| Posted: Oct 20, 2011 | |
Global carbon nanotubes market - industry beckons |
|
| (Nanowerk Spotlight) Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have recently emerged as one of the most important classes of nanomaterials having enormous potential to spark off the next industrial revolution. CNTs' unique and extraordinary properties such as extremely high electrical and thermal conductivities, very small diameters (less than 100 nm), large aspect ratios (length/diameter ratios, greater than 1000), outstanding mechanical properties, a tip-surface area near the theoretical limit (the smaller the tip-surface area, the more concentrated the electric field, and the greater the field enhancement factor)1 and an excellent price-performance ratio, make it an ideal candidate for electronic devices, chemical/electrochemical and biosensors, transistors, electron field emitters, lithium-ion batteries, white light sources, hydrogen storage cells, cathode ray tubes (CRTs), electrostatic discharge (ESD) and electrical-shielding applications. | |
| In fact, several products enabled by carbon nanotubes are already in the market, such as racquets, golf clubs, surfboards, ice hockey sticks, mass transportation fuel system components, battery electrode additives, plastics additives and masterbatches. MWCNTs-enabled engineering and specialty thermoplastics such as polycarbonate (PC), Polyetherimide (PEI), and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) have been used in cleanrooms for the production of computer chips and hard drives, because they dissipate static electricity and, therefore, will not attract airborne contaminants. | |
| More than 100 companies around the world today are manufacturing carbon nanotubes and this number is expected to increase to more than 200 within the next five years, while there are more than 1,000 companies and institutions that are actively engaged in CNTs Research and Development (R&D). | |
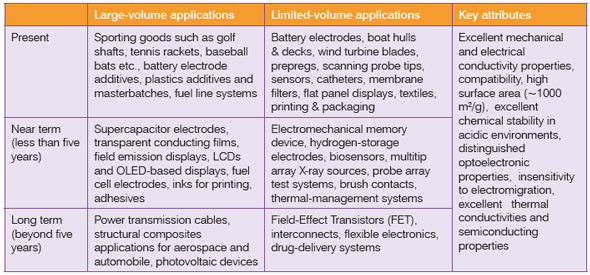
| Currently, carbon nanotubes account for a 28% market share of overall nanomaterials demand. In terms of production capacity, Asia-Pacific leads, followed by North America and the European Union. Table 1 shows CNTs-enabled applications grouped as present, near term and long term, and as categories related to large volume and limited volume segments and their key attributes. | |
 |
|
| Table 1. Summary of CNTs-Enabled Applications. Adapted from the paper on "Potential Applications of Carbon Nanotubes" by P. M. Ajayan et al.2 | |
| This article looks at the market size, applications, processing technology and end-user products of carbon nanotubes. In addition, the study looked at industry leaders in the value chain, potential applications, products which are under development and are likely to enter the market in the next five to ten years. For this study, we have surveyed industry professionals/stakeholders in the CNTs value chain, extracted information from our proprietary in-house databases/ inter-linked databases as well as researched other primary and secondary sources and triangulated data and the findings are presented in this article. | |
| Market Outlook | |
| The market size findings are based on the analysis carried out by the CKMNT's teams. We present here an excerpt from the upcoming market research report titled "Global Carbon Nanotubes Market". | |
| The global CNTs market is highly consolidated and oligopolistic in nature, dominated by a few large suppliers/producers operating in multiple industry segments. The global CNTs industry turned over around $668.3 million in 2010, with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) production value of approximately $631.5 million and single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) production value of around $36.8 million, and is forecast to grow to $1.1 billion by 2016 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.5%. | |
| Used across a wide range of industries including plastics and composites, electrical and electronics, and energy as well as a range of industrial sectors, CNTs have become an essential ingredient or reinforcement material for these industries, with its usage growing broadly in line with the global economy. | |
 |
|
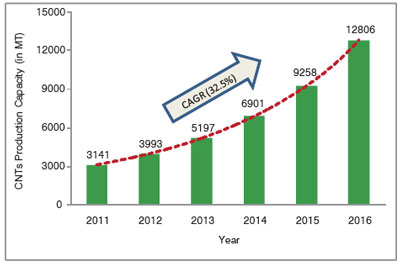
| Fig. 1: Next five years forecast (2011-2016) for global CNTs market. | |
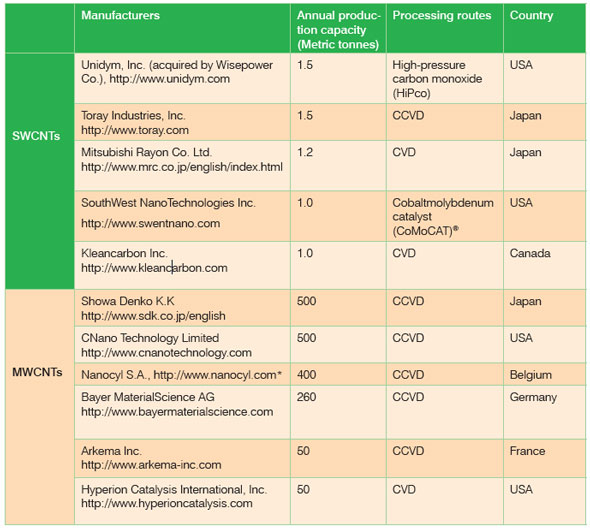
| The production capacity of CNTs has increased significantly in the last five years, nowadays hundreds of tons are produced to meet the market demand. CNTs market is on the upswing with lowering costs and improving performance, availability and end user adaptability. Table 2 shows major carbon nanotubes producers and their annual production capacity for 2010. It is also to be noted that there are a number of MWCNT producers other than those shown in Table 2 such as Nanocomp Technologies Inc. (NCTI), USA, Eden Energy Limited, Australia, Iljin Nanotech, South Korea, NanoCarbon Technologies (NCT) Ltd., Japan, Ube Industries, Japan etc., but they have not been included here as their production capacity is less than 50 MT annum. | |
| Only about 25% of the global CNTs production capacity was produced in 2010 while average production at full capacity is estimated to be about 40- 50% in 2016. At the end of the 2010 calendar year, production capacity for CNTs reached an estimated 2,500 metric tons and is expected to exceed 12,800 metric tons in 2016 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 32.5% (Fig. 1). During the same year, Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest share of CNTs production at 1122.6 metric tons (44.2%), ahead of North America at 740.1 metric tons (29.2%) and Europe at 608.5 metric tons (24%). | |
| Asia-Pacific has the largest installed capacity of CNTs mainly due to the significant presence of electrical & electronics market, which is dominated by Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, China and Singapore. In 2010, the US captured the first largest share of the CNTs market while Japan ranked second, ahead of China and Germany. Japan is the prominent leader in the production of carbon nanotubes including MWCNTs and SWCNTs, but China and South Korea are expeditiously catching up. Among the European Union, France is expected to take the lead in CNTs production. A number of developing nations, most notably China and India, will become increasingly important, as high-end plastics & composites and electronics production shifts to these regions. | |
 |
|
| Table 2: Major Carbon Nanotubes Producers and their Annual Production Capacity for 2010. * Nanocyl also produces SWCNTs and DWCNTs, but on a smaller scale. | |
| In the next five years, the proposed production capacities for CNTs are bound to take a big leap forward. MWCNTs production capacities will reach nearly 12766 metric tons by 2016, mainly driven by polymers and composites applications in automotive components, aerospace structural parts, lithium-ion battery, Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) and other markets, while SWCNT's growth will be steady but not as high as in the case of MWCNTs, due to higher prices and limited end-user adaptability such as electrical & electronics market. | |
| CNTs market is facing a huge gap between demand and supply due to low volume utilisation of CNTs by end users. In order to bridge this gap, manufacturers should be ready to capitalize on that future demand, which is expected to grow rapidly over the next five to ten years. | |
| Demand is growing for CNTs used in the production of technology-intensive products. The expanding range of applications includes electronic packaging, touch panels, automotive parts, industrial components, medical devices, racquets, golf clubs, surfboards, ice hockey sticks, mass transportation fuel system components, battery electrode additives, plastics additives and masterbatches. Carbon nanotubes encompass a wide range of markets across plastics & composites, electrical and electronics, energy and others. | |
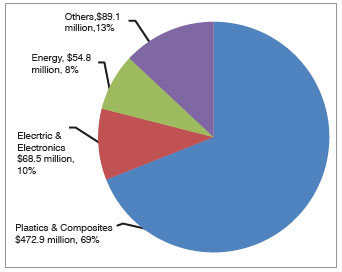
| The largest share of global CNTs is accounted for by plastics and composites with sales of $472.9 million in 2010, representing 69% of the market (Fig. 2). Plastics and composites will remain the most significant markets through to 2016. Electrical and electronics industries accounted for 10% of the CNTs market share followed by energy (8%). The electronics and data storage market is likely to see the biggest penetration by 2016, with the performance-enhancing properties of carbon nanotubes allowing electronics manufacturers to meet demanding market needs across a variety of applications, including interconnects, displays, memory, storage and others. The energy sector will also witness rapid growth, with enhanced performance requirements for batteries, wind turbine blades, photovoltaic cells and other applications in the next five to ten years. | |
 |
|
| Fig. 2: Global CNTs market by industry. | |
| Market Drivers | |
| CNT's demand is influenced by a number of diverse factors. While the economy plays a most important role in influencing the size and growth of the market, there are a number of other market drivers which can be seen as having a direct influence on CNTs demand or, at any rate, the nature of this demand, irrespective of the performance of the economy. These include: | |
|
|
|
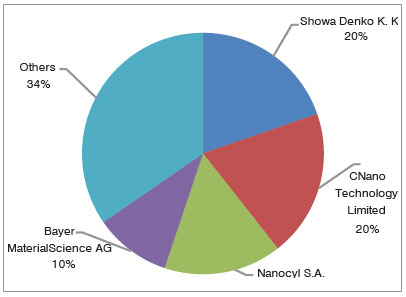
| Despite more than 100 CNTs manufacturing companies, the majority of the market share (66%) is held by four relatively large-scale manufacturers (Fig.3). Plastics & composites, fuel line systems, batteries, electrostatic discharge, and field emission devices are the most prominent and commercially viable current applications. Next generation products will be adopting CNTs in nano electromechanical systems (NEMS), supercapacitor electrodes, power transmission cables, structural composites applications for aerospace and automobile sectors, photovoltaic devices, transparent conducting films, field-effect transistors, interconnects, flexible electronics, and drug-delivery systems, which will yield greatly increased revenues for the CNTs players over the next 5-10 years. International industrial giants such as IBM, Intel, Hexcel, Samsung, NEC Corp., Renault, Yonex, EcoloCap Solutions, and Hunstman Corp. are developing a variety of current and future CNTs-enabled applications for various industries. | |
 |
|
| Fig. 3: Global CNTs market by major players. | |
| Prices for CNTs are expected to fall by an average of about 15% over the next five years as large companies begin to produce commercial-scale volumes of CNTs as well as expanding CNTs production capacity. For example, Arkema's 400 ton/year plant is scheduled for startup in 20113 while Bayer MaterialScience AG has envisioned to build an industrial-scale production plant with an annual capacity of 3,000 metric tons by the financial year 2012-20134. Large multi-nationals such as Showa Denko K.K, Arkema Inc., Toray Industries, and Bayer MaterialScience AG have significantly ramped up production levels. In addition to capacity expansion, companies in China and Russia are also producing significantly cheaper carbon nanotubes. | |
| The most widely used techniques for CNT synthesis are: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD), arc discharge and laser ablation. In 2010, CVD and CCVD techniques together captured approximately 83% of the global carbon nanotubes market share, followed by arc discharge (12%) processing method and laser ablation (5%), primarily due to its high degree of control, easy scalability, large-scale production output, high purity and yield compared to other available technologies. As for large-scale production of carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), Morinobu Endo developed Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD) continuous process, wherein metal catalyst (iron particles), benzene (for the pyrolysis), and Ar/H2 gases are fed from the upper end of a vertical furnace, and the resulting CNTs are collected from the lower end while the furnace temperature is kept at 1100°C5. In 2003, Prof. Morinobu Endo, Faculty of Engineering, Shinshu University, and Showa Denko K.K. established a joint venture for the commercialization of MWCNTs. | |
| Conclusions | |
| There are over a hundred companies around the world in the carbon nanotubes market, making it extremely competitive. The major players such as Arkema Inc., Showa Denko K.K., Nanocyl S.A., Bayer MaterialScience AG, Hyperion Catalysis International Inc., and Thomas Swan are building commercial levels of capacity and bringing prices down significantly. Established manufactures may have excellent market and cost advantages due to their proprietary product technology, favorable access to raw materials, government subsidies, favorable locations, and learning or experience curve efficiencies. Product know-how is a key factor for success in CNTs. Most recently, producers have increasingly focused on the production of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, with significant efforts being directed towards purity and yields as well as lowering the costs. The main markets at present are plastics and composites, electrical and electronics and energy. These will remain the most significant markets through to 2016. | |
| However, a number of issues, including high costs, inconsistent quality across the supply chain, dispersion and compatibility with matrix materials, and toxicology still need to be addressed. Once these issues are resolved, growth in global CNTs demand is expected to accelerate in the next five years. | |
| Note: A comprehensive Report on "Global Carbon Nanotubes Market" is slated to be released by CKMNT in the future. Interested readers may contact info@ ckmnt.com for further details. | |
| References | |
| 1. "Production and Applications of Carbon nanotubes, Carbon nanofibers, Fullerenes, Graphene and Nanodiamonds: A Global Technology Survey and Market Analysis", February 2011, published by Innovative Research and Products, Inc | |
| 2. M. Endo, M. S. Strano and P. M. Ajayan, "Potential Applications of Carbon nanotubes" Topics in Applied Physics, 111(2008) 13-61 | |
| 3. web link no longer exists | |
| 4. web link no longer exists | |
| 5. M. Endo, "Grow Carbon Fibers in the Vapor Phase", American Chemical Society, ChemTech,18 (1988) 568-576 | |
| By Vivek Patel, Centre for Knowledge Management of Nanoscience and Technology (CKMNT). For more information, interested readers may please contact Vivek Patel at [email protected]. | |
|
Become a Spotlight guest author! Join our large and growing group of guest contributors. Have you just published a scientific paper or have other exciting developments to share with the nanotechnology community? Here is how to publish on nanowerk.com. |
|
