric phenomena have been intensively explored. Among them, very recent innovative research has been intensively carried out to convert external mechanical stimuli such as body movements, heartbeat, blood flow, and ultrasonic wave into electricity, resulting in piezoelectric power-driven wireless self-powered systems. Such a piezoelectric power generation aims to capture the normally wasted energy surrounding a system and converts it into usable energy for operating electrical devices. New work by a nanotechnology research team in Korea has now demonstrated that it is possible to use sound as a power source to drive nanogenerators based on piezoelectric nanowires.
Sep 23rd, 2010
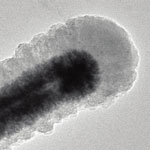 Most of today's lithium-ion batteries rely on anodes made from graphite, a form of carbon. There are several candidate electrodes to replace graphite as the anode for lithium-ion batteries. Such electrodes like silicon or tin have very high capacities but suffer from poor efficiency and cyclic stability as they experience large volume change and particle pulverization during repeated cycling. Silicon-based anodes, for instance, theoretically offer as much as a ten-fold capacity improvement over graphite, but silicon-based anodes have so far not been stable enough for practical use. Researchers have now used the macromolecular structure of self-assembled Tobacco mosaic virus as templates to fabricate stable three-dimensional current collectors for high power and high energy density Li-ion batteries.
Most of today's lithium-ion batteries rely on anodes made from graphite, a form of carbon. There are several candidate electrodes to replace graphite as the anode for lithium-ion batteries. Such electrodes like silicon or tin have very high capacities but suffer from poor efficiency and cyclic stability as they experience large volume change and particle pulverization during repeated cycling. Silicon-based anodes, for instance, theoretically offer as much as a ten-fold capacity improvement over graphite, but silicon-based anodes have so far not been stable enough for practical use. Researchers have now used the macromolecular structure of self-assembled Tobacco mosaic virus as templates to fabricate stable three-dimensional current collectors for high power and high energy density Li-ion batteries.
Aug 24th, 2010
 Supercapacitors, also called electric double layer capacitors (EDLC), store energy in two closely spaced layers with opposing charges and offer fast charge/discharge rates and the ability to sustain millions of cycles. It is frequently stated that supercapacitors bridge the gap between batteries and electrolytic ('conventional') capacitors, but contemporary devices have a lower specific energy than Li-ion batteries and are orders of magnitude slower than electrolytic capacitors. A research team has now shown that by moving from porous carbon with a network of pores inside particles as electrode material to exposed surfaces of nanostructured carbon onions of 6-7 nm diameter, it is possible to reach the discharge rate (power) of electrolytic capacitors, but with volumetric capacitance about four orders of magnitude higher. Moreover, observed discharge rates up to 200 V/second are about three orders of magnitude higher than conventional supercapacitors.
Supercapacitors, also called electric double layer capacitors (EDLC), store energy in two closely spaced layers with opposing charges and offer fast charge/discharge rates and the ability to sustain millions of cycles. It is frequently stated that supercapacitors bridge the gap between batteries and electrolytic ('conventional') capacitors, but contemporary devices have a lower specific energy than Li-ion batteries and are orders of magnitude slower than electrolytic capacitors. A research team has now shown that by moving from porous carbon with a network of pores inside particles as electrode material to exposed surfaces of nanostructured carbon onions of 6-7 nm diameter, it is possible to reach the discharge rate (power) of electrolytic capacitors, but with volumetric capacitance about four orders of magnitude higher. Moreover, observed discharge rates up to 200 V/second are about three orders of magnitude higher than conventional supercapacitors.
Aug 19th, 2010
 Previous research has shown that high performance piezoelectric ceramics PZT (lead zirconate titanate) could be printed as nanoribbons onto biocompatible and flexible substrates for applications such as harvesting energy from human motion like walking or breathing. While some motions, such as walking, only require flexibility, others, such as breathing, require that the materials be not just flexible but also stretchable. However, the PZT ribbons cannot stand stretching operation modes due to their brittle nature, which leads to cracking. The research team therefore has been looking to overcome this difficulty by fashioning the piezoelectric ribbons into wavy shapes, and integrating them with stretchable silicone rubber, such that the composite material can withstand large amounts of elastic strain.
Previous research has shown that high performance piezoelectric ceramics PZT (lead zirconate titanate) could be printed as nanoribbons onto biocompatible and flexible substrates for applications such as harvesting energy from human motion like walking or breathing. While some motions, such as walking, only require flexibility, others, such as breathing, require that the materials be not just flexible but also stretchable. However, the PZT ribbons cannot stand stretching operation modes due to their brittle nature, which leads to cracking. The research team therefore has been looking to overcome this difficulty by fashioning the piezoelectric ribbons into wavy shapes, and integrating them with stretchable silicone rubber, such that the composite material can withstand large amounts of elastic strain.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





