Showing Spotlights 49 - 56 of 643 in category All (newest first):
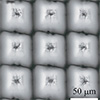 Innovative hybridized technique combines ultrafast laser ablation with controllable in-situ nanoparticle deposition, enabling iterative, layered fabrication of complex multi-tiered hierarchical surface micro- and nanostructures.
Innovative hybridized technique combines ultrafast laser ablation with controllable in-situ nanoparticle deposition, enabling iterative, layered fabrication of complex multi-tiered hierarchical surface micro- and nanostructures.
Nov 28th, 2023
 Researchers develop flexible electronic sensor skins with extreme resilience that maintains accurate strain and temperature measurements when submerged in harsh acids or swung between scorching heat and subzero icy seawater.
Researchers develop flexible electronic sensor skins with extreme resilience that maintains accurate strain and temperature measurements when submerged in harsh acids or swung between scorching heat and subzero icy seawater.
Nov 27th, 2023
 Ingenious auxetic shape-memory alloy wire lattice textile realizes zone-specified actuation to convey readily discerned complex tactile sensations, enabling intuitive navigation when immersed in virtual environments.
Ingenious auxetic shape-memory alloy wire lattice textile realizes zone-specified actuation to convey readily discerned complex tactile sensations, enabling intuitive navigation when immersed in virtual environments.
Nov 25th, 2023
 The Synthescope concept represents a visionary fusion of synthesis with atomic-scale fabrication in the field of materials science.
The Synthescope concept represents a visionary fusion of synthesis with atomic-scale fabrication in the field of materials science.
Nov 9th, 2023
 Rresearchers report a new liquid templating strategy for engineering highly tunable, durable aerogels. The customizable gels showed improved emi shielding and record oil absorption.
Rresearchers report a new liquid templating strategy for engineering highly tunable, durable aerogels. The customizable gels showed improved emi shielding and record oil absorption.
Nov 3rd, 2023
 Researchers developed a method to assemble 2D nanosheets like MXene in 3D configurations using an infiltrated porous ceramic scaffold. This overcomes nanosheet restacking and may enable advances in energy, electronics, catalysis and more.
Researchers developed a method to assemble 2D nanosheets like MXene in 3D configurations using an infiltrated porous ceramic scaffold. This overcomes nanosheet restacking and may enable advances in energy, electronics, catalysis and more.
Oct 31st, 2023
 DLP 3D printing of photonic colloidal glasses creates intricately shaped materials with tunable structural color properties. Combining rational design and digital manufacturing opens new possibilities.
DLP 3D printing of photonic colloidal glasses creates intricately shaped materials with tunable structural color properties. Combining rational design and digital manufacturing opens new possibilities.
Oct 28th, 2023
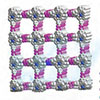 New research shows that solution-processed hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks can be used to improve resistive memory technology, offering potential benefits for electronic device performance and sustainability.
New research shows that solution-processed hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks can be used to improve resistive memory technology, offering potential benefits for electronic device performance and sustainability.
Oct 27th, 2023
 Innovative hybridized technique combines ultrafast laser ablation with controllable in-situ nanoparticle deposition, enabling iterative, layered fabrication of complex multi-tiered hierarchical surface micro- and nanostructures.
Innovative hybridized technique combines ultrafast laser ablation with controllable in-situ nanoparticle deposition, enabling iterative, layered fabrication of complex multi-tiered hierarchical surface micro- and nanostructures.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





